Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes /issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.081
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.078
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.082
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.080
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.079
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.077
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.014
2024, 37(4): 341-353.
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.039
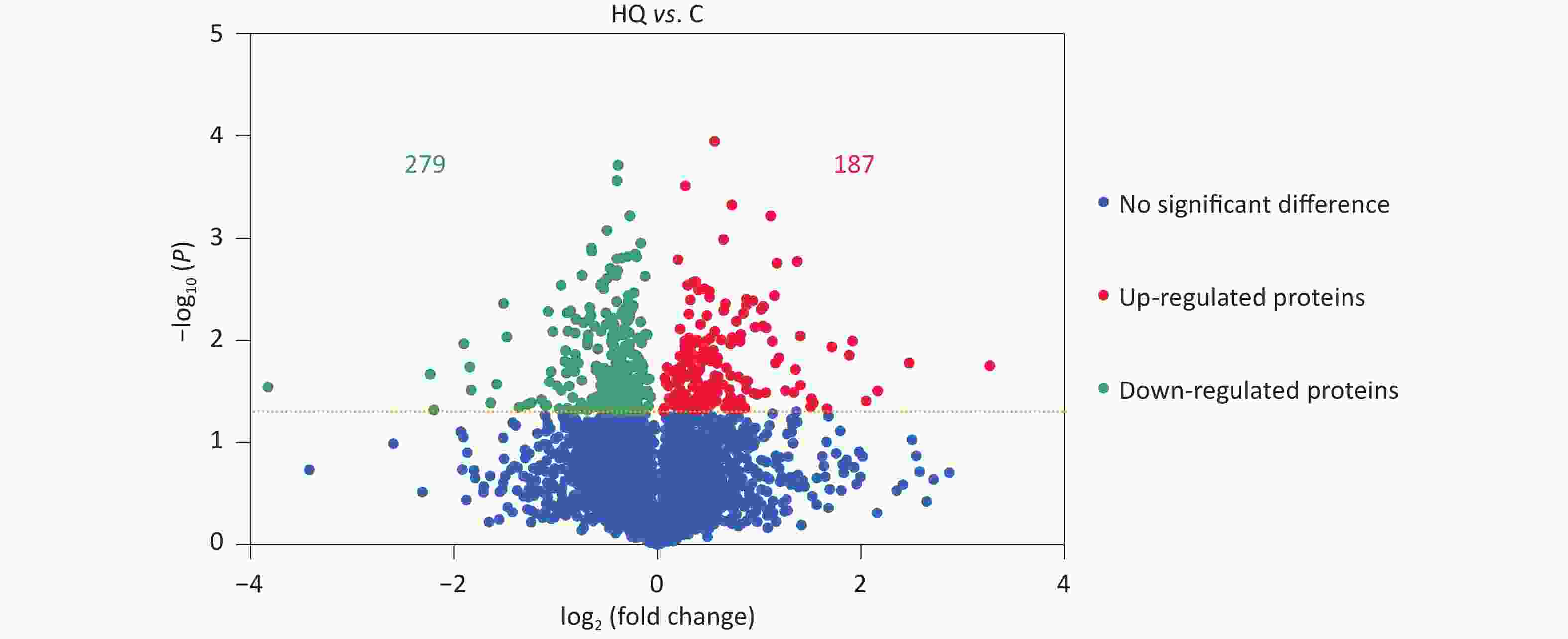
Objective Hydroquinone (HQ), one of the phenolic metabolites of benzene, is widely recognized as an important participant in benzene-induced hematotoxicity. However, there are few relevant proteomics in HQ-induced hematotoxicity and the mechanism hasn’t been fully understood yet. Methods In this study, we treated K562 cells with 40 μmol/L HQ for 72 h, examined and validated protein expression changes by Label-free proteomic analysis and Parallel reaction monitoring (PRM), and performed bioinformatics analysis to identify interaction networks. Results One hundred and eighty-seven upregulated differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) and 279 downregulated DEPs were identified in HQ-exposed K562 cells, which were involved in neutrophil-mediated immunity, blood microparticle, and other GO terms, as well as the lysosome, metabolic, cell cycle, and cellular senescence-related pathways. Focusing on the 23 DEGs and 5 DEPs in erythroid differentiation-related pathways, we constructed the network of protein interactions and determined 6 DEPs (STAT1, STAT3, CASP3, KIT, STAT5B, and VEGFA) as main hub proteins with the most interactions, among which STATs made a central impact and may be potential biomarkers of HQ-induced hematotoxicity. Conclusion Our work reinforced the use of proteomics and bioinformatic approaches to advance knowledge on molecular mechanisms of HQ-induced hematotoxicity at the protein level and provide a valuable basis for further clarification.
