Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes /issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.008
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.019
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.018
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.017
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.016
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.015
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.014
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.013
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.012
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.011
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.119
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.151
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.009
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.005
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.170
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.167
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.166
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.163
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.160
Column
2026, 39(2): 131-145.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.159
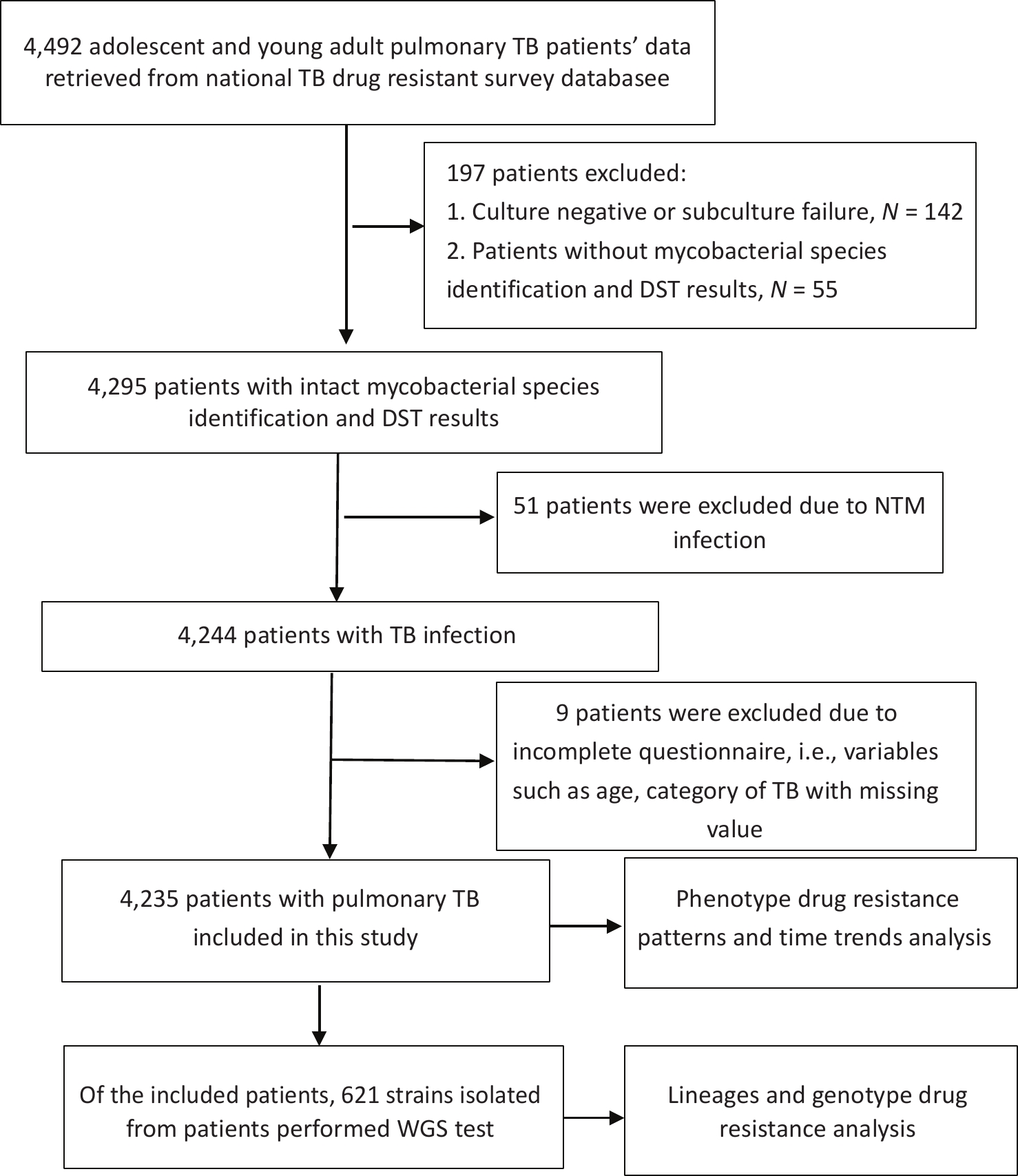
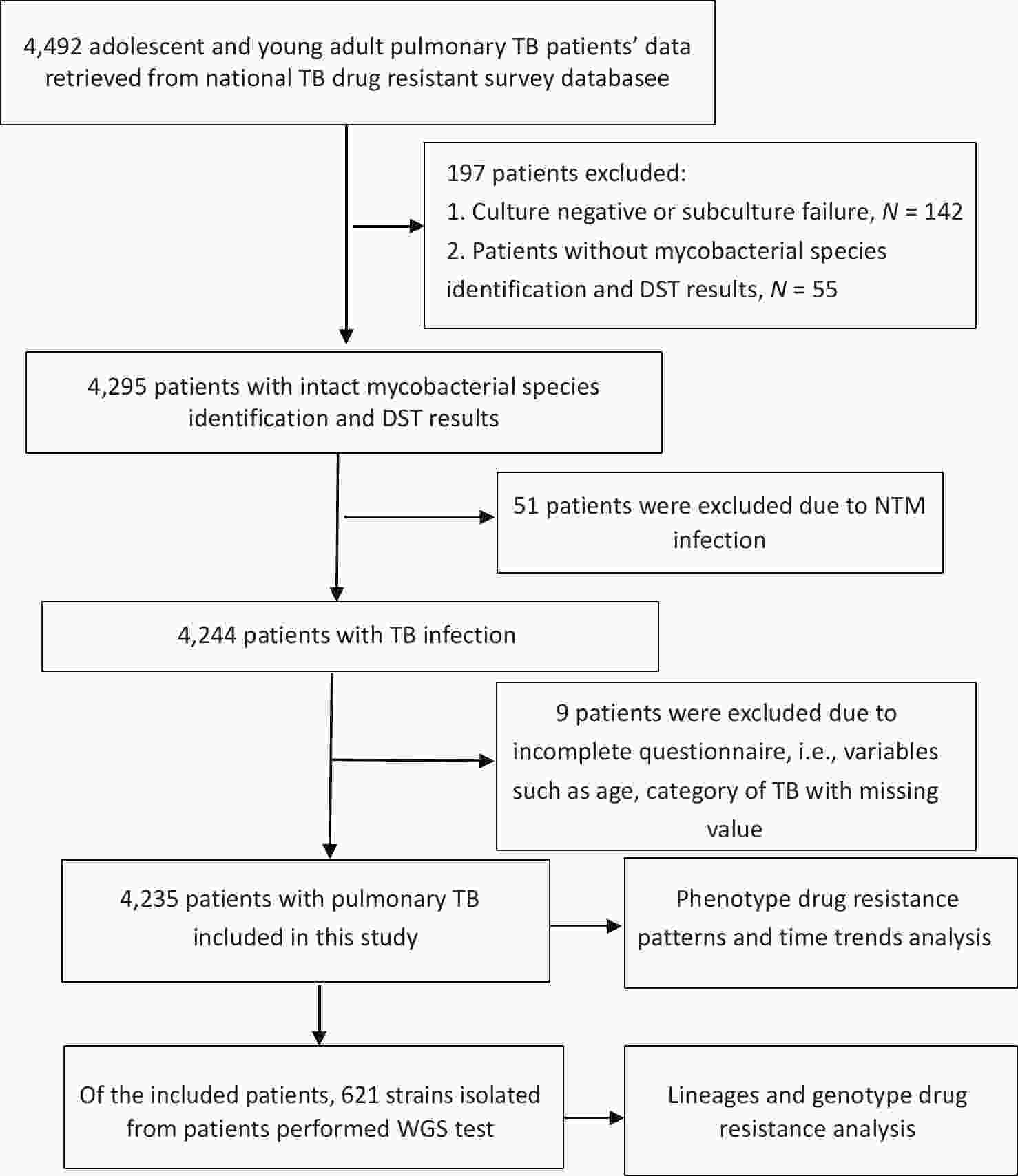
Objective To determine the proportions of drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB), its trends, and the drug resistance-conferring mutations among patients with pulmonary TB aged 10–24 years in China. Methods The data of patients with pulmonary TB were retrieved from a national drug-resistant TB survey for analysis. Joinpoint regression software was used to analyze time trends. We also used whole genome sequencing to analyze the lineages and drug resistance-conferring mutations of 621 isolates. Results Among 4,235 patients with pulmonary TB, the proportion of new cases of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) was 3.18% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.37–4.15) for adolescents and 3.76% (95% CI: 3.03–4.60) for