Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes /issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.136
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.134
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.168
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.121
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.104
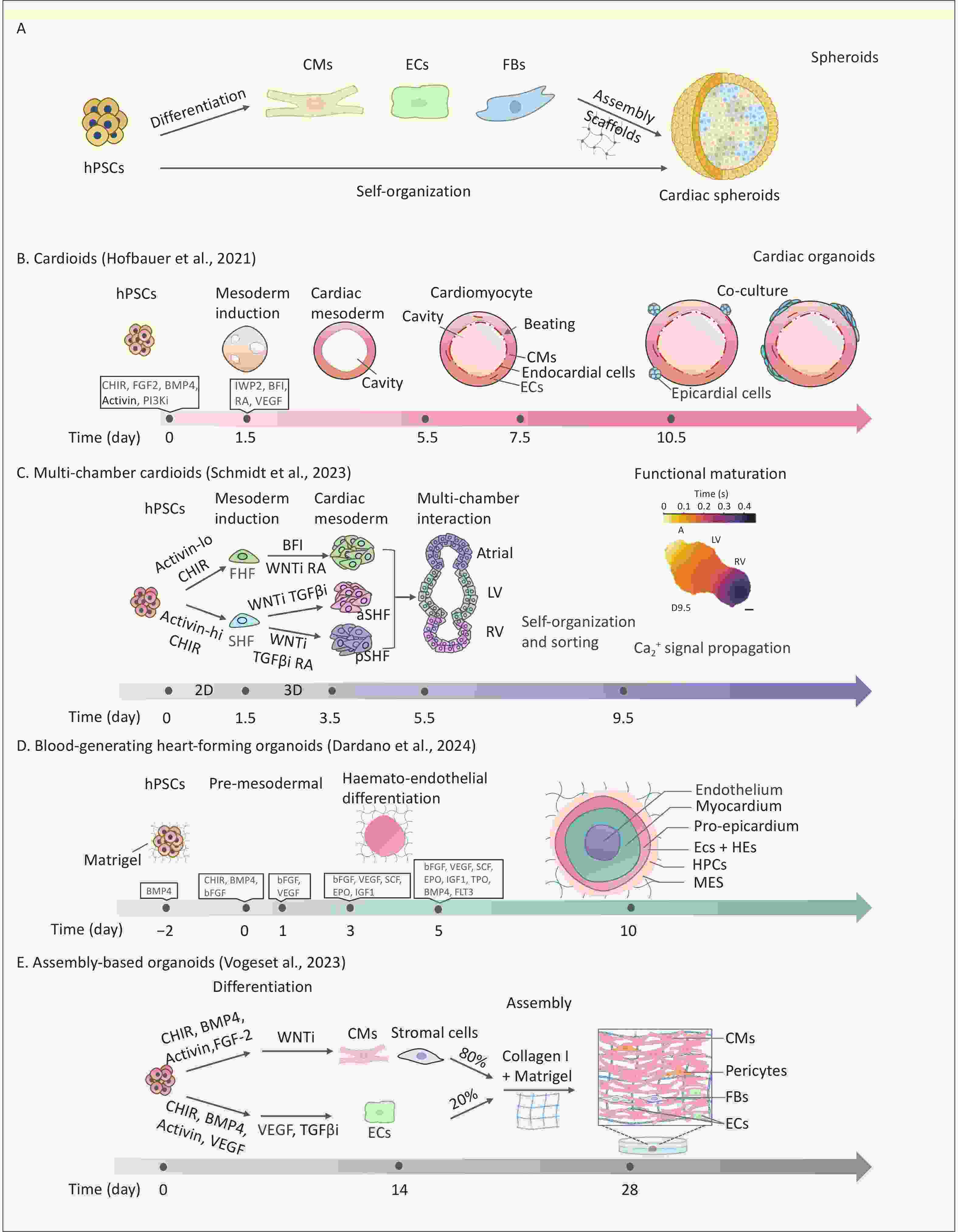
Human cardiac organoids have revolutionized the study of cardiac development, disease modeling, drug discovery, and regenerative therapies. This review systematically discusses strategies and progress in the construction of cardiac organoids, categorizing them into three main types: cardiac spheroids, self-organizing/assembloid organoids, and organoid-on-a-chip systems. This review uniquely integrates the advances in vascularization, organ-on-chip design, and environmental cardiotoxicity modeling within cardiac organoid platforms, offering a critical synthesis that is absent in the literature. In the context of escalating environmental threats to cardiovascular health, there is an urgent need for physiologically relevant models to accurately identify cardiac toxicants and elucidate their underlying mechanisms of action. This review highlights advances in cardiac organoid applications for disease modeling—including congenital heart defects and acquired cardiovascular diseases—drug development, toxicity screening, and the study of environmentally induced cardiovascular pathogenesis. In addition, it critically examines ongoing challenges and underscores opportunities brought by bioengineering approaches. Finally, we propose future directions for developing standardized cardiac organoid platforms with clinical predictability, aiming to expand the utility of this technology across broader research applications.