2024, 37(4): 354-366.
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.040
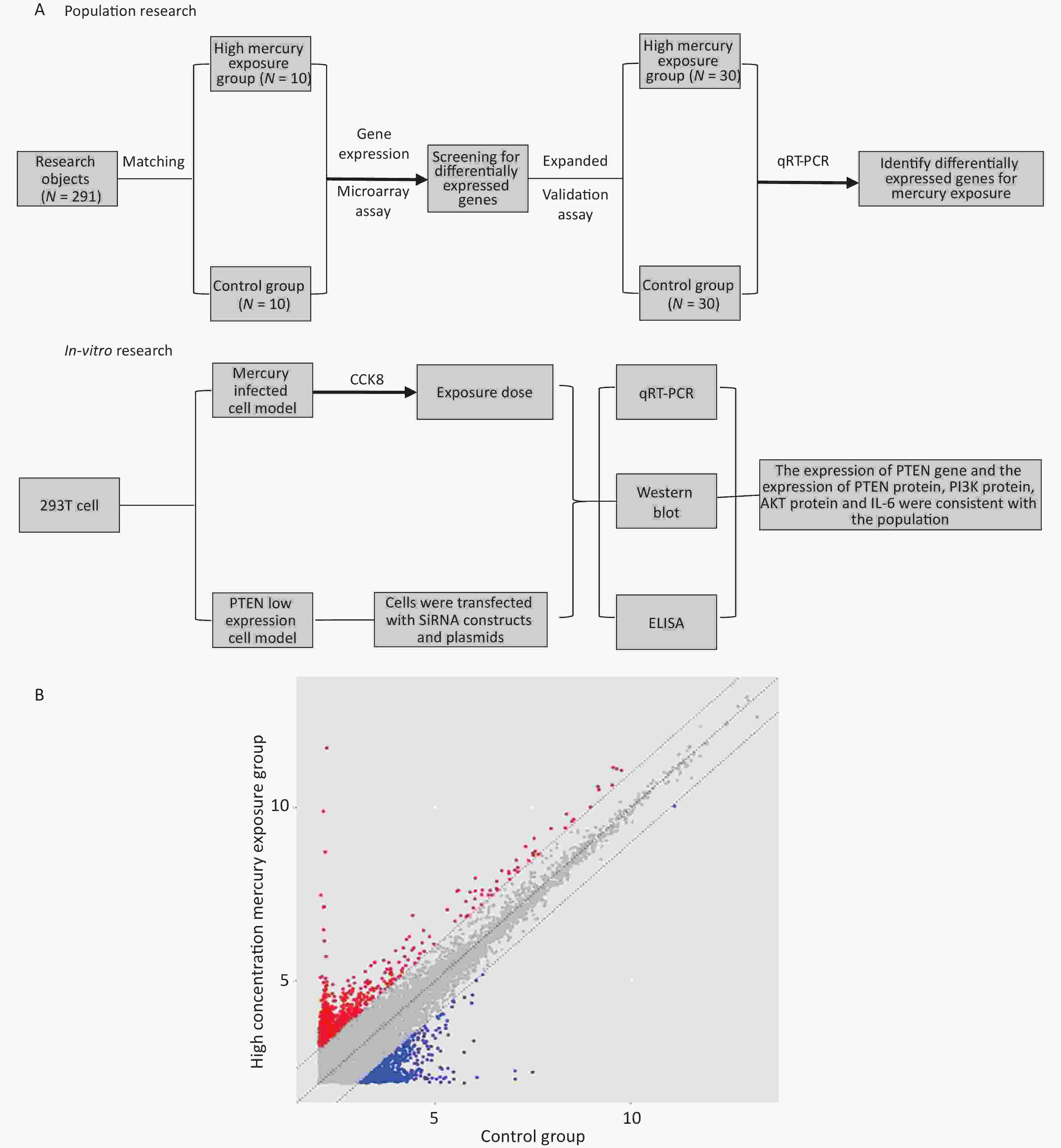
Objective This study investigated the impact of occupational mercury (Hg) exposure on human gene transcription and expression, and its potential biological mechanisms. Methods Differentially expressed genes related to Hg exposure were identified and validated using gene expression microarray analysis and extended validation. Hg-exposed cell models and PTEN low-expression models were established in vitro using 293T cells. PTEN gene expression was assessed using qRT-PCR, and Western blotting was used to measure PTEN, AKT, and PI3K protein levels. IL-6 expression was determined by ELISA. Results Combined findings from gene expression microarray analysis, bioinformatics, and population expansion validation indicated significant downregulation of the PTEN gene in the high-concentration Hg exposure group. In the Hg-exposed cell model (25 and 10 μmol/L), a significant decrease in PTEN expression was observed, accompanied by a significant increase in PI3K, AKT, and IL-6 expression. Similarly, a low-expression cell model demonstrated that PTEN gene knockdown led to a significant decrease in PTEN protein