, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2024.081
Objective Microcystin-leucine-arginine (MC-LR) exposure induces lipid metabolism disorders in the liver. Secreted frizzled-related protein 5(SFRP5)is a natural antagonist of winglesstype MMTV integration site family, member 5A (Wnt5a) and an anti-inflammatory adipocytokine. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether MC-LR can induce lipid metabolism disorders in hepatocytes and whether SFRP5, which has anti-inflammatory effects, can alleviate the effects of hepatic lipid metabolism by inhibiting the Wnt5a/Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway. Methods We exposed mice to MC-LR in vivo to induce liver lipid metabolism disorders. Subsequently, mouse hepatocytes that overexpressed SFRP5 or did not express SFRP5 were exposed to MC-LR, and the effects of SFRP5 overexpression on inflammation and Wnt5a/JNK activation by MC-LR were observed. Results MC-LR exposure induced liver lipid metabolism disorders in mice and significantly decreased SFRP5 mRNA and protein levels in a concentration-dependent manner. SFRP5 overexpression in AML12 cells suppressed MC-LR-induced inflammation. Overexpression of SFRP5 also inhibited Wnt5a and phosphorylation of JNK. Conclusion MC-LR can induce lipid metabolism disorders in mice, and SFRP5 can attenuate lipid metabolism disorders in the mouse liver by inhibiting Wnt5a/JNK signaling.
ZHANG Wei Jia,
ZHAO Jie Rong,
YIN Qi Kai,
LIU Sheng Hui,
WANG Rui Chen,
FU Shi Hong,
LI Fan,
HE Ying,
NIE Kai,
LIANG Guo Dong,
XU Song Tao,
YANG Guang,
WANG Huan Yu
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2024.078
Objective Genotypes (G) 1, 3, and 5 of the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) have been isolated in China, but the dominant genotype circulating in Chinese coastal areas remains unknown. We searched for G5 JEV-infected cases and attempted to elucidate which JEV genotype was most closely related to human Japanese encephalitis (JE) in the coastal provinces of China. Methods In this study, we collected serum specimens from patients with JE in three coastal provinces of China (Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Shandong) from 2018 to 2020 and conducted JEV cross-neutralization tests against G1, 3, and 5. Results Acute serum specimens from clinically reported JE cases were obtained for laboratory confirmation from hospitals in Shandong (92 patients), Zhejiang (192 patients), and Guangdong (77 patients), China, from 2018 to 2020. Seventy of the 361 serum specimens were laboratory-confirmed to be infected with JEV. Two cases were confirmed to be infected with G1 JEV, 32 with G3 JEV, and two with G5 JEV. Conclusion G3 was the primary infection genotype among JE cases with a definite infection genotype, and the infection caused by G5 JEV was confirmed serologically in China.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2024.082
Objective Chlorination is often used to disinfect recreational water in large amusement parks; however, the health hazards of chlorination disinfection by-products (DBPs) to occupational populations are unknown. This study aimed to assess the exposure status of chlorinated DBPs in recreational water and the health risks to employees of large amusement parks. Methods Exposure parameters of employees of three large amusement parks in Shanghai were investigated using a questionnaire. Seven typical chlorinated DBPs in recreational water and spray samples were quantified by gas chromatography, and the health risks to