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.090
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.064
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.170
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.169
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.167
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.166
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.165
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.164
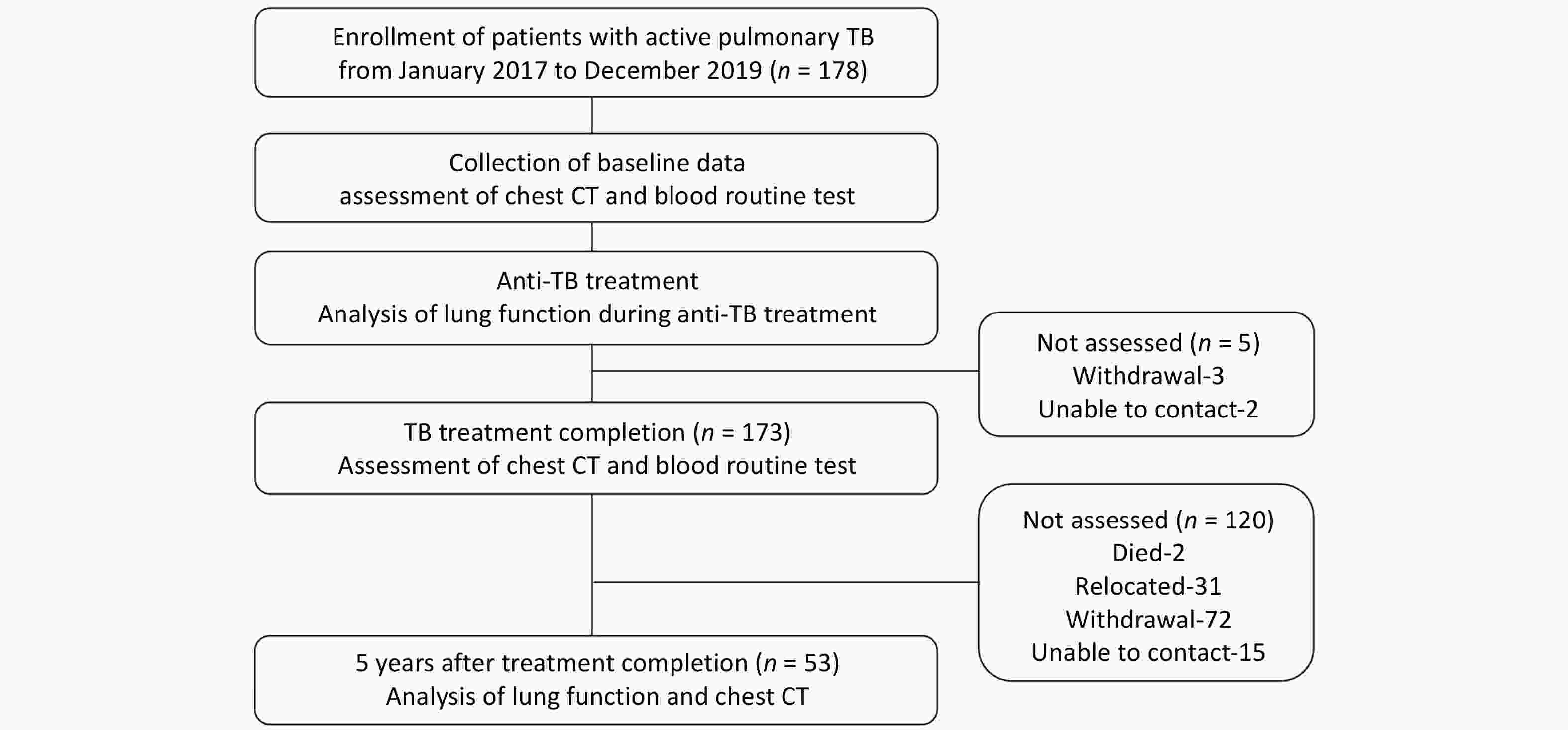
Tuberculosis (TB) continues to pose a significant threat to global public health, necessitating rapid and precise diagnostic methods and comprehensive detection of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to facilitate timely clinical management. Traditional diagnostic techniques suffer from extended turnaround times and limited ability to comprehensively profile AMR, often resulting in delayed therapeutic interventions. High-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies have revolutionized pathogen research by significantly improving diagnostic speed and accuracy. In the context of TB, diverse sequencing strategies and platforms are being employed to fulfill specific research goals, ranging from elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying AMR to characterizing the genomic diversity among clinical isolates. This review systematically examines current progress in the application of HTS for rapid pathogen identification, comprehensive AMR profiling, epidemiological studies, advances in novel drugs, and vaccine development. Furthermore, we address existing technological limitations and bioinformatics challenges and explore the future directions necessary for effectively integrating HTS-based methodologies into global TB control efforts.
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.163
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.162
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.161
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.160
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.159
2025, 38(10): 1179-1193.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.128
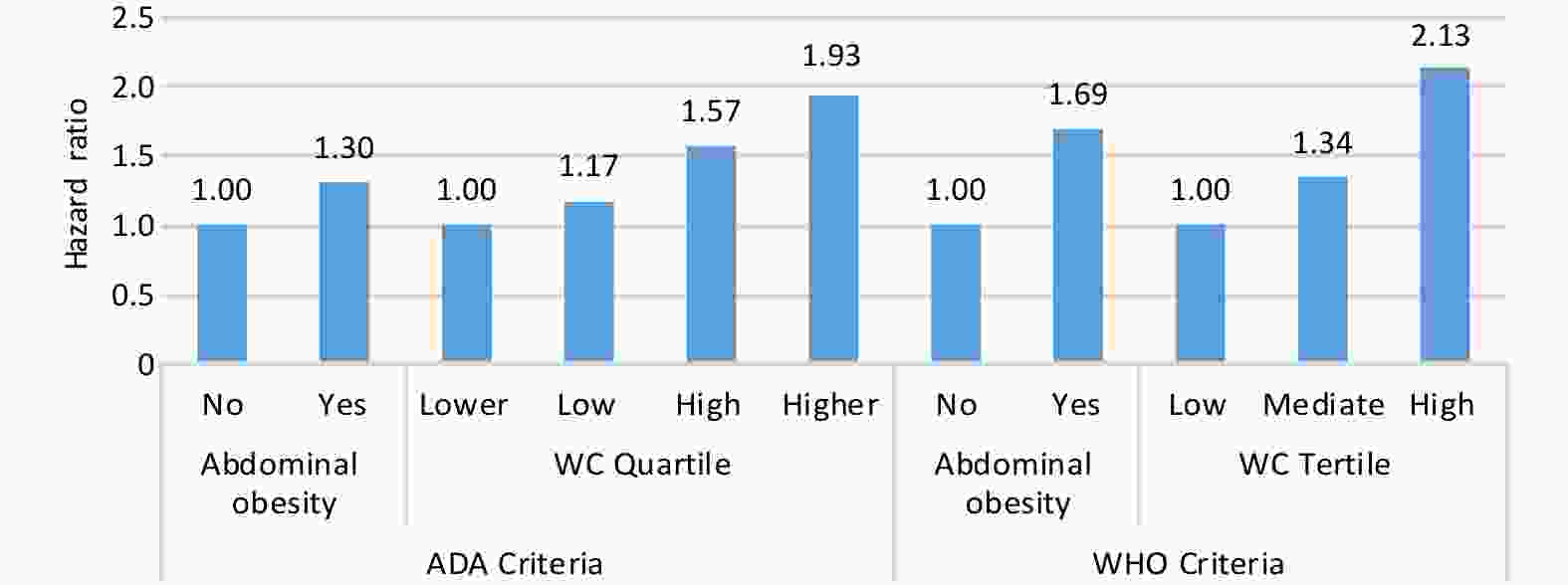