expression and a substantial increase in PI3K, AKT, and IL-6 levels. Conclusion This is the first study to report that Hg exposure downregulates the PTEN gene, activates the PI3K/AKT regulatory pathway, and increases the expression of inflammatory factors, ultimately resulting in kidney inflammation.
2024, 37(4): 367-376.
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.041
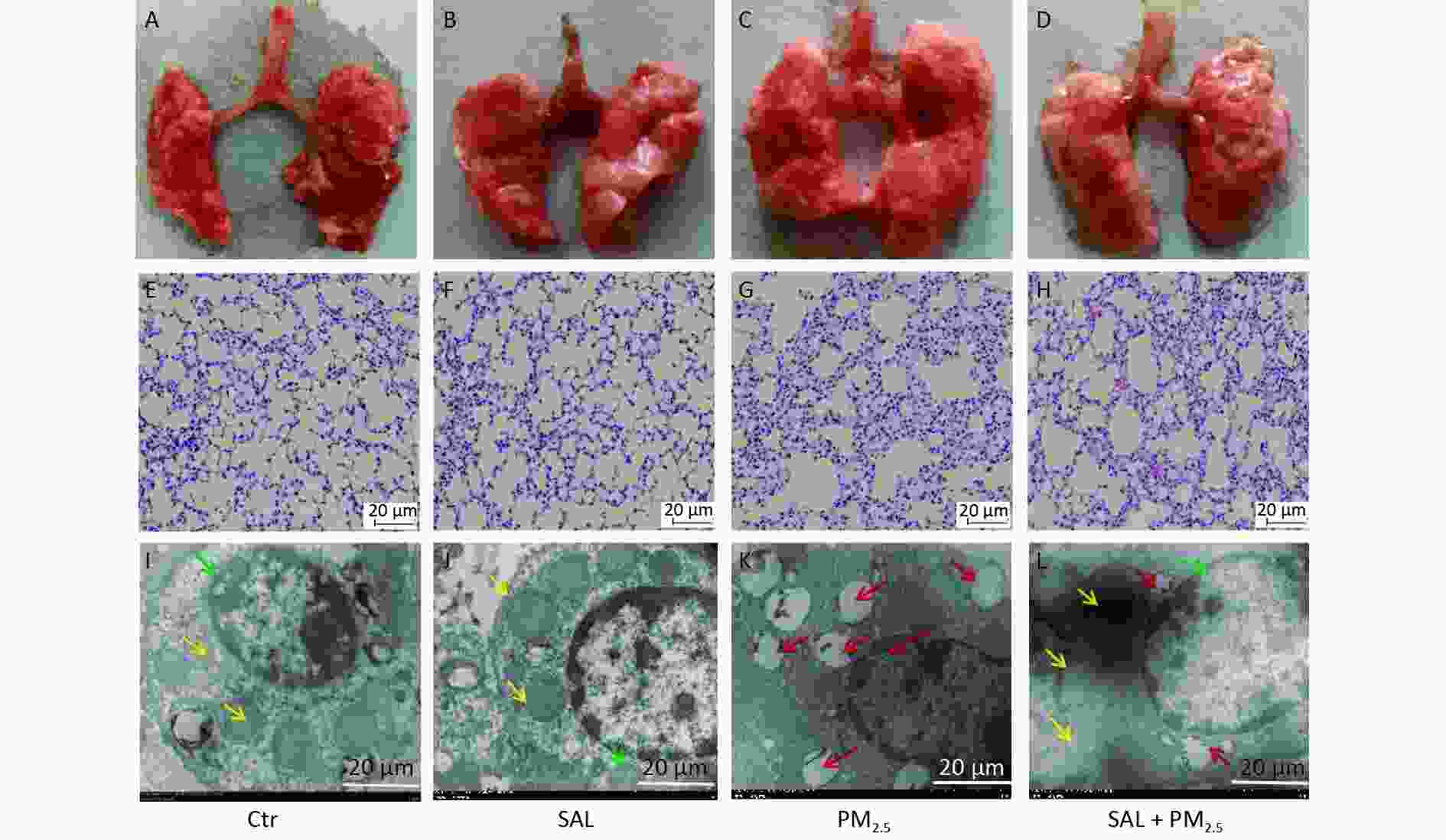
Objective This study aimed to clarify the intervention effect of salidroside (SAL) on lung injury caused by PM2.5 in mice and illuminate the function of SIRT1-PGC-1ɑ axis. Methods Specific pathogen-free (SPF) grade male C57BL/6 mice were randomly assigned to the following groups: control group, SAL group, PM2.5 group, SAL+PM2.5 group. On the first day, SAL was given by gavage, and on the second day, PM2.5 suspension was given by intratracheal instillation. The whole experiment consist of a total of 10 cycles, lasting 20 days. At the end of treatment, blood samples and lung tissues were collected and analyzed. Observation of pathological changes in lung tissue using inverted microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The expression of inflammatory, antioxidants, apoptosis, and