amusement park employees exposed to chlorinated DBPs were evaluated according to the WHO's risk assessment framework. Results Trichloroacetic acid, dibromochloromethane, bromodichloromethane, and dichloroacetic acid were detected predominantly in recreational water. The carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks of the five DBPs did not exceed the risk thresholds. In addition, the carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risks of mixed exposure to DBPs were within the acceptable risk limits. Conclusion Typical DBPs were widely detected in recreational water collected from three large amusement parks in Shanghai; however, the health risks of DBPs and their mixtures were within acceptable limits.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2024.080
Objective Our study aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of the current status and dynamic trends of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) prevalence in Sichuan, the second most heavily affected province in China, and to explore future interventions. Methods The epidemiological, behavioral, and population census data from multiple sources were analyzed to extract inputs for an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) Epidemic Model (AEM). Baseline curves, derived from historical trends in HIV prevalence, were used, and the AEM was employed to examine future intervention scenarios. Results In 2015, the modeled data suggested an adult HIV prevalence of 0.191% in Sichuan, with an estimated 128,766 people living with HIV/AIDS and 16,983 individuals with newly diagnosed infections. Considering current high-risk behaviors, the model predicts an increase in the adult prevalence to 0.306% by 2025, projecting an estimated 212,168 people living with HIV/AIDS and 16,555 individuals with newly diagnosed infections. Conclusion Heterosexual transmission will likely emerge as the primary mode of AIDS transmission in Sichuan. Furthermore, we anticipate a stabilization in the incidence of AIDS with a concurrent increase in prevalence. Implementing comprehensive intervention measures aimed at high-risk groups could effectively alleviate the spread of AIDS in Sichuan.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2024.079
Objective To systematically summarize the published literature on the genetic variants associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Methods Literature from Web of Science, PubMed, and Embase between January 1980 and September 2022 was systematically searched. Meta-analyses of the genetic variants were conducted using at least five data sources. The epidemiologic credibility of the significant associations was graded using the Venice criteria. Results Based on literature screening, 399 eligible studies were included, comprising 381 candidate gene association, 16 genome-wide association, and 2 whole-exome sequencing studies. We identified 465 genetic variants in 173 genes in candidate gene association studies, and 25 genetic variants in 17 genes were included in the meta-analysis. The meta-analysis identified 11 variants in 10 genes that were significantly associated with NAFLD, with cumulative epidemiological evidence of an association graded as strong for two variants in two genes (HFE, TNF), moderate for four variants in three genes (TM6SF2, GCKR, and ADIPOQ), and weak for five variants in five genes (MBOAT7, PEMT, PNPLA3, LEPR, and MTHFR). Conclusions This study identified six variants in five genes that had moderate to strong evidence of an association with NAFLD, which may help understand the genetic architecture of NAFLD risk.