Objective This study aimed to explore the association between body mass index (BMI) and mortality based on the 10-year population-based multicenter prospective study. Methods A general population-based multicenter prospective study was conducted at four sites in rural China between 2013 and 2023. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards models and restricted cubic spline analyses were used to assess the association between BMI and mortality. Stratified analyses were performed based on the individual characteristics of the participants. Results Overall, 19,107 participants with a sum of 163,095 person-years were included and 1,910 participants died. The underweight (< 18.5 kg/m2) presented an increase in all-cause mortality (adjusted hazards ratio [aHR] = 2.00, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.66–2.41), while overweight (≥ 24.0 to < 28.0 kg/m2) and obesity (≥ 28.0 kg/m2) presented a decrease with an aHR of 0.61 (95% CI: 0.52–0.73) and 0.51 (95% CI: 0.37–0.70), respectively. Overweight (aHR = 0.76, 95% CI: 0.67–0.86) and mild obesity (aHR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.59–0.87) had a positive impact on mortality in people older than 60 years. All-cause mortality decreased rapidly until reaching a BMI of 25.7 kg/m2 (aHR = 0.95, 95% CI: 0.92–0.98) and increased slightly above that value, indicating a U-shaped association. The beneficial impact of being overweight on mortality was robust in most subgroups and sensitivity analyses. Conclusion This study provides additional evidence that overweight and mild obesity may be inversely related to the risk of death in individuals older than 60 years. Therefore, it is essential to consider age differences when formulating health and weight management strategies.
2025, 38(10): 1194-1204.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.112
Objective To investigate the relationship between physical activity and genetic risk and their combined effects on the risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Methods This prospective cohort study included 318,085 biobank participants from the UK. Physical activity was assessed using the short form of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire. The participants were stratified into low-, intermediate-, and high-genetic-risk groups based on their polygenic risk scores. Multivariate Cox regression models and multiplicative interaction analyses were used. Results During a median follow-up period of 13 years, 9,209 participants were diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. For low genetic risk, compared to low physical activity, the hazard ratios (HRs) for moderate and high physical activity were 0.853 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.748–0.972) and 0.831 (95% CI: 0.727–0.950), respectively. For intermediate genetic risk, the HRs were 0.829 (95% CI: 0.758–0.905) and 0.835 (95% CI: 0.764–0.914), respectively. For participants with high genetic risk, the HRs were 0.809 (95% CI: 0.746–0.877) and 0.818 (95% CI: 0.754–0.888), respectively. A significant interaction was observed between genetic risk and physical activity. Conclusion Moderate or high levels of physical activity were associated with a lower risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease across all genetic risk groups, highlighting the need to tailor activity interventions for genetically susceptible individuals.
2025, 38(10): 1205-1216.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.122
Objective The role of cold spells of different intensities in the economic burden of death is crucial for health adaptation to climate change, especially in a multi-site setting. The objective of the study was to explore the economic burden of mortality attributable to cold spells Methods We performed a two-stage time-series analysis using the Value of Statistical Life (VSL) approach to evaluate the economic impact of mortality related to cold spells of varying lengths and intensities. This analysis employed a case-crossover design, with a distributed lag nonlinear model (DLNM) used for analysis. Analysis was stratified according to age, sex, and region of origin. The results of the assessment show that cold spells have an enormous impact on the economic losses of mortality due to climate change and aging. Results Totally, 8.3% (95% CI: 0.0%, 16.0%) to 13.8% (95% CI: 1.0%, 24.8%) of VSL were ascribed to cold spells, accounting for economic losses of 4.71 (95% CI: 0.34, 8.47) to 11.45 (95% CI: 0.00, 21.00) billion CNY, in the cold season. The population aged over 65 y and females are particularly vulnerable. Economic impacts in warmer regions, such as the southern and subtropical zones, are more extensive than those in the northern and temperate zones. Conclusion Customizing cold spell prevention measures for vulnerable populations or regions is vital to alleviating the socioeconomic burden.