young adults; for previously treated patients, MDR-TB accounted for 11.25% (95% CI: 5.28–20.28) of adolescents and 11.05% (95% CI: 6.88–16.55) of young adults. The proportion of patients with MDR-TB remained stable among both new and previously treated patients aged 10–24 years during the study period. Through whole genome sequencing, we found that the most common mutations in the MDR-TB strains were Ser315Thr in the katG gene (71.74%) and Ser450Leu in the rpoB gene (50.00%). Conclusion This study revealed a high proportion of MDR-TB among adolescents and young adults, indicating that urgent and comprehensive measures are needed to reduce the emergence and transmission of drug-resistant TB among this population in China.
2026, 39(2): 146-157.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.121
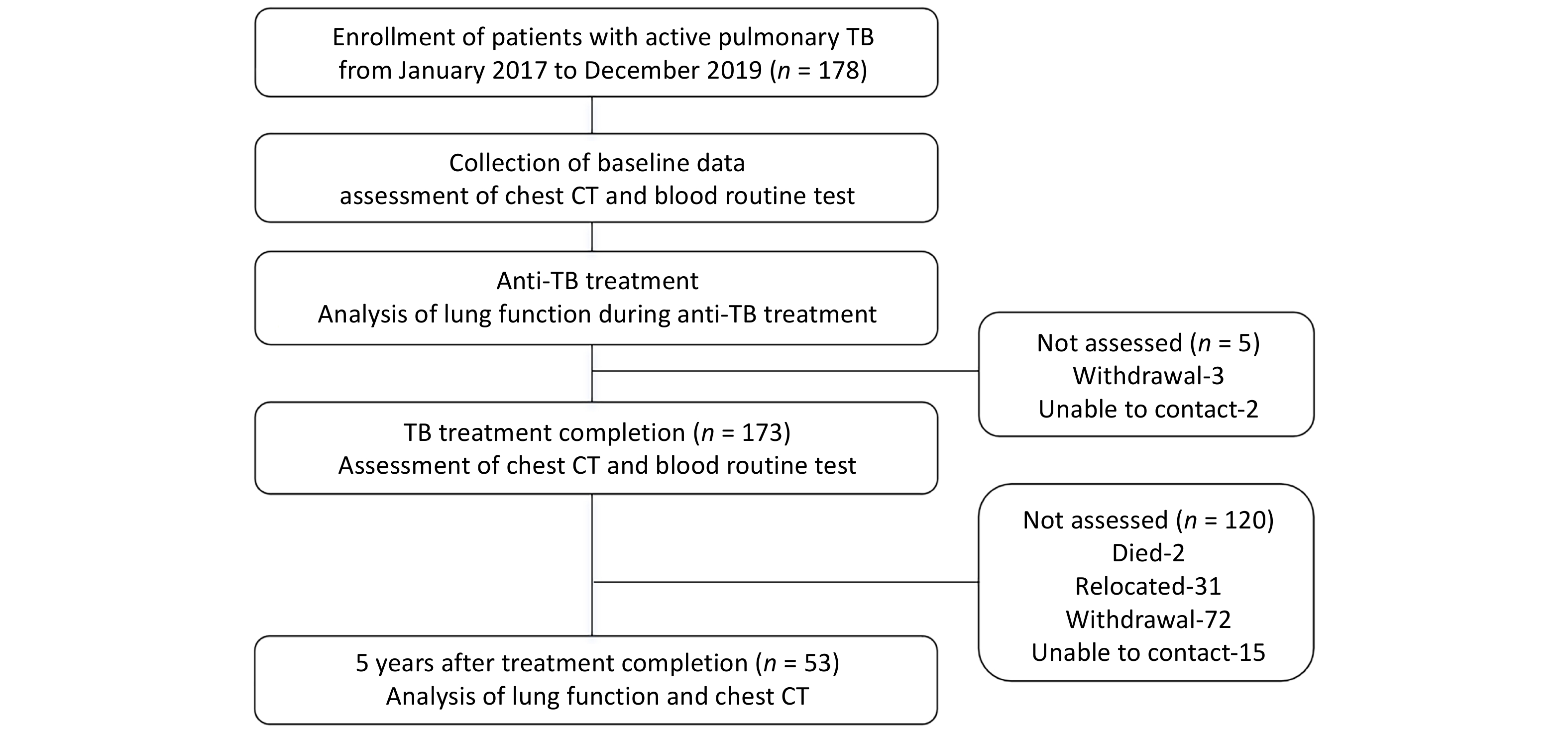
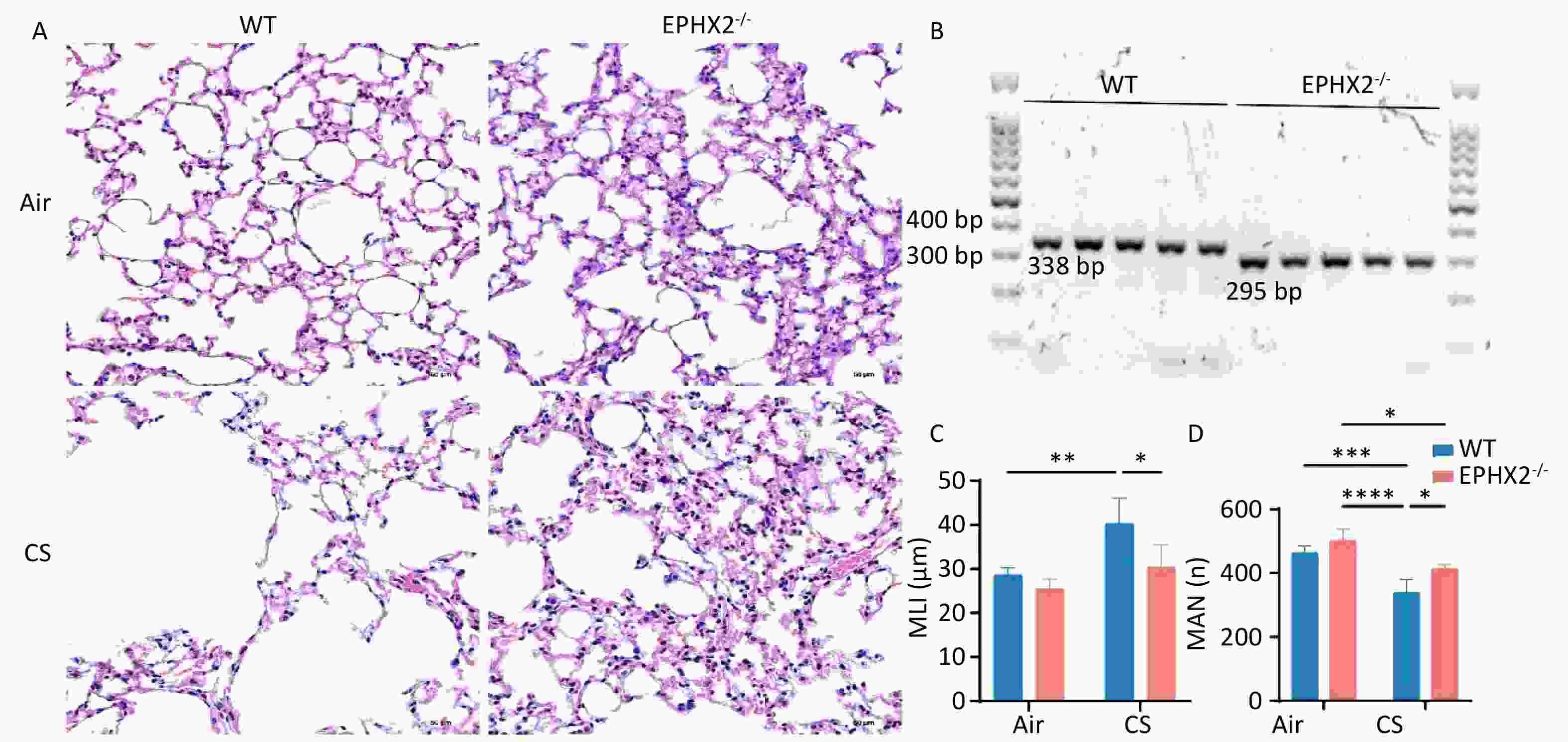
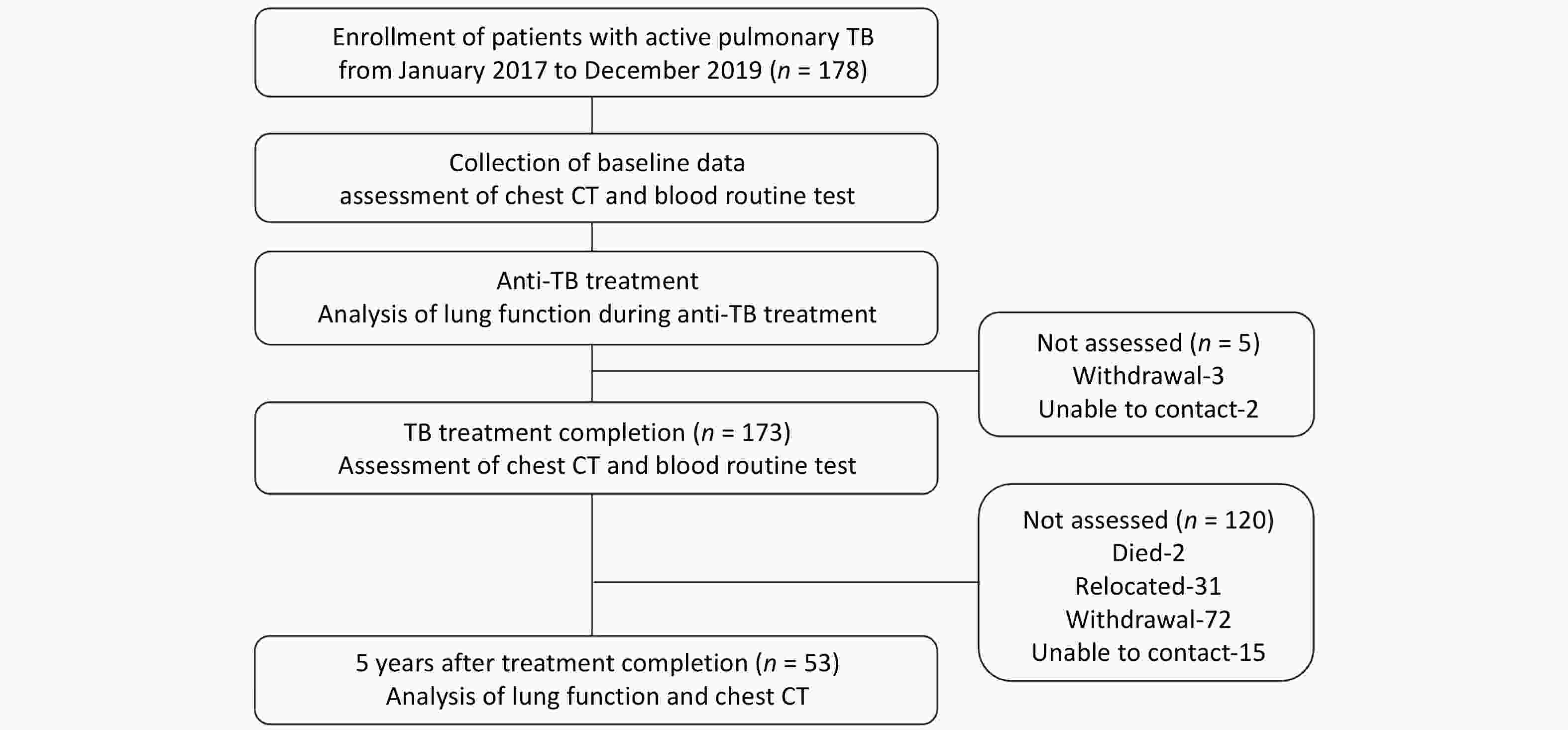
Objective Post tuberculosis lung disease (PTLD) manifests in various forms, including tuberculosis-associated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (TB-COPD), yet the clinical features of PTLD remain undercharacterized. This study aimed to assess longitudinal changes in lung function over a 5-year period and to identify predictors of airflow obstruction in a cohort of patients treated for active pulmonary TB. Methods Patients with active pulmonary TB were enrolled in this study and were followed during treatment, at treatment completion and five years post-treatment. Assessments included lung function and chest CT, analyzing longitudinal trends and airflow obstruction risk factors. Results Among 53 patients (mean age 36.9 ± 13.9 years; 64.2% male), 7 patients (13.2%) exhibited airflow obstruction. At the 5-year follow-up, the mean FEV1/FVC declined significantly (76.27% ± 12.04% vs. 80.23% ± 11.02%, P < 0.001) and 9 patients (17.0%) exhibited airflow obstruction. Seven of these patients predominantly showed air trapping consistent with small airway disease on chest CT, aligning with TB-COPD phenotype. Notably, four young-to-middle-aged