SIRT1-PGC-1ɑ proteins were detected by Western blotting. Results Exposure to PM2.5 leads to obvious morphological and pathologica changes in the lung of mice. PM2.5 caused a decline in levels of antioxidant-related enzymes and protein expressions of HO-1, Nrf2, SOD2, SIRT1 and PGC-1ɑ, and an increase in the protein expressions of IL-6, IL-1β, Bax, caspase-9 and cleaved caspase-3. However, SAL reversed the aforementioned changes caused by PM2.5 by activating the SIRT1-PGC-1α pathway. Conclusion SAL can activate SIRT1-PGC-1ɑ to ameliorate PM2.5-induced lung injury.
2024, 37(4): 377-386.
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.042
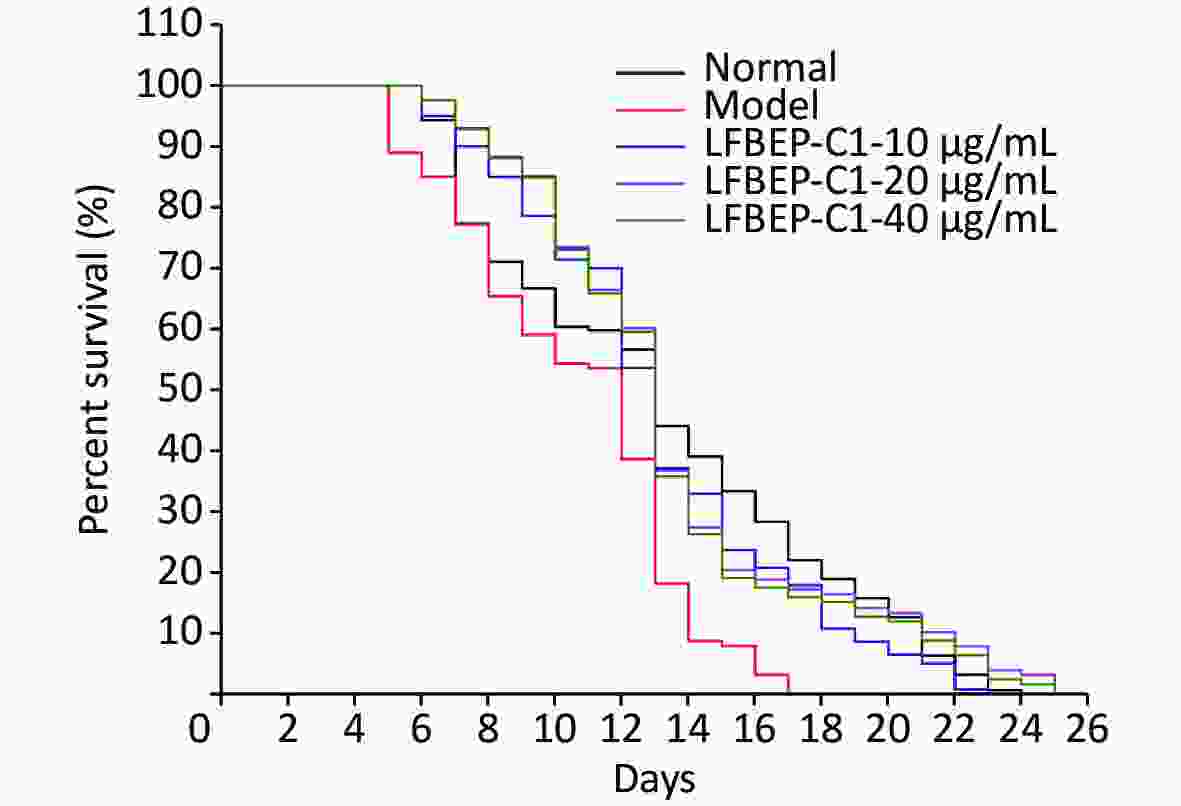
Objective This study aimed to investigate the lipid-lowering activity of LFBEP-C1 in high glucose-fed Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). Methods In this study, the fermented barley protein LFBEP-C1 was prepared and tested for its potential anti-obesity effects on C. elegans. The worms were fed Escherichia coli OP50 (E. coli OP50), glucose, and different concentrations of LFBEP-C1. Body size, lifespan, movement, triglyceride content, and gene expression were analyzed. The results were analyzed using ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparison test. Results Compared with the model group, the head-swing frequency of C. elegans in the group of LFBEP-C1 at 20 μg/mL increased by 33.88%, and the body-bending frequency increased by 27.09%. This indicated that LFBEP-C1 improved the locomotive ability of C. elegans. The average lifespan of C. elegans reached 13.55 days, and the body length and width of the C. elegans decreased after LFBEP-C1 intake. Additionally, LFBEP-C1 reduced the content of lipid accumulation and triglyceride levels. The expression levels of sbp-1, daf-2, and mdt-15 significantly decreased, while those of daf-16, tph-1, mod-1, and ser-4 significantly increased after LFBEP-C1 intake. Changes in these genes explain the signaling pathways that regulate lipid metabolism. Conclusion LFBEP-C1 significantly reduced lipid deposition in C. elegans fed a high-glucose diet and alleviated the adverse effects of a high-glucose diet on the development, lifespan, and exercise behavior of C. elegans. In addition, LFBEP-C1 regulated lipid metabolism mainly by mediating the expression of genes in the sterol regulatory element-binding protein, insulin, and 5-hydroxytryptamine signaling pathways.
2024, 37(4): 387-398.
