Jie Sun,
Junyan Xi,
Zhishen Wu,
Wangjian Zhang,
Jianjun Bai,
Yining Xiang,
Yucan Zhang,
Jiajia Wang,
Shihao Wang,
Jing Gu,
Yuantao Hao,
Xiao Lin
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.008
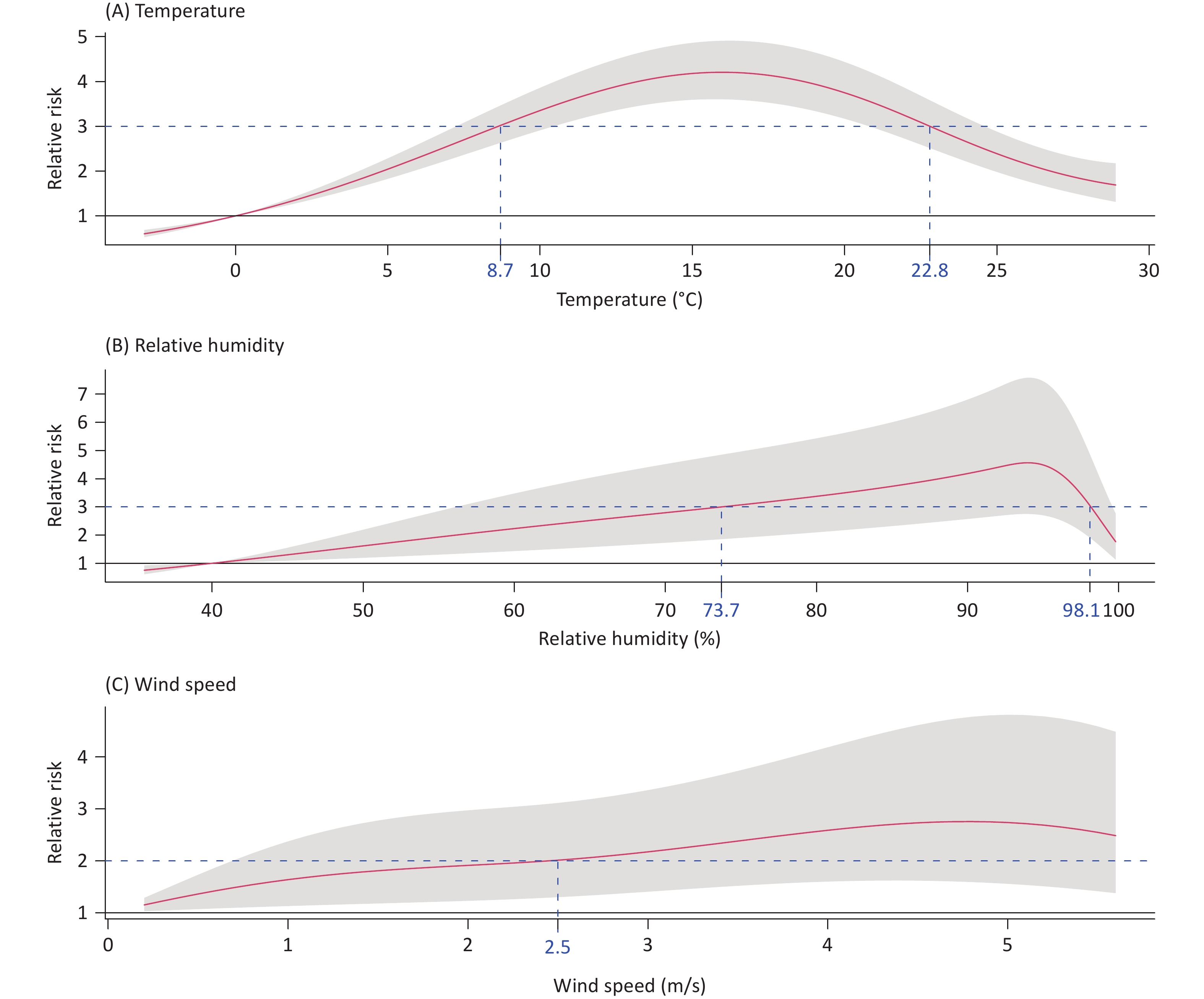
Objective Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) transmission is sensitive to temperature-humidity interactions; however, the role of wind speed in modifying these effects remains unknown. This study investigated how wind speed modifies the combined effects of temperature and humidity on HFMD burden and identified subgroups of individuals with increased vulnerability to these climate exposures. Methods We analyzed data from 524,100 HFMD cases and daily meteorological measurements across Guizhou, China, between 2012 and 2019. Disease burden was quantified as the number of years lived with disability. Exposure-response relationships and lag effects were modeled via distributed lag non-linear models. Additive interactions were assessed based on the proportions attributable to the interaction. The effects of sex, ethnicity, and urbanization were examined using stratified analyses. Results Meteorological factors showed synergistic effects on HFMD burden. The peak burden occurred at moderate mean temperatures (8.7–22.8 °C) combined with high relative humidity (> 73.7%), showing a 2.4-fold