patients (< 60 years old) had persistent obstruction over the five years. Conclusion The initial test revealed that 13.2% of patients presented with airflow obstruction. By the 5-year follow-up, this proportion had increased to 17.0%, with most cases demonstrating imaging findings aligning with TB-COPD, even among younger, non-smoking individuals. These findings emphasize the importance of long-term follow-up and routine lung function assessments in TB survivors.
2026, 39(2): 158-170.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.169
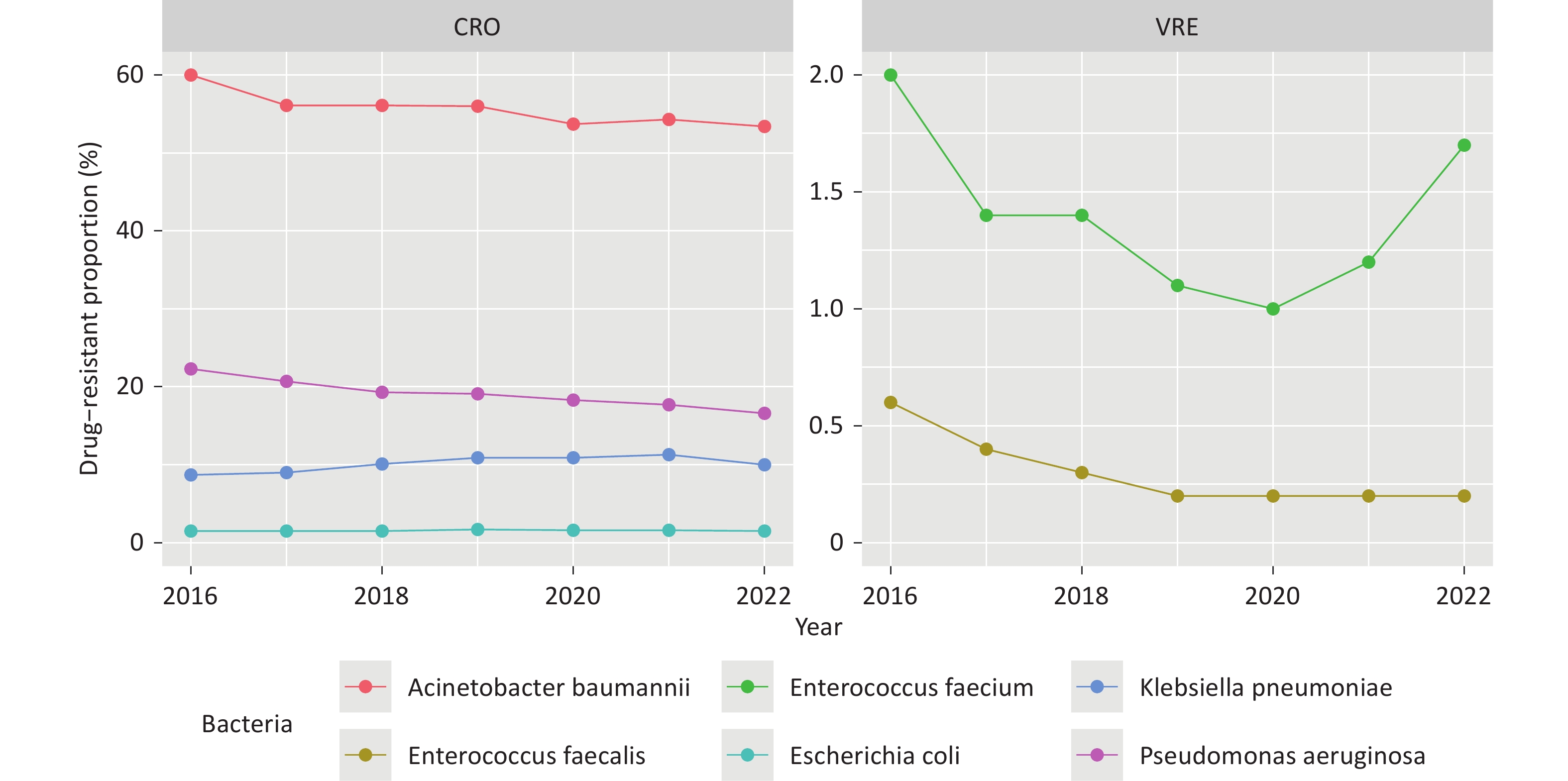
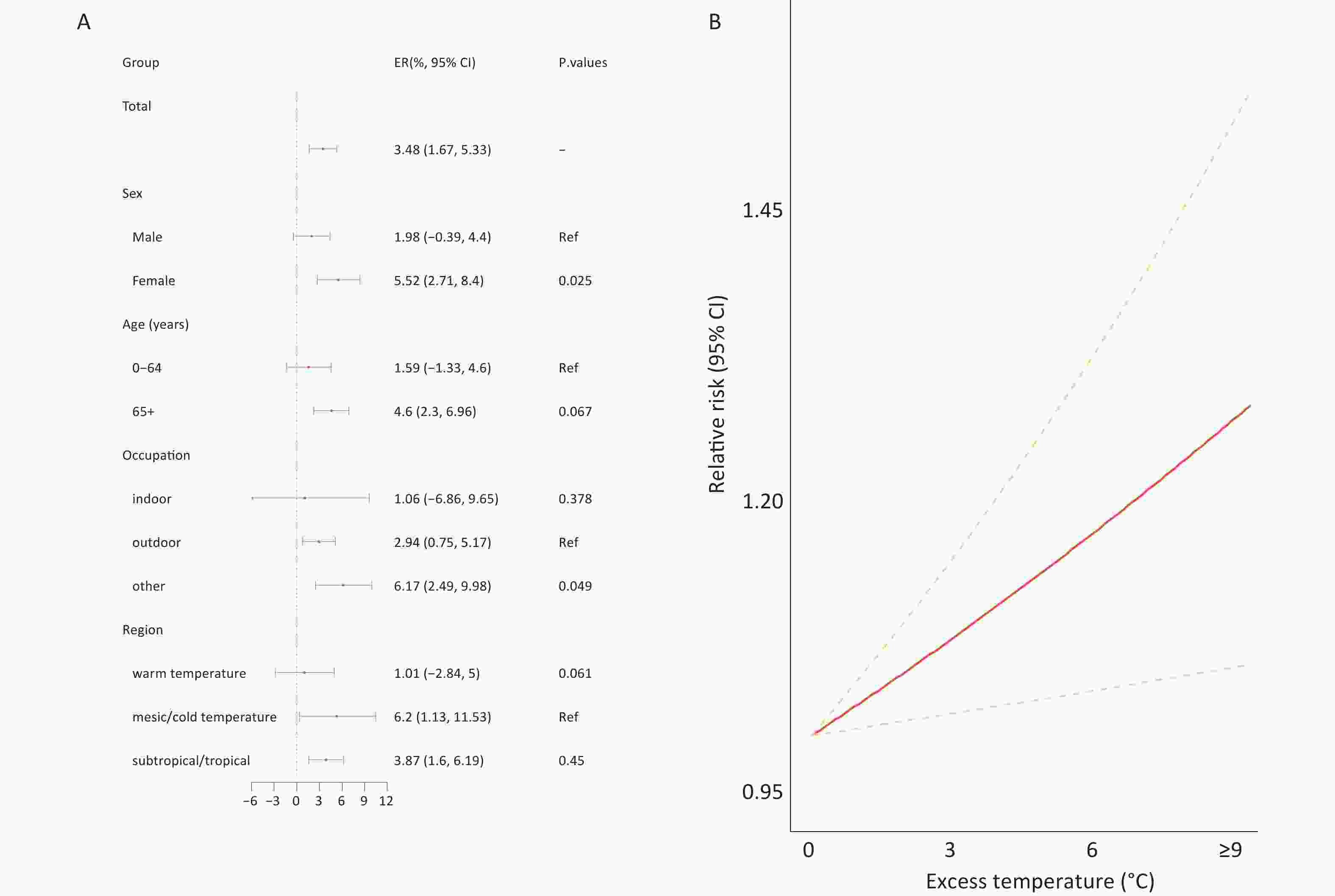
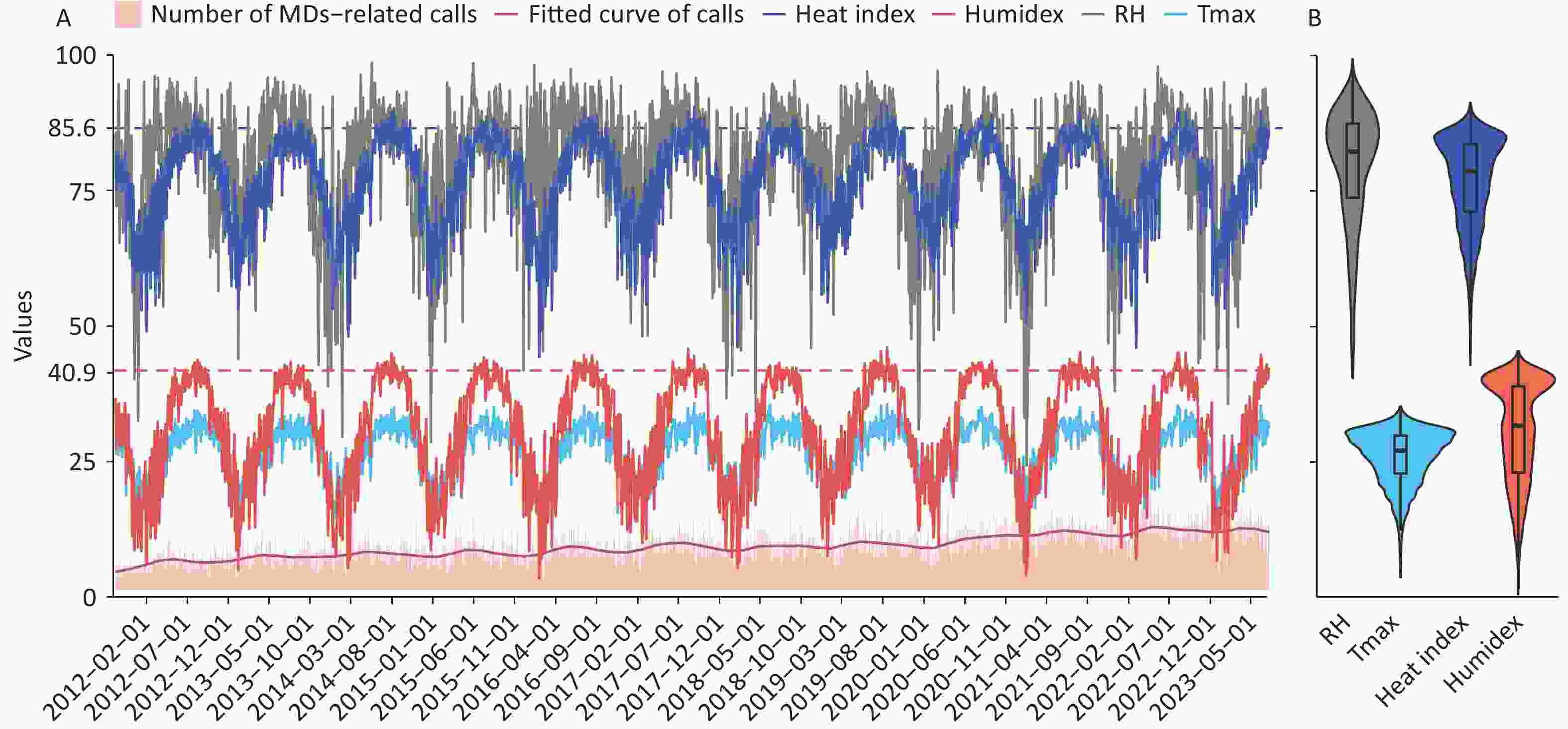
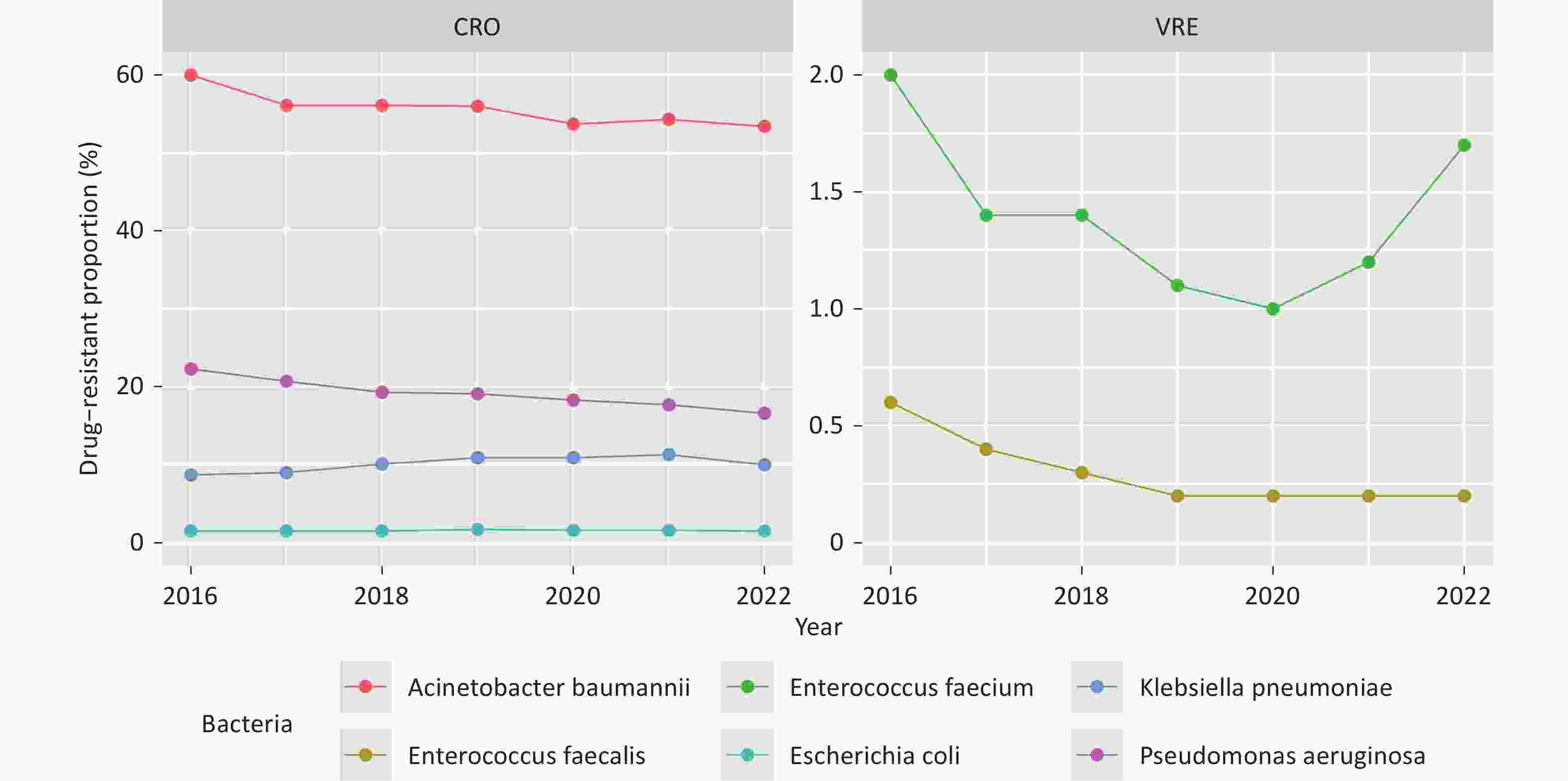
Objective To examine national trends in antibiotic consumption and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) among six WHO-priority bacterial pathogens in China from 2016 to 2022. Methods This ecological study analyzed national and provincial data from the China Antibacterial Resistance Surveillance System (CARSS) and the National Hospital Information Network. Beta regression models assessed temporal trends, and hierarchical models evaluated associations between antibiotic use and resistance. Results From 2016 to 2022, carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium and E. faecalis significantly declined (β < 0, P < 0.010), while carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae increased (β = 0.081, P < 0.001). Nationwide antibiotic consumption rose across 10 major classes. Positive associations were found between carbapenem use and resistance in A. baumannii (z = 2.719, P = 0.007) and P. aeruginosa (z = 3.241, P = 0.001), and between vancomycin use and resistance in E. faecium (z = 4.510, P = 0.001) and E. faecalis (z = 3.210, P = 0.001). Conclusion Carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae increased significantly in China, while other resistant pathogens declined. Resistance patterns were linked to the use of multiple antibiotic classes, underscoring the need for strengthened antibiotic stewardship and surveillance.