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.043
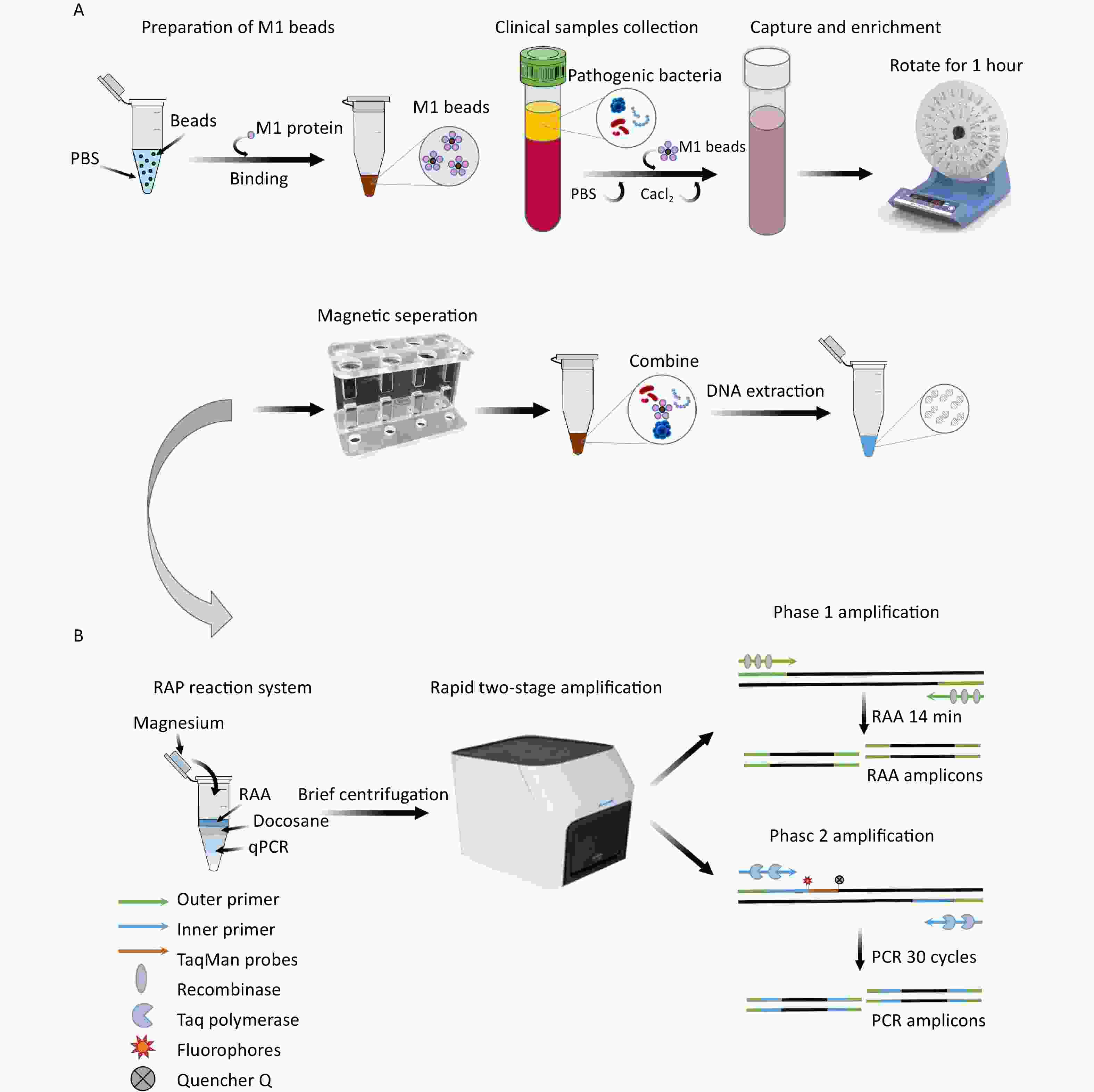
Objective Recombinase-aided polymerase chain reaction (RAP) is a sensitive, single-tube, two-stage nucleic acid amplification method. This study aimed to develop an assay that can be used for the early diagnosis of three types of bacteremia caused by Staphylococcus aureus (SA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA), and Acinetobacter baumannii (AB) in the bloodstream based on recombinant human mannan-binding lectin protein (M1 protein)-conjugated magnetic bead (M1 bead) enrichment of pathogens combined with RAP. Methods Recombinant plasmids were used to evaluate the assay sensitivity. Common blood influenza bacteria were used for the specific detection. Simulated and clinical plasma samples were enriched with M1 beads and then subjected to multiple recombinase-aided PCR (M-RAP) and quantitative PCR (qPCR) assays. Kappa analysis was used to evaluate the consistency between the two assays. Results The M-RAP method had sensitivity rates of 1, 10, and 1 copies/μL for the detection of SA, PA, and AB plasmids, respectively, without cross-reaction to other bacterial species. The M-RAP assay obtained results for < 10 CFU/mL pathogens in the blood within 4 h, with higher sensitivity than qPCR. M-RAP and qPCR for SA, PA, and AB yielded Kappa values of 0.839, 0.815, and 0.856, respectively (P < 0.05). Conclusion An M-RAP assay for SA, PA, and AB in blood samples utilizing M1 bead enrichment has been developed and can be potentially used for the early detection of bacteremia.