2025, 38(10): 1217-1229.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.125
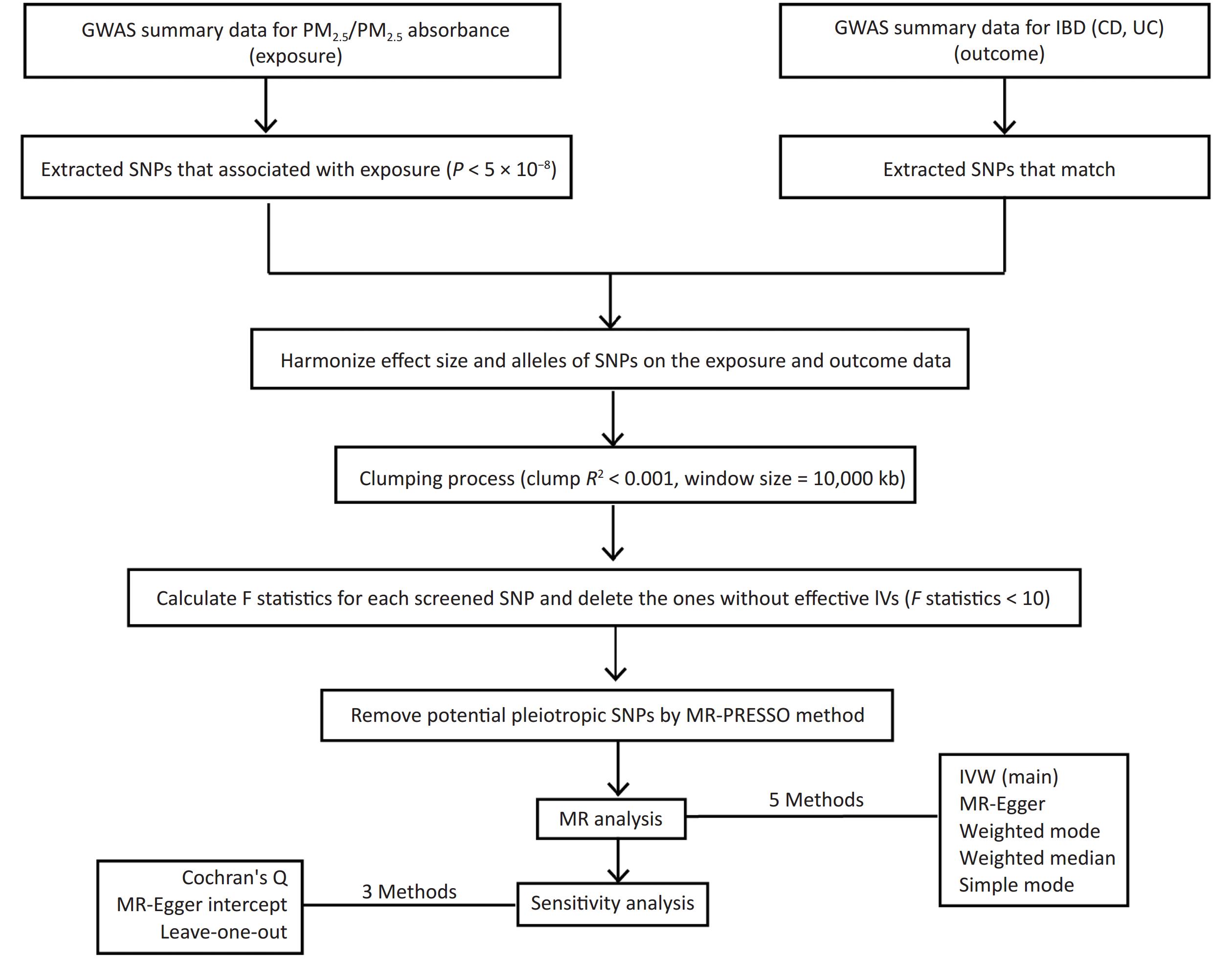
Objective To investigate the association of various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) metabolites with diverse subtypes of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk. Methods A novel predicting risk of cardiovascular disease EVENTs PREVENT equation was used to estimate the 10-year diverse subtypes of CVD risk, and their associations with PAH metabolites were analyzed using multiple logistic regression models, the weighted quantile sum (WQS) model, the quantile g-computation (qgcomp) model, and a stratified analysis of subgroups. Results For this study, six thousand seven hundred and forty-five participants were selected, and significant positive associations were observed between PAHs, naphthalene (NAP), and fluorene (FLU), and the risks of total CVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), and heart failure (HF). NAP and FLU were the primary contributors to the effects of PAH mixtures, and their associations with total CVD, ASCVD, and HF risk were significant in younger participants (30 ≤ age < 50 years); however, the associations of phenanthrene (PHEN) with ASCVD, HF, coronary heart disease (CHD), and stroke were dominant in aging participants (age ≥ 50 years). Notably, pyrene (PYR) was negatively associated with the risk of ASCVD, HF, CHD, and stroke. Similarly, negative associations of PYR with the four CVD subtypes were noticeable in aging participants. Conclusion Different PAHs metabolites had different impacts on each CVD subtype among different age groups. Notably, the protective effects of PYR on ASCVD, HF, CHD, and stroke were noticeable in aging individuals.