2026, 39(2): 171-182.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.161
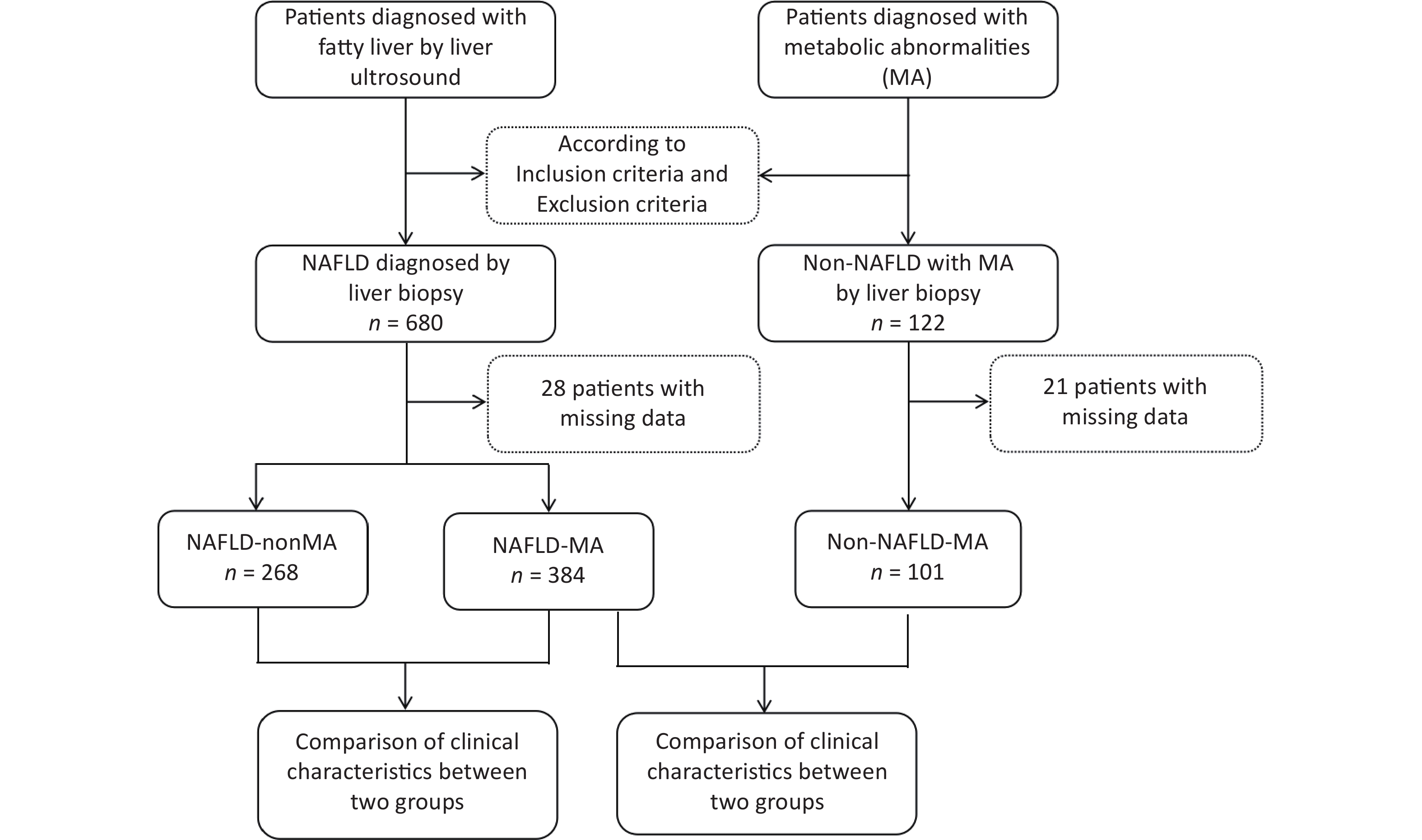
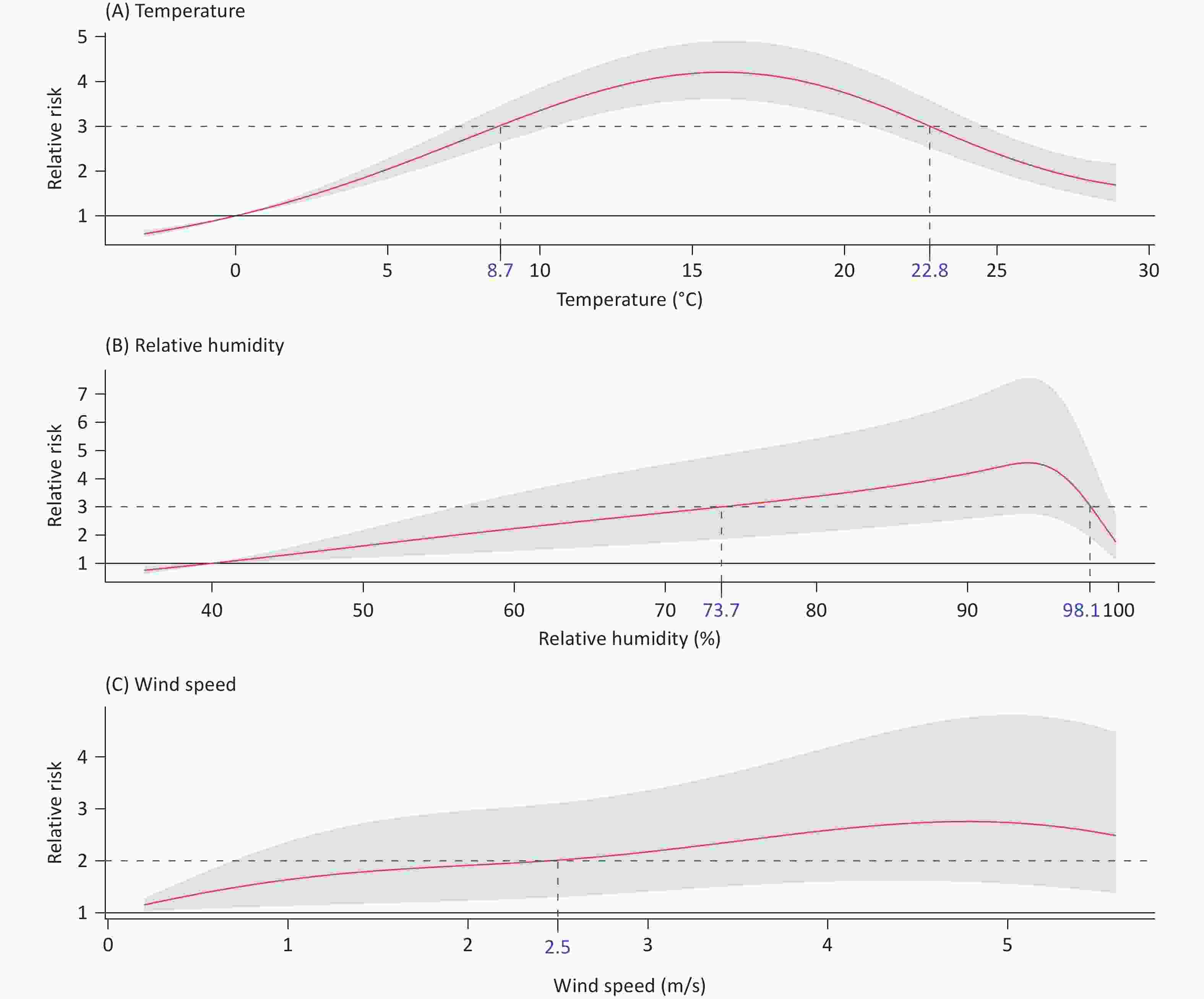
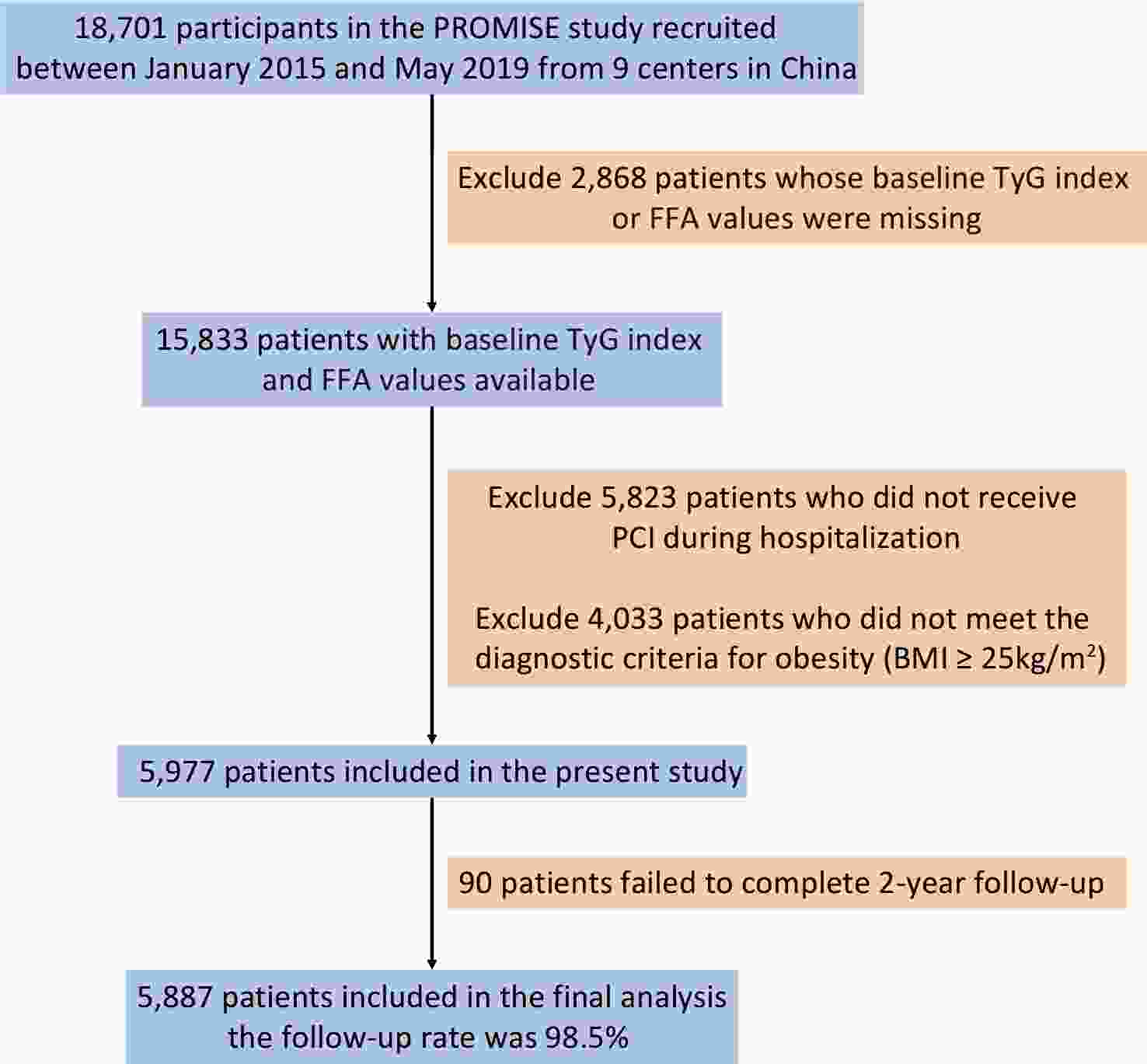
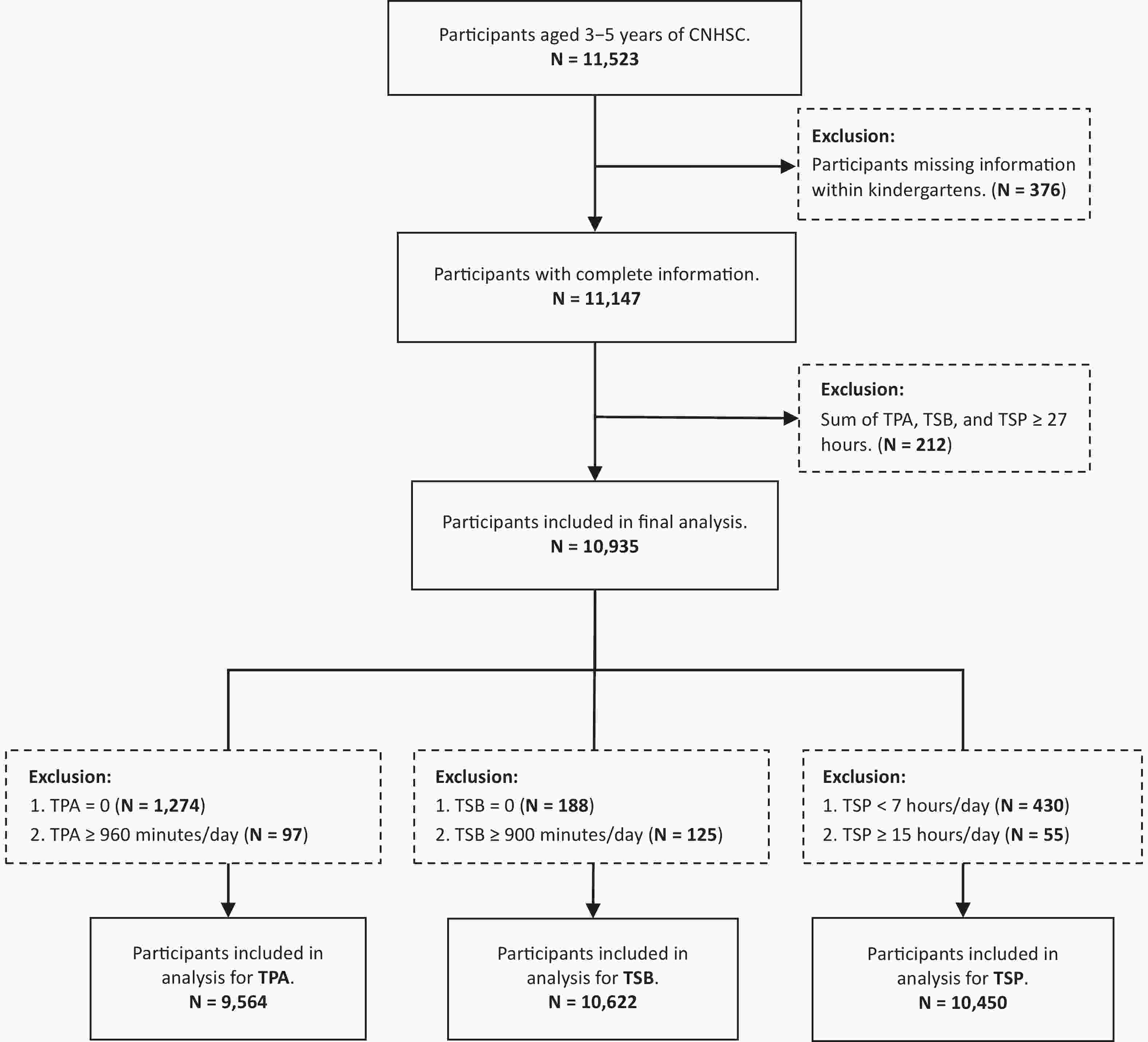
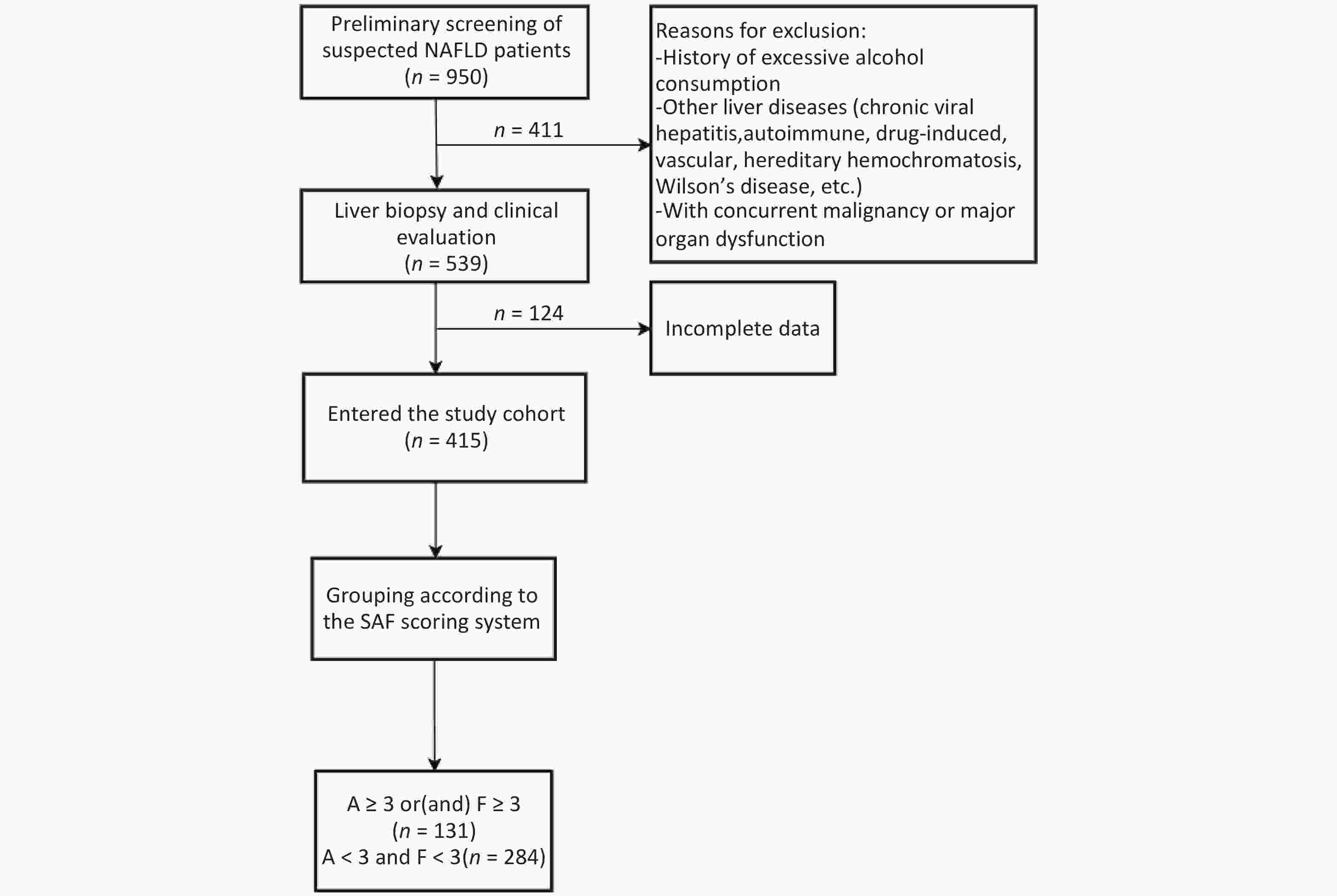
Objective To analyze the diagnostic efficacy of lipid-related insulin resistance (IR) markers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic abnormalities (MA). Method Patients with NAFLD with MA, non-NAFLD patients with MA, and patients with NAFLD without MA underwent liver biopsy. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C), visceral obesity index (VAI), lipid accumulation product (LAP), and triglyceride glucose (TyG) index were analyzed. The diagnostic efficacy of these indicators of NAFLD was also evaluated. Results In the NAFLD-MA group, BMI, HOMA-IR, LAP, VAI, TyG index, and TG/HDL-C ratio were higher than those in the non-NAFLD-MA group (P < 0.001). Logistic regression indicated that BMI and TyG index were independent risk factors for NAFLD. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves analysis revealed that the Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) for TyG-BMI was 0.819, and the optimal cutoff for NAFLD was TyG-BMI 39.77. For patients with NAFLD with or without MA, logistic regression analysis suggested that age, TG level, and TyG index were independent risk factors. The area under the ROC curve showed that AUC for the TyG index was 0.724. The optimal cutoff for NAFLD-non MA was a TyG index of 1.580. Conclusion TyG index has diagnostic value in both types of NAFLD; however, TyG-BMI is better in patients with NAFLD with MA and may be an effective screening indicator alone in patients with NAFLD without MA.