Objective This study aimed to determine the current epidemiological status of PLWHA aged ≥ 50 years in China from 2018 to 2021. It also aimed to recommend targeted interventions for the prevention and treatment of HIV/AIDS in elderly patients. Methods Data on newly reported cases of PLWHA, aged ≥ 50 years in China from 2018 to 2021, were collected using the CRIMS. Trend tests and spatial analyses were also conducted. Results Between 2018 and 2021, 237,724 HIV/AIDS cases were reported among patients aged ≥ 50 years in China. The main transmission route was heterosexual transmission (91.24%). Commercial heterosexual transmission (CHC) was the primary mode of transmission among males, while non-marital non-CHC ([NMNCHC]; 60.59%) was the prevalent route in women. The proportion of patients with CHC decreased over time (Z = 67.716, P < 0.01), while that of patients with NMNCHC increased (Z = 153.05, P < 0.01). The sex ratio varied among the different modes of infection, and it peaked at 17.65 for CHC. The spatial analysis indicated spatial clustering, and the high-high clustering areas were mainly distributed in the southwestern and central-southern provinces. Conclusion In China, PLWHA, aged ≥ 50 years, were predominantly infected through heterosexual transmission. The primary modes of infection were CHC and NMNCHC. There were variations in the sex ratio among different age groups, infected through various sexual behaviors. HIV/AIDS cases exhibited spatial clustering. Based on these results, the expansion of HIV testing, treatment, and integrated behavioral interventions in high-risk populations is recommended to enhance disease detection in key regions.
2024, 37(4): 406-417.
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.026
Objective This study aimed to efficiently reduce the release of radon from water bodies to protect the environment. Methods Based on the sizes of the experimental setup and modular float, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) was used to assess the impact of the area coverage rate, immersion depth, diffusion coefficient, and radon transfer velocity at the gas–liquid interface on radon migration and exhalation of radon-containing water. Based on the numerical simulation results, an estimation model for the radon retardation rate was constructed. The effectiveness of the CFD simulation was evaluated by comparing the experimental and simulated variation values of the radon retardation rate with the coverage area rates. Results The effect of radon transfer velocity on radon retardation in water bodies was minor and insignificant according to the appropriate value; therefore, an estimation model of the radon retardation rate of the coverage of a radon-containing water body was constructed using the synergistic impacts of three factors: area coverage rate, immersion depth, and diffusion coefficient. The deviation between the experimental and simulated results was < 4.3%. Conclusion Based on the numerical simulation conditions, an estimation model of the radon retardation rate of covering floats in water bodies under the synergistic effect of multiple factors was obtained, which provides a reference for designing covering floats for radon retardation in radon-containing water.
2015, 28(1): 57-71.
doi: 10.3967/bes2015.006
2022, 35(7): 573-603.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.079
2018, 31(2): 87-96.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.011
2012, 25(3): 317-324.
doi: 10.3967/0895-3988.2012.03.010
2003, 16(3): 246-255.
2019, 32(8): 559-570.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.074
2014, 27(8): 606-613.
doi: 10.3967/bes2014.093
2019, 32(9): 659-672.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.085
2018, 31(9): 637-644.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.088
2018, 31(3): 208-214.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.026
2016, 29(3): 212-218.
doi: 10.3967/bes2016.026
2019, 32(8): 578-591.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.076
2019, 32(6): 419-426.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.057
2022, 35(5): 381-392.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.054
2019, 32(10): 769-778.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.096
2017, 30(5): 384-389.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.051
Current Issue
-
2022 Impact Factor 3.5
-
2022 Journal Citation Reports






















 Quick Links
Quick Links