KONG Zi Qing,
LIU Li Qun,
HUANG De Qin,
WANG Yu Tong,
LI Jing Jie,
ZHANG Zheng,
WANG Xi Xi,
LIU Chuan Ling,
ZHANG Ya Di,
SHAO Jia Kang,
ZHU Yi Min,
CHEN Yi Meng,
LIU Mei,
ZHAO Wei Hong
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2024.014
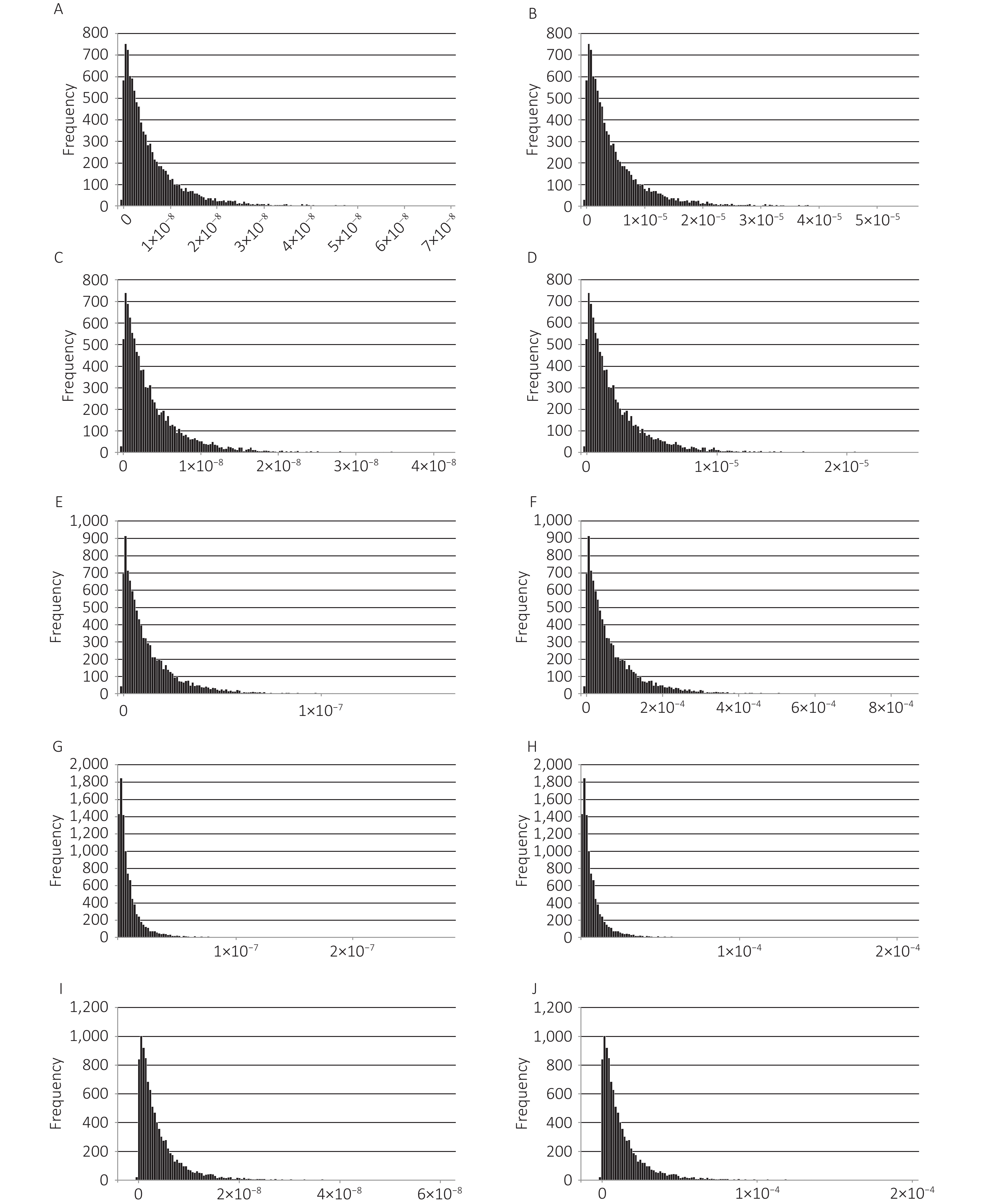
Objective This study aimed to comprehensively analyze and compare the clinicopathological features and prognosis of Chinese patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-low early breast cancer (BC) and HER2-IHC0 BC. Methods Patients diagnosed with HER2-negative BC (N = 999) at our institution between January 2011 and December 2015 formed our study population. Clinicopathological characteristics, association between estrogen receptor (ER) expression and HER2-low, and evolution of HER2 immunohistochemical (IHC) score were assessed. Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test were used to compare the long-term survival outcomes (5-year follow-up) between the HER2-IHC0 and HER2-low groups. Results HER2-low BC group tended to demonstrate high expression of ER and more progesterone receptor (PgR) positivity than HER2-IHC0 BC group (P < 0.001). The rate of HER2-low status increased with increasing ER expression levels (Mantel-Haenszel χ2 test, P < 0.001, Pearson’s R = 0.159, P < 0.001). Survival analysis revealed a significantly longer overall survival (OS) in HER2-low BC group than in HER2-IHC0 group (P = 0.007) in the whole cohort and the hormone receptor (HR)-negative group. There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of disease-free survival (DFS). The discordance rate of HER2 IHC scores between primary and metastatic sites was 36.84%. Conclusion HER2-low BC may not be regarded as a unique BC group in this population-based study due to similar clinicopathological features and prognostic roles.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2024.077
Objective A high sodium (HS) diet is believed to affect bone metabolism processes. Clarifying its impact on osseointegration of titanium (Ti) implants holds significant implications for postoperative dietary management of implanted patients. Methods This investigation probed the impact of sodium ions (Na+) on neovascularization and osteogenesis around Ti implants in vivo, utilizing micro-computed tomography, hematoxylin and eosin staining, and immunohistochemical analyses. Concurrently, in vitro experiments assessed the effects of varied Na+ concentrations and exposure durations on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and MC3T3-E1 cells. Results In vivo, increased dietary sodium (0.8%-6%) led to a substantial decline in CD34 positive HUVECs and new bone formation around Ti implants, alongside an increase in inflammatory cells. In vitro, an increase in Na+ concentration (140 mmol/L–150 mmol/L) adversely affected the proliferation, angiogenesis, and migration of HUVECs, especially with prolonged exposure. While MC3T3-E1 cells initially exhibited less susceptibility to high Na+ concentrations compared to HUVECs during short-term exposure, prolonged exposure to a HS environment progressively diminished their proliferation, differentiation, and osteogenic capabilities. Conclusion These findings suggest that HS diet had a negative effect on the early osseointegration of Ti implants by interfering with the process of postoperative vascularized bone regeneration.

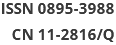



















 Quick Links
Quick Links