2026, 39(2): 183-191.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.094
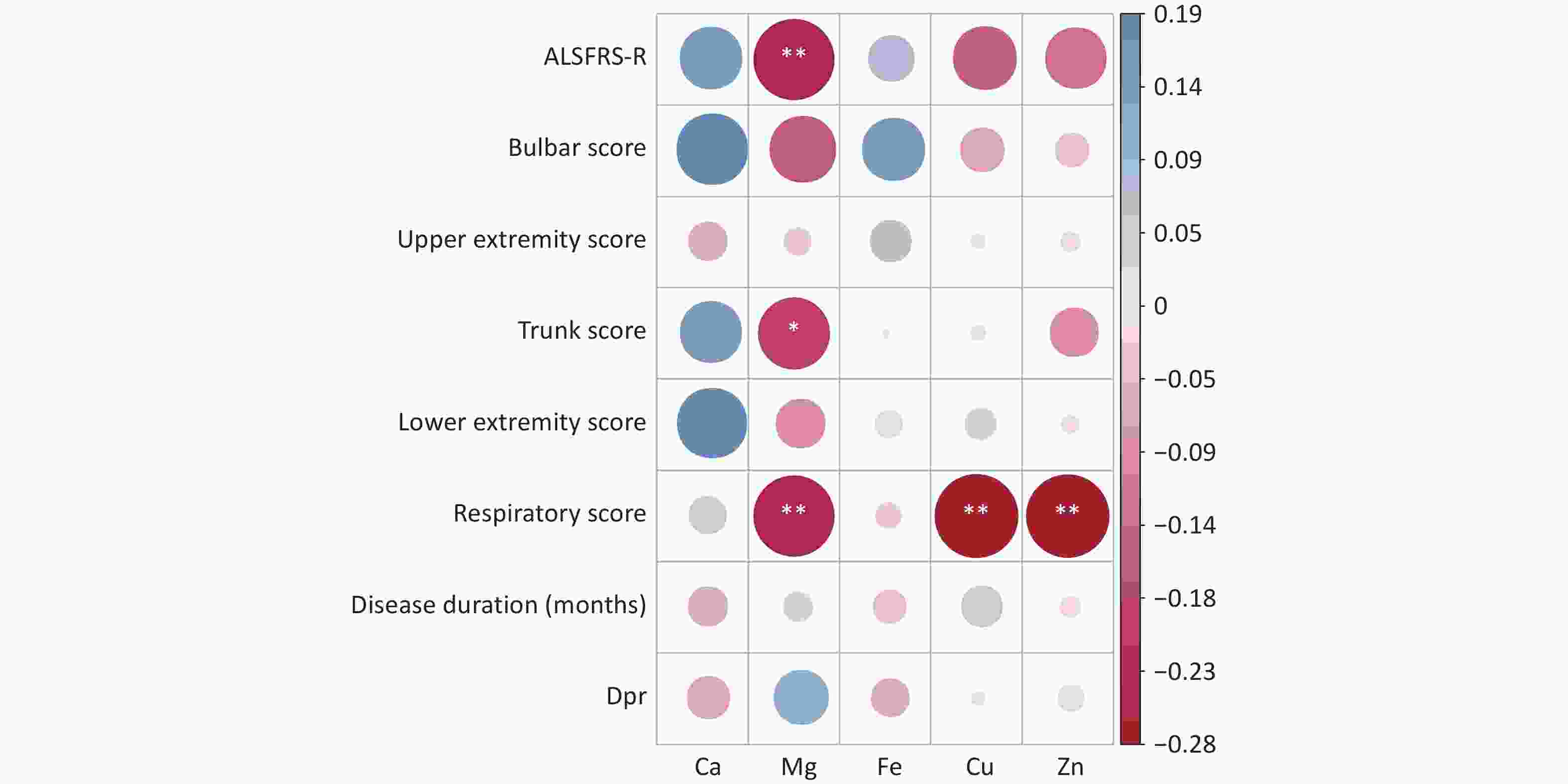
Objective The associations of serum trace element levels with disease progression and survival duration were assessed in individuals diagnosed with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (sALS) in China. Methods Clinical data, including diagnostic indicators, clinical characteristics, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale-Revised (ALSFRS-R) scores, and serum concentrations of calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn), were collected for hospitalized patients with sALS between 2018 and 2021. Correlation analysis, random forest analysis, and the Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test were used to evaluate the relations between serum trace element levels, disease progression, and survival duration. Results Lower serum Ca levels and higher Mg levels were observed in patients with ALSFRS-R scores < 39. Serum Mg was significantly negatively correlated with ALSFRS-R, trunk, and respiratory scores. Serum Cu and Zn also showed significant negative correlations with the respiratory score, whereas Ca and Fe were not significantly correlated with the ALSFRS-R score. The serum levels of Ca, Mg, Cu, Zn, and Fe remained consistent regardless of the site of disease onset. ALSFRS-R analysis revealed that serum Ca and Mg had a substantial effect on the total ALSFRS-R score, with serum Mg significantly influencing the course of the disease. Notably, low serum Mg levels were associated with extended survival times in patients with sALS. Conclusion Serum levels of Ca and Mg play critical roles in the progression of sALS, and a reduced serum Mg level is related to an extended survival time.