2025, 38(10): 1230-1245.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.129
Objectives To characterize fine particulate matter (PM2.5)-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) emitted from different cooking fumes and their exposure routes and assess their health-associated impact to provide a reference for health risk prevention from PAH exposure across different age and sex groups. Methods Sixteen PM2.5-bound PAHs emitted from 11 cooking styles were analyzed using GC-MS/MS. The health hazards of these PAHs in the Handan City population (stratified by age and sex) were predicted using the incremental lifetime cancer risk (ILCR) model. The respiratory deposition doses (RDDs) of the PAHs in children and adults were calculated using the PM2.5 deposition rates in the upper airway, tracheobronchial, and alveolar regions. Results The total concentrations of PM2.5-bound PAHs ranged from 61.10 to 403.80 ng/m3. Regardless of cooking styles, the ILCRtotal values for adults (1.23 × 10−6 to 3.70 × 10−6) and older adults (1.28 × 10−6 to 3.88 × 10−6) exceeded the acceptable limit of 1.00 × 10–6. With increasing age, the ILCRtotal value first declined and then increased, varying substantially among the population groups. Cancer risk exhibited particularly high sensitivity to short exposure to barbecue-derived PAHs under equivalent body weights. Furthermore, barbecue, Sichuan and Hunan cuisine, Chinese cuisine, and Chinese fast food were associated with higher RDDs for both adults and children. Conclusion ILCRtotal values exceeded the acceptable limit for both females and males of adults, with all cooking styles showing a potentially high cancer risk. Our findings serve as an important reference for refining regulatory strategies related to catering emissions and mitigating health risks associated with cooking styles.
2025, 38(10): 1246-1254.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.123
Objective Recaticimab (SHR-1209) significantly reduces low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. However, its effect on glucose metabolism remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate its effect on glycemic parameters in a Chinese population. Methods Recaticimab versus placebo was administered in a 5:1 ratio to 110 hyperlipidemia patients who were followed up for 24 weeks. Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels were measured at baseline every 12 weeks. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels were measured at baseline at week 1, 3, 5, 8, 12, 16, 20, and 24. Repeated-measures mixed-effects models were used to determine the longitudinal association between reacticimab and FPG and HbA1c levels. Results Among the 81 participants with normal glucose metabolism, HbA1c levels significantly decreased (F = 4.568, P = 0.036). In the 29 participants with abnormal glucose metabolism, a significant time effect was observed for FPG levels (F = 2.492, P = 0.016). For participants with normal and abnormal glucose metabolism, no significant group × time interaction effects on FPG or HbA1c levels were identified. Conclusion Recaticimab showed no adverse glycemic effects in participants with normal or abnormal glucose metabolism, indicating its safety in patients with or without diabetes.