increase versus the reference. High wind speed (> 2.5 m/s) further increased this effect, with a 3.1-fold increase in burden. This joint effect was attributable to the additive interaction involving wind speed and remained robust in stratified analyses that identified heightened vulnerability among boys, minority areas, and urban agglomerations. Conclusion The HFMD burden was highest under specific combinations of temperature and humidity, and further increased with concurrent exposure to high wind speeds. Public health strategies for HFMD prevention should incorporate wind speed monitoring into early warning systems and address vulnerable subgroups, including boys and populations in minority areas and urban agglomerations.
Yang Shen,
Boji Wu,
Zhen Liu,
Yuanqi Yang,
Chun Li,
Siming Gong,
Shizhu Bian,
Xi Liu,
Chen Zhang,
Jihang Zhang,
Chuan Liu,
Zhexue Qin
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.014
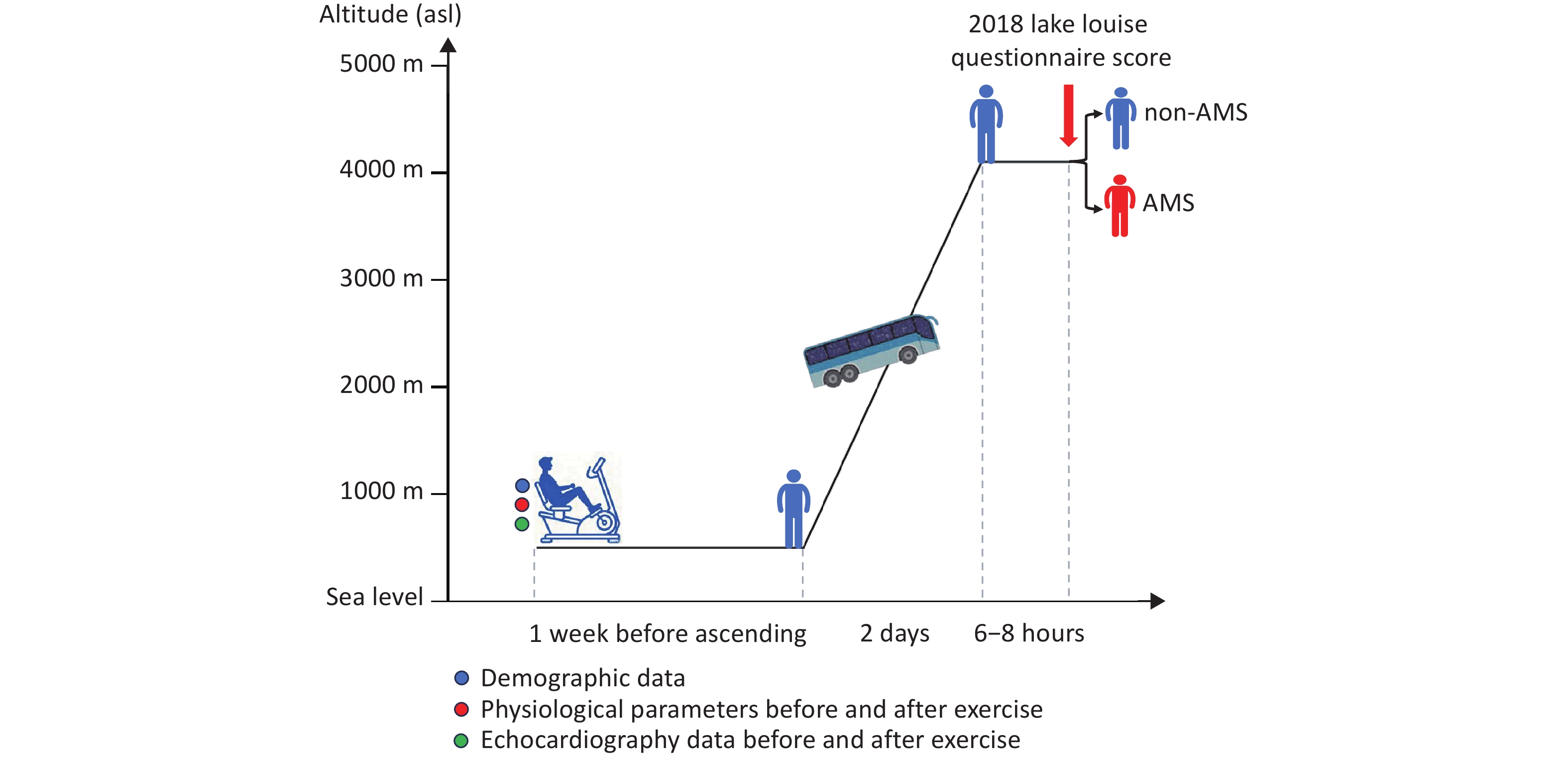
Objective Stress-induced changes in echocardiographic parameters reflect cardiac reserve function. This study aimed to identify predictors of acute mountain sickness (AMS) using exercise stress echocardiography (ESE) before ascent. Methods In this prospective cohort study, 104 healthy adults were enrolled and treated using ESE using a mechanically braked bicycle ergometer at a low altitude (LA) (500 m). Physiological data and echocardiographic parameters were collected before and during exercise. An ascent from 500 m to 4,100 m was completed by the bus within two days. AMS was identified using the Lake Louise Questionnaire. Results Among the 104 participants, 49 developed AMS at 4,100 m. Compared with individuals without AMS, those with AMS had a higher low-altitude (500 m) heart rate (HR) but lower stroke volume (SV) at rest, lower cardiac output (CO) and SV during exercise, and lower rates of change in CO, SV, and HR. Multivariate regression analysis revealed that female sex (odds ratio [OR] = 3.17, P = 0.039) and the rate of change in CO during exercise (OR = 0.98, P = 0.001) were independent risk factors for AMS. Participants with the lowest CO change rate after ESE presented the highest AMS risk. Conclusion ESE could serve as an effective screening tool for AMS susceptibility, and blunted CO augmentation during exercise is an independent predictive marker for AMS risk.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.009
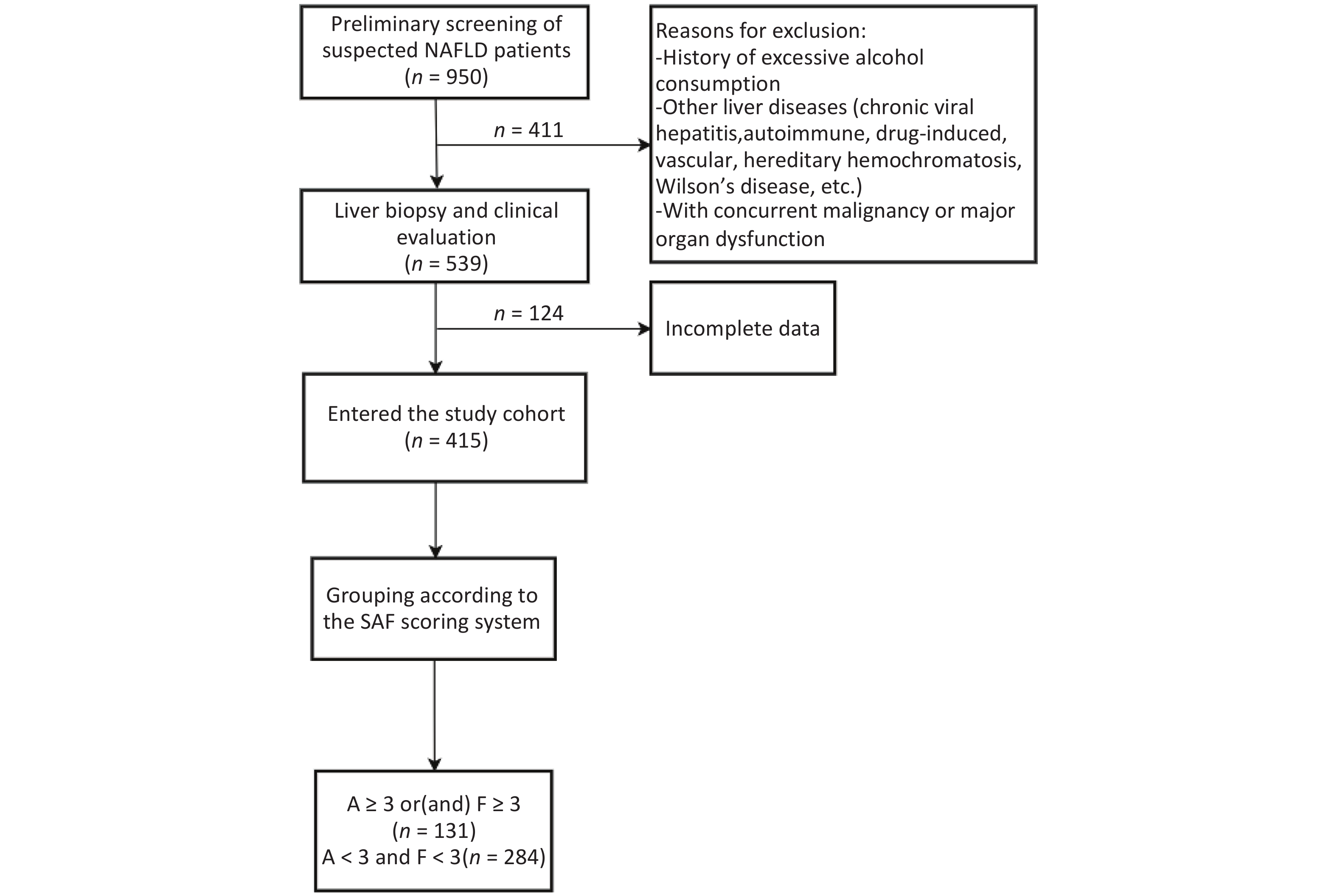
Objective To investigate risk factors associated with significant histologic lesions in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) using the SAF (Steatosis, Activity, Fibrosis) scoring system and to develop a risk prediction model. Methods In this retrospective cohort of 415 biopsy-proven MASLD patients (2018–2022), participants were stratified into significant lesion (SAF activity grade ≥ 3 and/or fibrosis stage ≥ 3, n = 131) and non-significant lesion (activity < 3 and fibrosis < 3, n = 284) groups. Demographic, laboratory, and imaging parameters including platelet count (PLT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), total bilirubin (TBIL), direct bilirubin (DBIL), total bile acids (TBA), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), fasting plasma glucose (FPG), uric acid (UA), laminin (LN), hyaluronic acid (HA), procollagen type III (PC-III), collagen type IV (C-IV), controlled attenuation parameter (CAP), and liver stiffness measurement (LSM) were analyzed. Results Patients with significant lesions had higher body mass index (BMI), proportion of high-fat diet, AST, ALT, TBA, UA, CAP, and LSM (all P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression identified BMI (OR = 1.182), UA (OR = 1.003), CAP (OR = 1.005), and LSM (OR = 1.104) as independent predictors of significant histologic lesions, with a model area under the curve of 75.18%. Conclusion BMI, hyperuricemia, hepatic steatosis (CAP), and fibrosis (LSM) are independent risk factors for advanced MASLD. A combined non-invasive assessment may enhance risk stratification in clinical practice.