2026, 39(2): 192-201.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.118
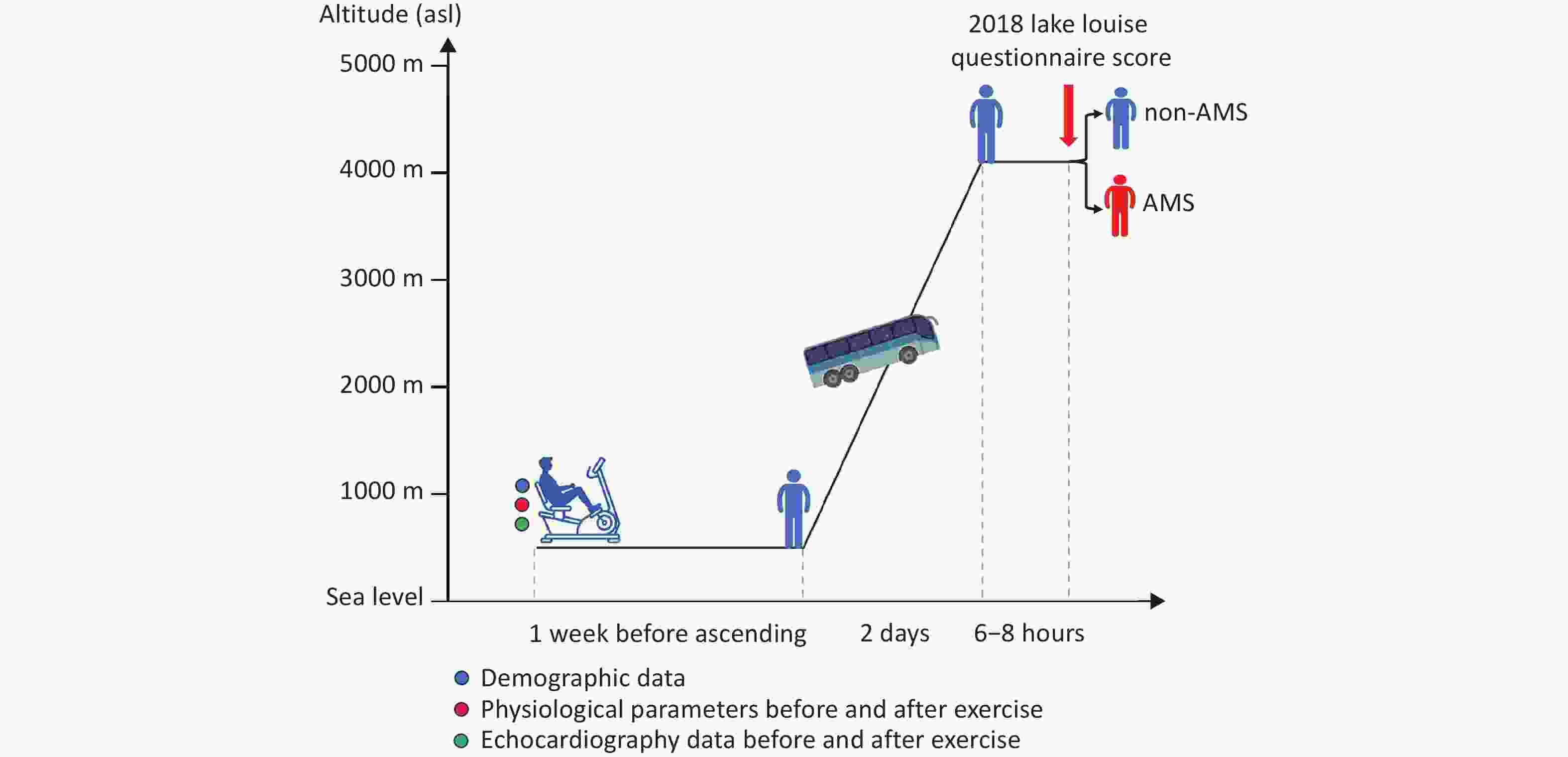
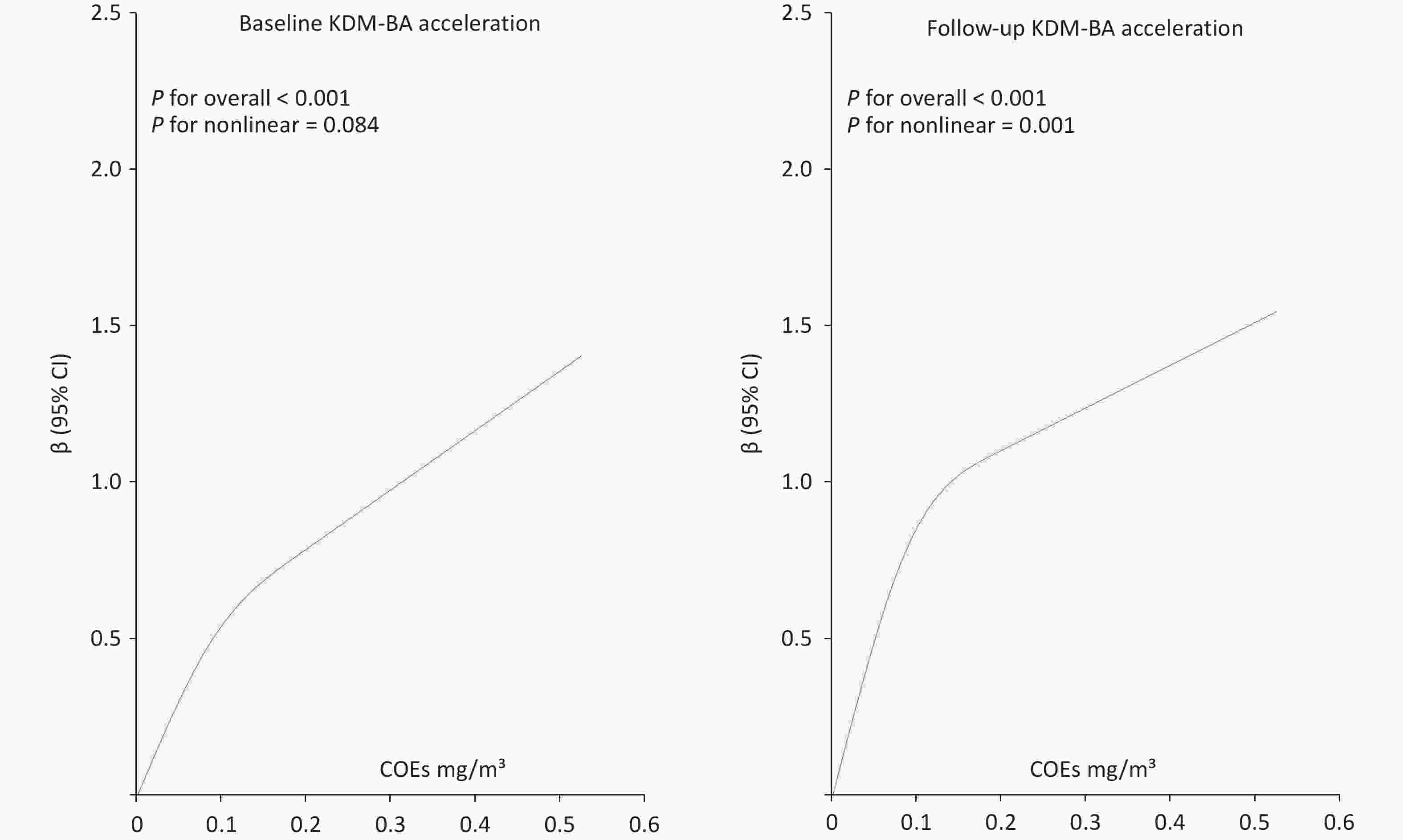
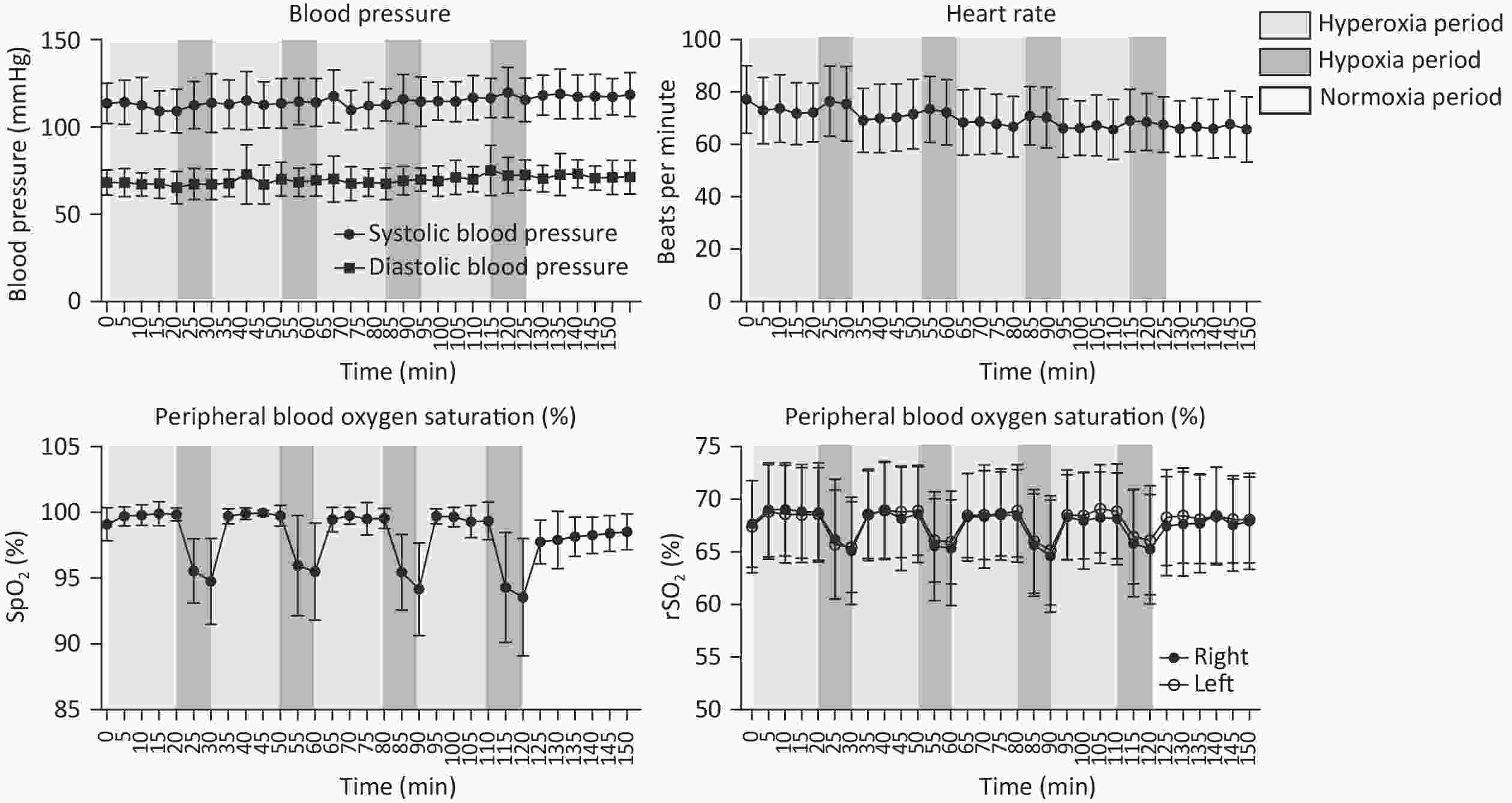
Objective Cerebral venous outflow disorders (CVOD) can impair cerebral perfusion and produce diverse, often debilitating symptoms, substantially reducing quality of life. Intermittent hypoxia-hyperoxia training (IHHT) has demonstrated therapeutic potential across various pathologies and may represent a promising non-pharmacological approach for CVOD management. Methods Patients with imaging-confirmed CVOD underwent 14 IHHT sessions, each comprising four cycles of 10-minute hypoxia (11% O2) stimulation and 20-minute hyperoxia (38% O2). Physiological parameters and adverse events were monitored throughout the intervention. Clinical scales, 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure, blood tests, jugular ultrasound, and perfusion imaging were assessed pre- and post-intervention. Results No participants experienced intolerable discomfort or severe adverse events; vital signs remained within normal ranges. No significant changes were observed in 24-hour blood pressure, blood cell counts, lipid profiles, or other blood markers. Notably, 60% of patients (n = 12) reported overall symptom improvement on the Patient Global Impression of Change scale. Headache severity, as measured by the visual analogue scale, significantly decreased (6.33 ± 1.22 vs. 4.89 ± 2.03, P = 0.016). In patients with internal jugular vein (IJV) stenosis, significant improvements were observed in regional cerebral blood flow (including the insula, occipital lobe, internal capsule, and lenticula) and left J3-segment IJV flow volume (107.27 [47.50, 160.00] vs. 140.83 [55.00, 210.00] mL/min, P = 0.011). Conclusion The current IHHT protocol is safe and well-tolerated in patients with CVOD. IHHT may alleviate CVOD-related symptoms by improving oxygen saturation, cerebral perfusion, and venous outflow pattern, supporting its potential as a non-invasive therapeutic strategy.