2025, 38(10): 1255-1269.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.092
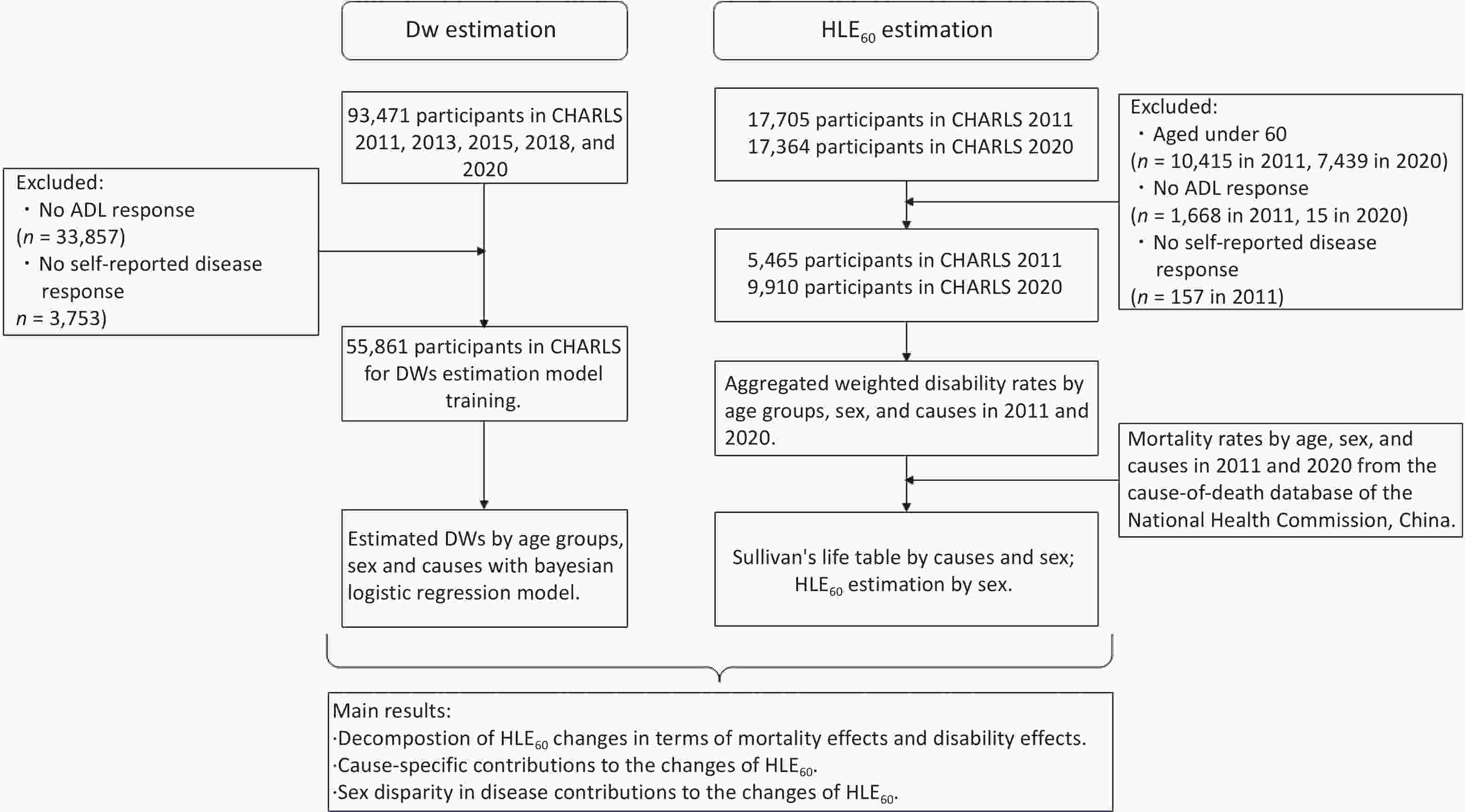
Objective To explore the relationship between serum chloride levels and prognosis in patients with hepatic coma in the intensive care unit (ICU). Methods We analyzed 545 patients with hepatic coma in the ICU from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV (MIMIC-IV) database. Associations between serum chloride levels and 28-day and 1-year mortality rates were assessed using restricted cubic splines (RCSs), Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves, and Cox regression. Subgroup analyses, external validation, and mechanistic studies were also performed. Results A total of 545 patients were included in the study. RCS analysis revealed a U-shaped association between serum chloride levels and mortality in patients with hepatic coma. The KM curves indicated lower survival rates among patients with low chloride levels (< 103 mmol/L). Low chloride levels were independently linked to increased 28-day and 1-year all-cause mortality rates. In the multivariate models, the hazard ratio (HR) for 28-day mortality in the low-chloride group was 1.424 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.041–1.949), while the adjusted hazard ratio for 1-year mortality was 1.313 (95% CI: 1.026–1.679). Subgroup analyses and external validation supported these findings. Cytological experiments suggested that low chloride levels may activate the phosphorylation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, promote the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and reduce neuronal cell viability. Conclusion Low serum chloride levels are independently associated with increased mortality in patients with hepatic coma.