Fei Zhao,
Zinan Zhao,
Di Chen,
Bolin Zhu,
Tianqi Zhang,
Yuanchao Zhu,
Xuelin Sun,
Liang Liang,
Nan Zheng,
Lili Zou,
Wenfeng Xu,
Sirui Guo,
Yue Wang,
Ming Zhao,
Xin Hu,
Pengfei Jin
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.169
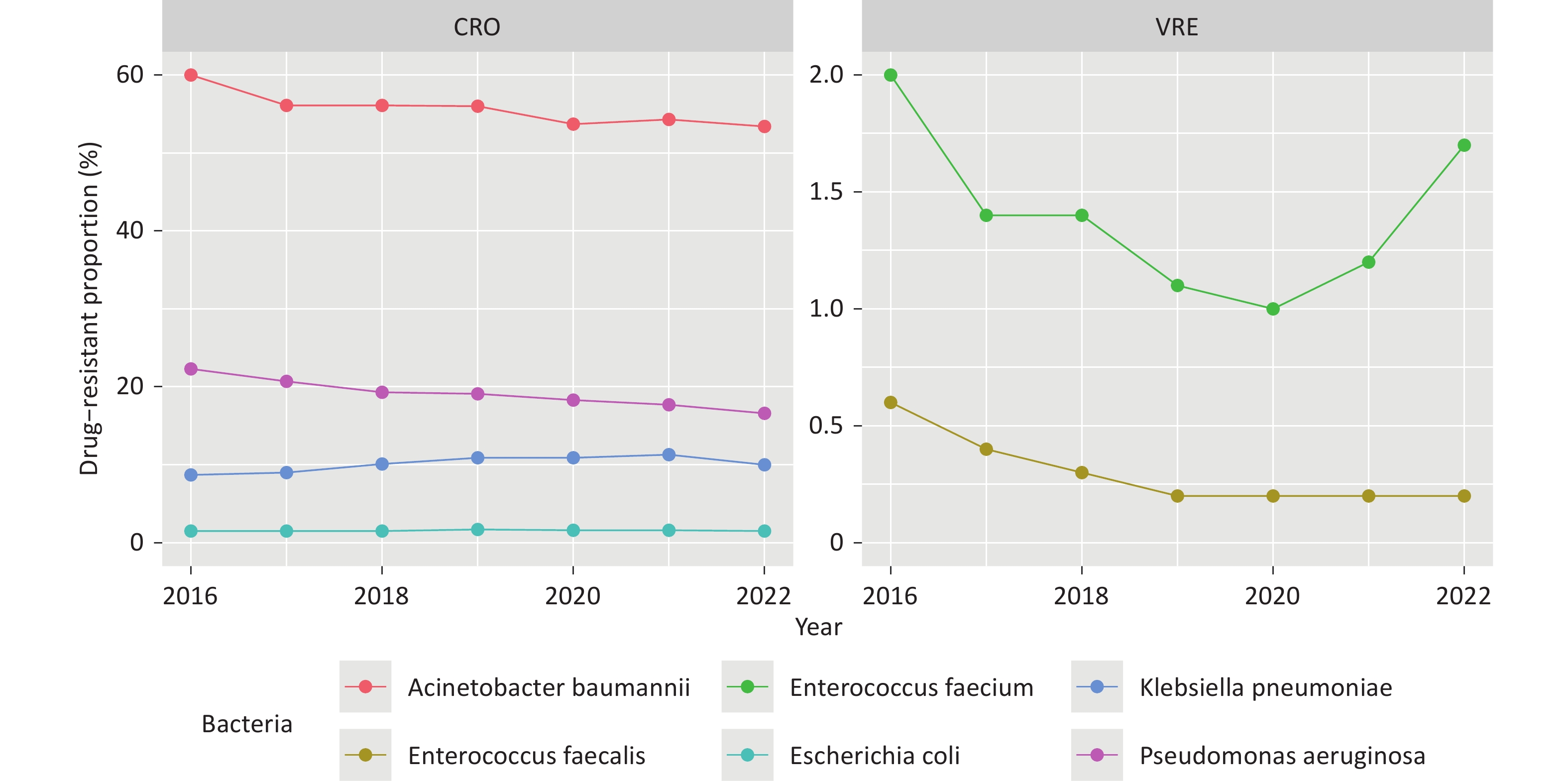
Objective To examine national trends in antibiotic consumption and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) among six WHO-priority bacterial pathogens in China from 2016 to 2022. Methods This ecological study analyzed national and provincial data from the China Antibacterial Resistance Surveillance System (CARSS) and the National Hospital Information Network. Beta regression models assessed temporal trends, and hierarchical models evaluated associations between antibiotic use and resistance. Results From 2016 to 2022, carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium and E. faecalis significantly declined (β < 0, P < 0.010), while carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae increased (β = 0.081, P < 0.001). Nationwide antibiotic consumption rose across 10 major classes. Positive associations were found between carbapenem use and resistance in A. baumannii (z = 2.719, P = 0.007) and P. aeruginosa (z = 3.241, P = 0.001), and between vancomycin use and resistance in E. faecium (z = 4.510, P = 0.001) and E. faecalis (z = 3.210, P = 0.001). Conclusion Carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae increased significantly in China, while other resistant pathogens declined. Resistance patterns were linked to the use of multiple antibiotic classes, underscoring the need for strengthened antibiotic stewardship and surveillance.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.121
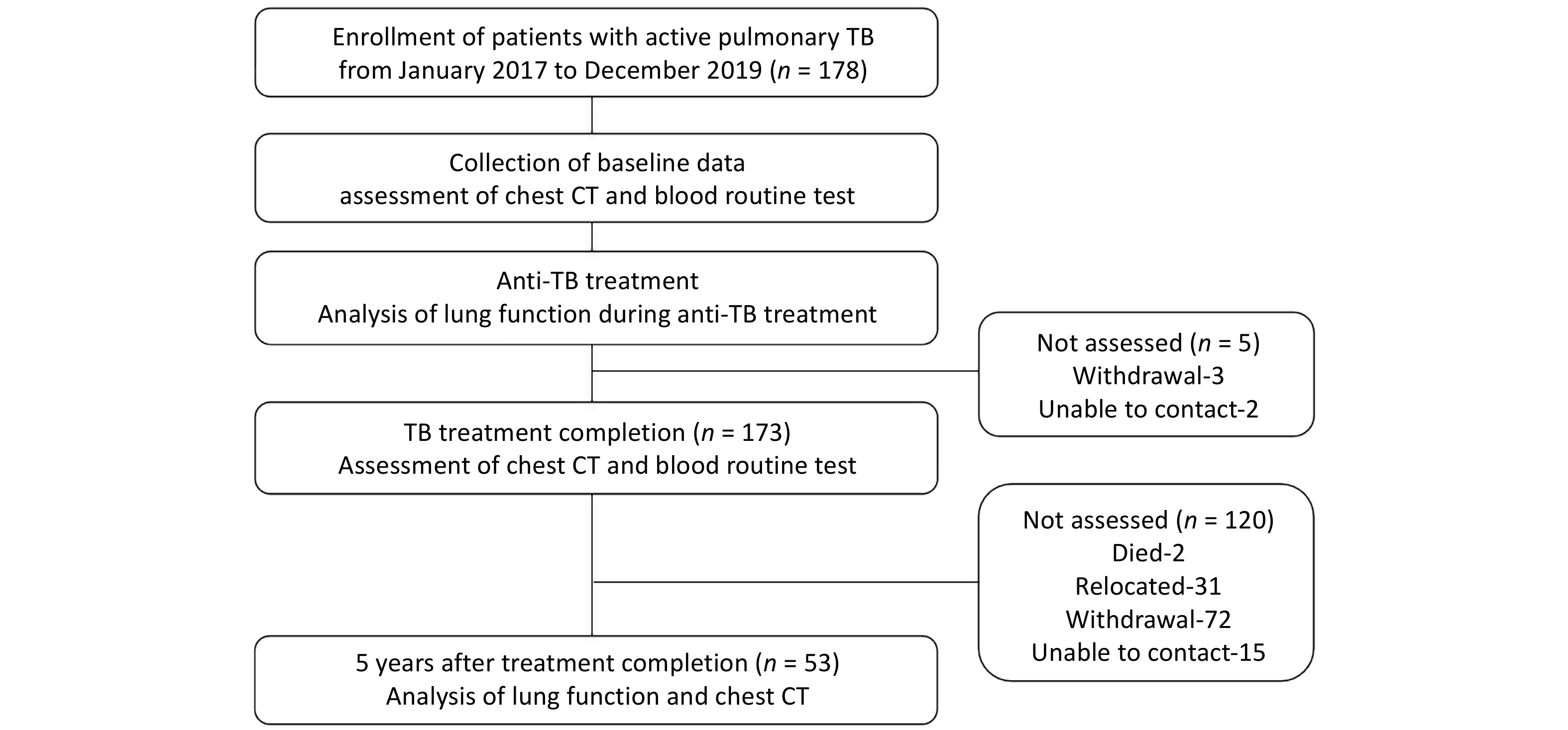
Objective Post tuberculosis lung disease (PTLD) manifests in various forms, including tuberculosis-associated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (TB-COPD), yet the clinical features of PTLD remain undercharacterized. This study aimed to assess longitudinal changes in lung function over a 5-year period and to identify predictors of airflow obstruction in a cohort of patients treated for active pulmonary TB. Methods Patients with active pulmonary TB were enrolled in this study and were followed during treatment, at treatment completion and five years post-treatment. Assessments included lung function and chest CT, analyzing longitudinal trends and airflow obstruction risk factors. Results Among 53 patients (mean age 36.9 ± 13.9 years; 64.2% male), 7 patients (13.2%) exhibited airflow obstruction. At the 5-year follow-up, the mean FEV1/FVC declined significantly (76.27% ± 12.04% vs. 80.23% ± 11.02%, P < 0.001) and 9 patients (17.0%) exhibited airflow obstruction. Seven