2026, 39(2): 202-214.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.162
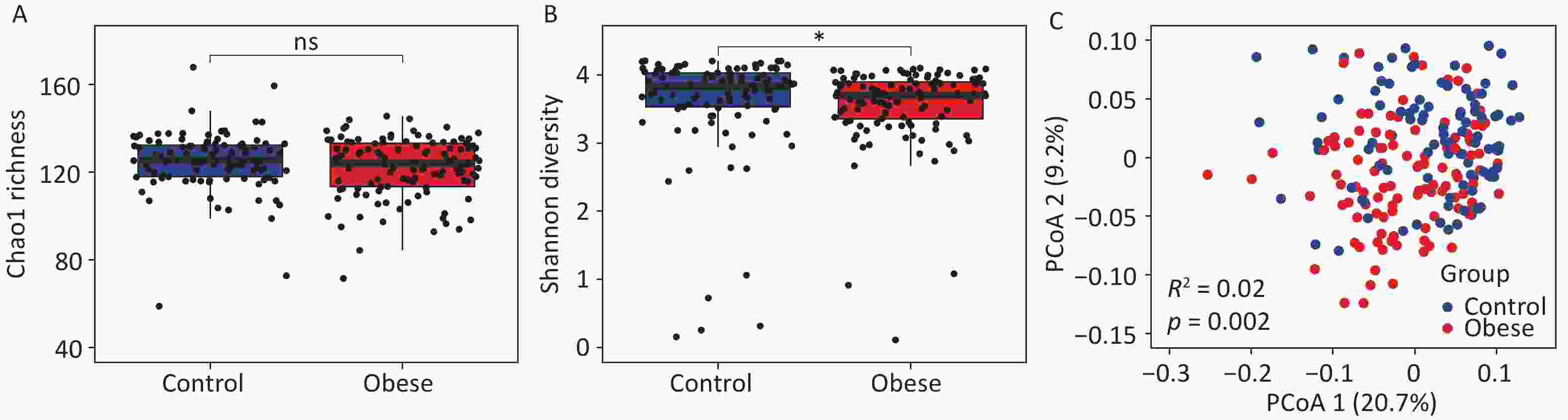
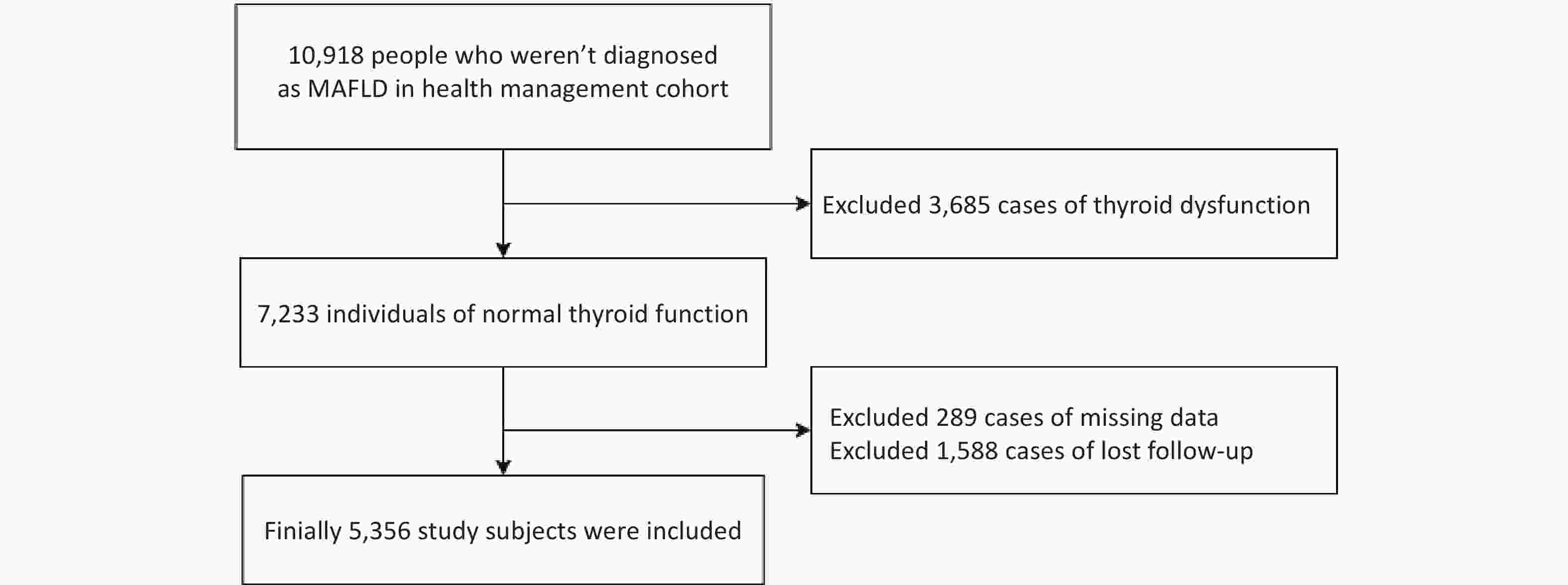
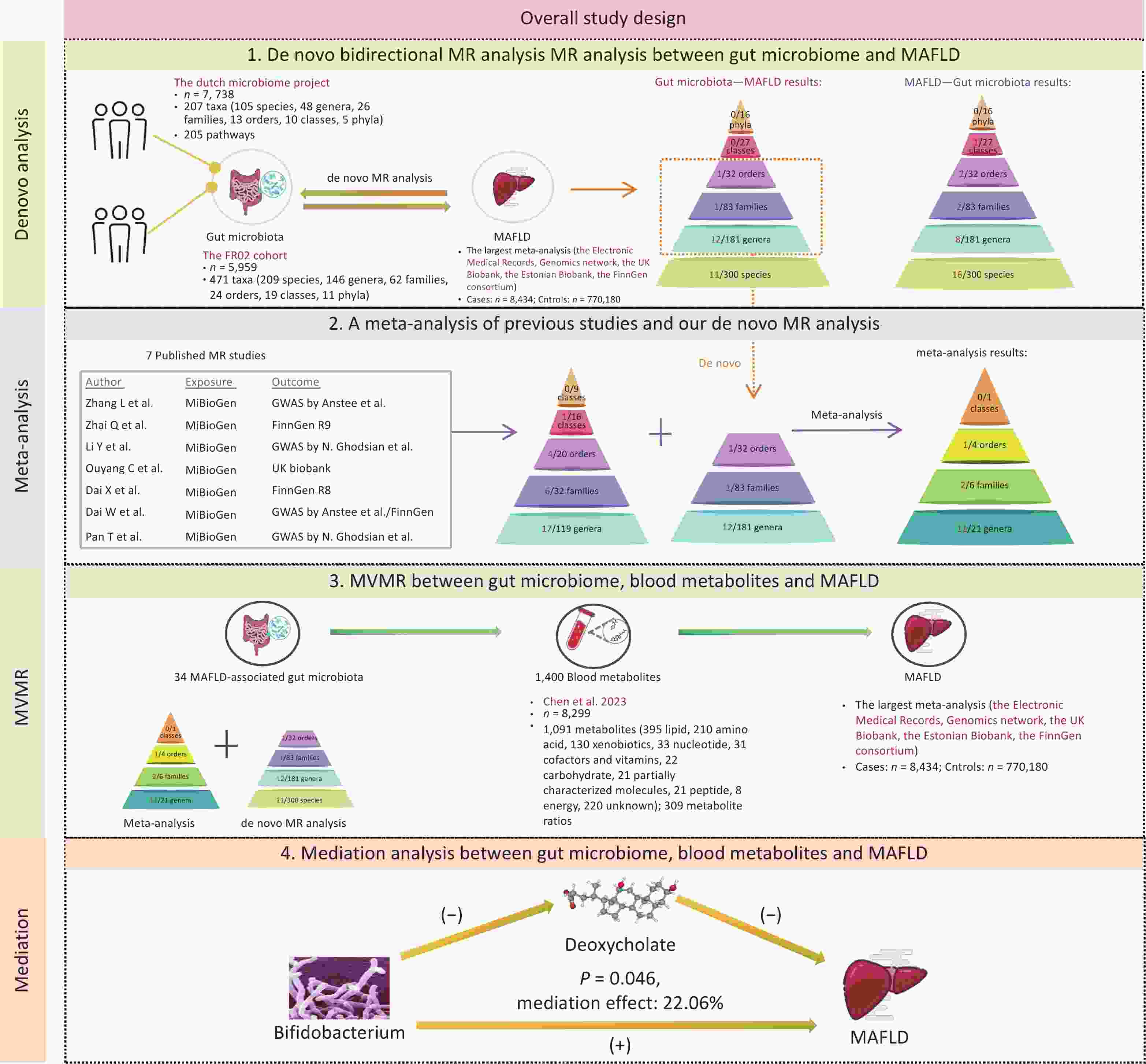
Objective Previous Mendelian randomization (MR) studies have suggested an association between the gut microbiome and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). However, the reliance on 16S rRNA sequencing data has led to inconsistent findings and limited species-level insights. To address this, we conducted a de novo MR analysis using species-level shotgun metagenomic data, combined it with a meta-analysis to consolidate the existing evidence, and explored metabolite-mediated pathways. Methods Bidirectional MR analyses were performed between 883 gut microbiota taxa (derived from shotgun metagenomic genome-wide association study) and MAFLD. Published MR studies (up to December 1, 2024) were identified using PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library for meta-analysis. Multivariable MR (MVMR) and mediation analyses were applied to assess the mediating effects of 1,400 blood metabolites. Results The de novo MR identified 25 MAFLD-associated microbial taxa. Integration with 7 published studies revealed 34 causal taxa, including 10 at the species level. Among the 1,400 metabolites, 53 showed causal links with MAFLD. MVMR and mediation analyses identified deoxycholate as a mediator of the effect of Bifidobacterium on MAFLD risk (22.06% mediation proportion). Conclusion This study elucidated the connections between species-level gut microbiota and MAFLD, highlighting the interplay between microbiota, metabolites, and disease pathogenesis. These findings provide novel insights into the potential therapeutic targets for MAFLD.
2026, 39(2): 215-222.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.117
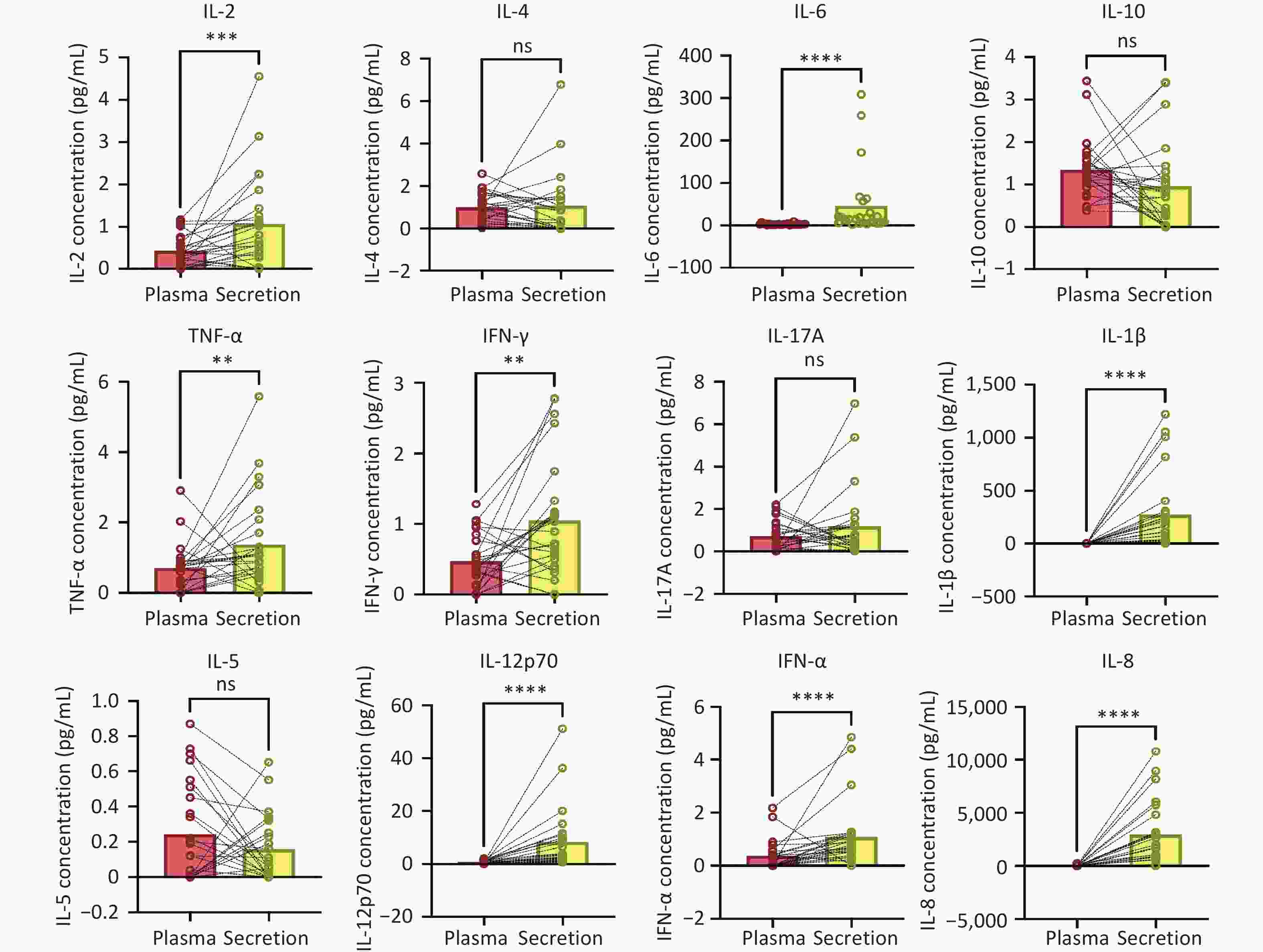
Objective The aim of this study was to analyze the correlation between the levels of 12 cytokines in the cervical microenvironment and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in patients with high-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV) infection. Methods Female patients (n = 73) with HR-HPV infection were enrolled and divided into a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) group (n = 33) and a non-HSIL (N-HSIL) group (n = 40), which include low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and inflammation. Healthy screening subjects (n = 31) with negative HR-HPV results were enrolled as a control group. We examined contemporaneous plasma and secretory cytokines from 25 study subjects to investigate the difference between systemic cytokine profiles and the local microenvironment immunity using the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. The 12 cytokines from cervical secretions were compared between the three groups using the Mann-Whitney test, and logistic regression was used to analyze HSIL and N-HSIL. Results There were statistical differences in eight cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-12p70, IFN-α, and IL-8) between cervical secretion and plasma of the same patient, and seven cytokines were statistically different between the control and other two groups. We selected four independent variables (TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-12p70, and IFN-α) commonly identified by univariate regression analysis and non-parametric tests for multivariate logistic regression analysis. Based on this model, HSIL could be predicted in patients with HR-HPV infection, with the area under the curve being 0.76. Conclusion The systemic cytokine profile cannot reflect the local microenvironment immunity, and the occurrence of HSIL is related to the cytokine levels in the cervical microenvironment.