2025, 38(10): 1270-1286.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.028
Objective Pneumoconiosis, a lung disease caused by irreversible fibrosis, represents a significant public health burden. This study investigates the causal relationships between gut microbiota, gene methylation, gene expression, protein levels, and pneumoconiosis using a multi-omics approach and Mendelian randomization (MR). Methods We analyzed gut microbiota data from MiBioGen and Esteban et al. to assess their potential causal effects on pneumoconiosis subtypes (asbestosis, silicosis, and inorganic pneumoconiosis) using conventional and summary-data-based MR (SMR). Gene methylation and expression data from Genotype-Tissue Expression and eQTLGen, along with protein level data from deCODE and UK Biobank Pharma Proteomics Project, were examined in relation to pneumoconiosis data from FinnGen. To validate our findings, we assessed self-measured gut flora from a pneumoconiosis cohort and performed fine mapping, drug prediction, molecular docking, and Phenome-Wide Association Studies to explore relevant phenotypes of key genes. Results Three core gut microorganisms were identified: Romboutsia (OR = 0.249) as a protective factor against silicosis, Pasteurellaceae (OR = 3.207) and Haemophilus parainfluenzae (OR = 2.343) as risk factors for inorganic pneumoconiosis. Additionally, mapping and quantitative trait loci analyses revealed that the genes VIM, STX8, and MIF were significantly associated with pneumoconiosis risk. Conclusions This multi-omics study highlights the associations between gut microbiota and key genes (VIM, STX8, MIF) with pneumoconiosis, offering insights into potential therapeutic targets and personalized treatment strategies.
2025, 38(10): 1287-1301.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.115
Objective This study aimed to investigate the effect of Astragalus (AST) on osteoporosis (OP) and the downstream mechanisms. Methods Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs) were induced to differentiate into osteogenic cells. After transfection with relevant plasmids, cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis were assessed. Alizarin red staining was used to detect calcium nodules in the cells, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining was used to detect ALP activity in the cells, and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blotting were used to determine RUNX2 and Osterix expression levels. An OP rat model was established using ovariectomy and micro-computed tomography scanning. Hematoxylin and eosin staining and Masson’s trichrome staining were used to evaluate the pathological conditions of bone tissues, while immunohistochemistry was conducted to detect RUNX2 in bone tissues. Results AST promoted the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs, reduced miR-181d-5p expression levels, and increased SOX11 expression levels. Restoring miR-181d-5p expression or reducing SOX11 expression levels reversed the effects of AST on the osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs. miR-181d-5p was found to target SOX11 in hBMSCs. AST improved OP in rats, and miR-181d-5p overexpression or SOX11 inhibition reversed the therapeutic effects of AST on OP in rats. Conclusion AST promoted the osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs and alleviated OP by targeting SOX11 via miR-181d-5p.
2025, 38(10): 1314-1319.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.131
2015, 28(1): 57-71.
doi: 10.3967/bes2015.006
2022, 35(7): 573-603.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.079
2023, 36(8): 669-701.
doi: 10.3967/bes2023.106
2018, 31(2): 87-96.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.011
2012, 25(3): 317-324.
doi: 10.3967/0895-3988.2012.03.010
2019, 32(8): 559-570.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.074
2014, 27(8): 606-613.
doi: 10.3967/bes2014.093
2018, 31(3): 208-214.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.026
2003, 16(3): 246-255.
2019, 32(9): 659-672.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.085
2022, 35(5): 381-392.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.054
2016, 29(3): 212-218.
doi: 10.3967/bes2016.026
2022, 35(7): 648-651.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.084
2018, 31(9): 637-644.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.088
2019, 32(8): 578-591.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.076
2019, 32(10): 769-778.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.096
2017, 30(5): 384-389.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.051
Current Issue
-
2024 Impact Factor 4.1
-
2024 Journal Citation Reports

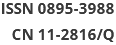












































 Quick Links
Quick Links