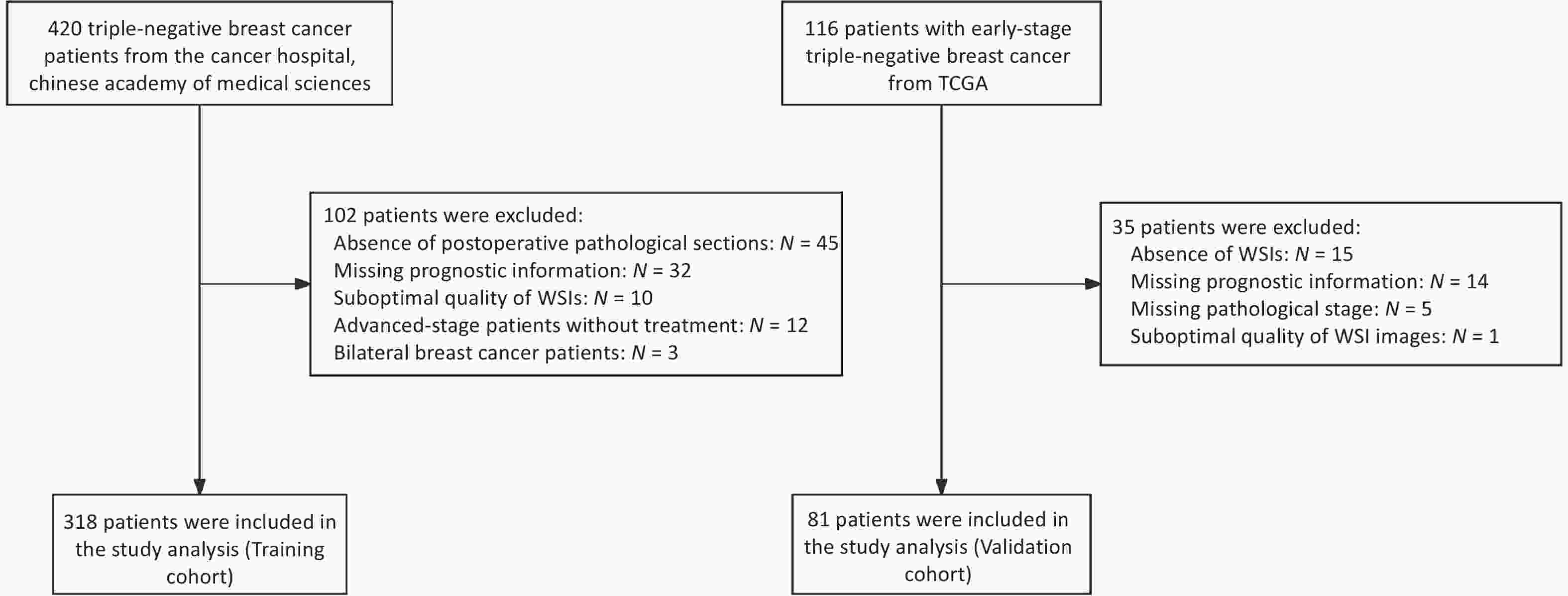
2026, 39(2): 223-233.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.164
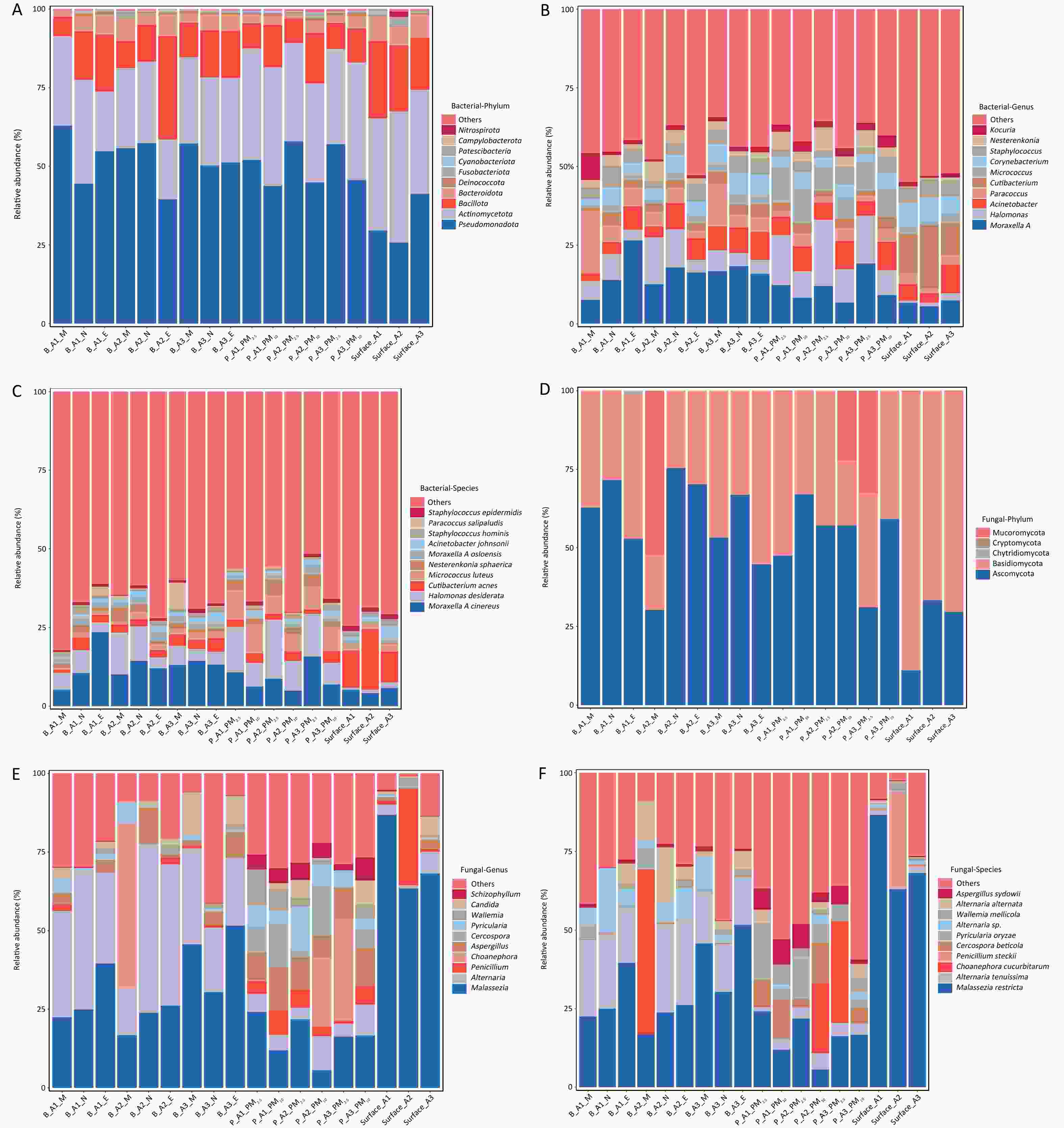
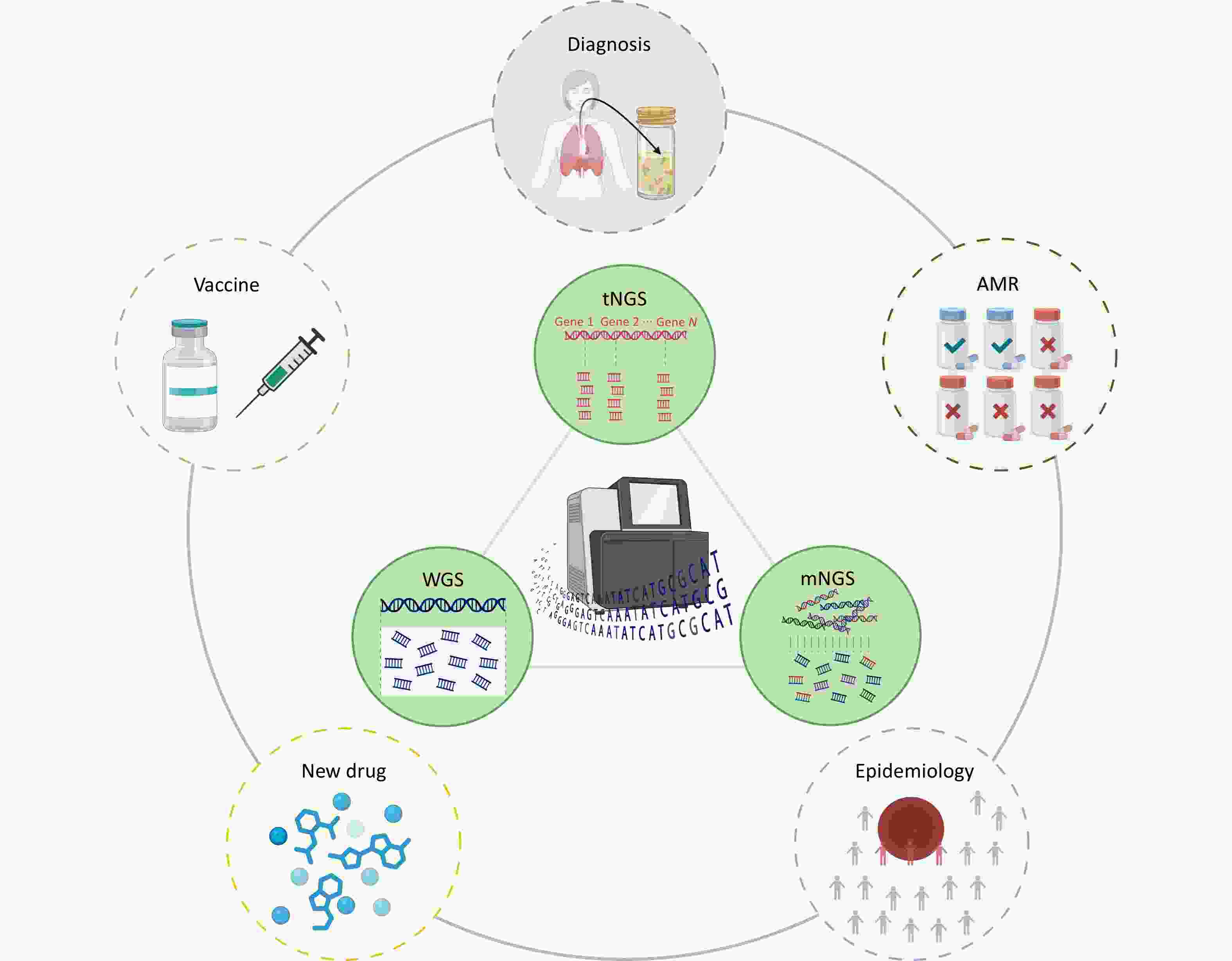
Tuberculosis (TB) continues to pose a significant threat to global public health, necessitating rapid and precise diagnostic methods and comprehensive detection of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to facilitate timely clinical management. Traditional diagnostic techniques suffer from extended turnaround times and limited ability to comprehensively profile AMR, often resulting in delayed therapeutic interventions. High-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies have revolutionized pathogen research by significantly improving diagnostic speed and accuracy. In the context of TB, diverse sequencing strategies and platforms are being employed to fulfill specific research goals, ranging from elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying AMR to characterizing the genomic diversity among clinical isolates. This review systematically examines current progress in the application of HTS for rapid pathogen identification, comprehensive AMR profiling, epidemiological studies, advances in novel drugs, and vaccine development. Furthermore, we address existing technological limitations and bioinformatics challenges and explore the future directions necessary for effectively integrating HTS-based methodologies into global TB control efforts.
2026, 39(2): 245-250.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.145
2015, 28(1): 57-71.
doi: 10.3967/bes2015.006
2022, 35(7): 573-603.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.079
2023, 36(8): 669-701.
doi: 10.3967/bes2023.106
2018, 31(2): 87-96.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.011
2012, 25(3): 317-324.
doi: 10.3967/0895-3988.2012.03.010
2019, 32(8): 559-570.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.074
2014, 27(8): 606-613.
doi: 10.3967/bes2014.093
2018, 31(3): 208-214.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.026
2024, 37(9): 949-992.
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.162
2003, 16(3): 246-255.
2019, 32(9): 659-672.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.085
2022, 35(5): 381-392.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.054
2022, 35(7): 648-651.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.084
2016, 29(3): 212-218.
doi: 10.3967/bes2016.026
2018, 31(9): 637-644.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.088
2019, 32(8): 578-591.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.076
2019, 32(10): 769-778.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.096
2017, 30(5): 384-389.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.051
Current Issue
-
2024 Impact Factor 4.1
-
2024 Journal Citation Reports



















 Quick Links
Quick Links