of these patients predominantly showed air trapping consistent with small airway disease on chest CT, aligning with TB-COPD phenotype. Notably, four young-to-middle-aged patients (< 60 years old) had persistent obstruction over the five years. Conclusion The initial test revealed that 13.2% of patients presented with airflow obstruction. By the 5-year follow-up, this proportion had increased to 17.0%, with most cases demonstrating imaging findings aligning with TB-COPD, even among younger, non-smoking individuals. These findings emphasize the importance of long-term follow-up and routine lung function assessments in TB survivors.
Mengen Guo,
Jiangmei Liu,
Guanhao He,
Jinlei Qi,
Jianxiong Hu,
Peng Yin,
Sujuan Chen,
Yulin Zhuo,
Yi Lin,
Xuelong Gu,
Tao Liu,
Ziqiang Lin,
Fengrui Jing,
Jinling You,
Wenjun Ma,
Fanna Liu,
Maigeng Zhou
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.013
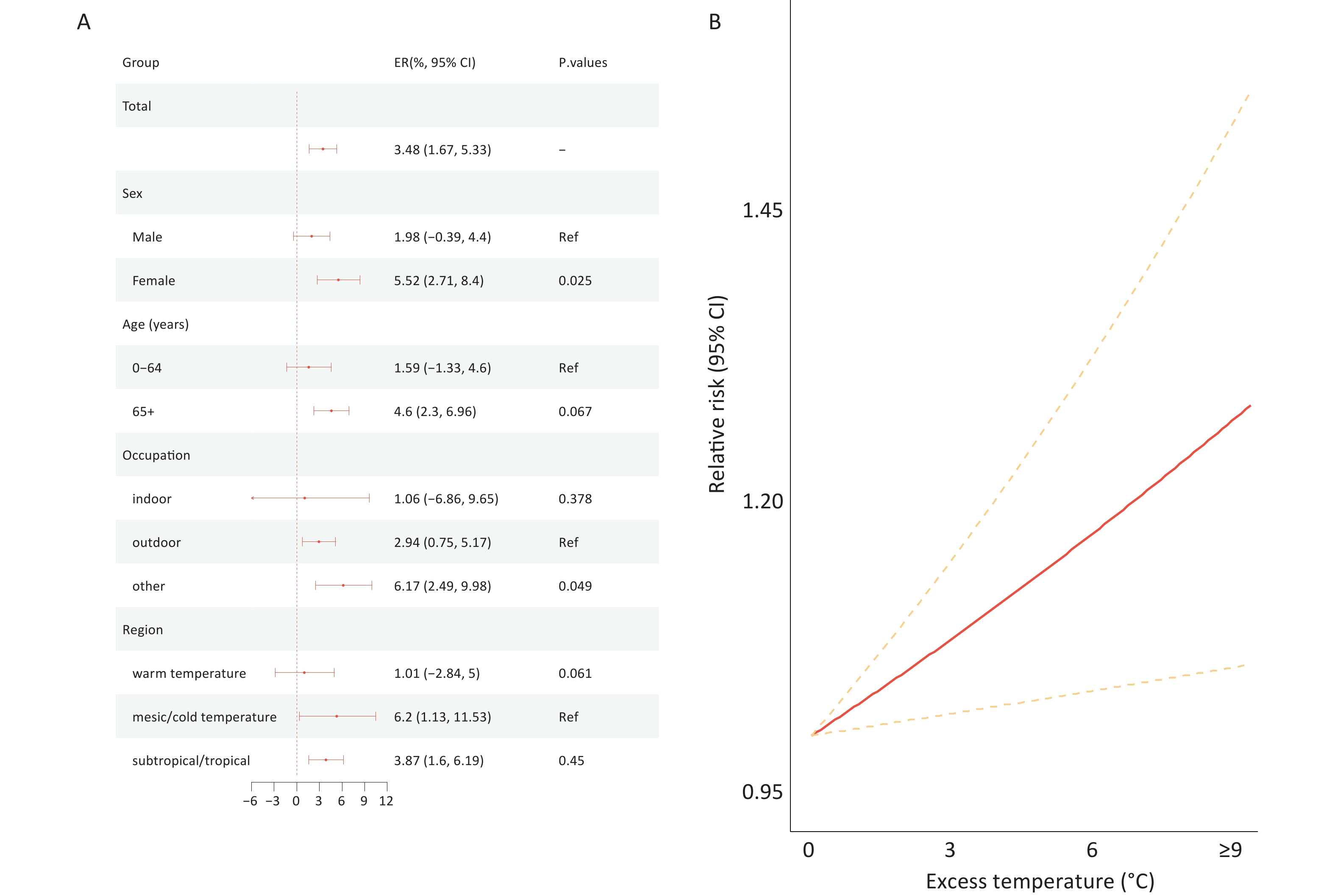
Objective Although many studies have examined temperature-related non-accidental mortality, the impact of heat waves on the mortality burden of chronic kidney disease (CKD) remains poorly understood. This study aimed to assess the CKD mortality burden associated with heat waves in China under global warming. Methods Mortality data on CKD from 2,790 counties/districts in China from 2004 to 2022 were collected from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention; meteorological data for the same period were obtained from the fifth-generation European Reanalysis Land dataset. A time-stratified case-crossover design combined with a distributed lag nonlinear model was used to examine the association between heat waves and CKD mortality. Future CKD mortality burdens attributable to heat waves under climate change and future population scenarios were projected. Results In total, 236,260 CKD deaths were included in this study. Compared to that during non–heat wave days, CKD mortality increased by 3.48% (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.67% to 5.33%) during heat waves, and the mortality risk escalated by 2.48% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.12% to 4.91%) for each 1 °C increment during heat wave days. Stratified analyses revealed that CKD mortality risks were greater for women (Excess Risk [ER] = 5.52%, 95% CI: 2.71% to 8.40%), individuals aged 65 years and older (ER = 4.60%, 95% CI: 2.30% to 6.96%), and people in mesic/cold regions (ER = 6.20%, 95% CI: 1.13% to 11.53%). The projections showed that the attributable fraction(AF) of CKD mortality due to heat waves would rise from 0.64% (95% CI: 0.52% to 0.78%) in the 2020s to 2.44% (95% CI: 1.97% to 2.95%) in the 2090s under the SSP5-8.5 scenario, with the highest burden in southeastern China, including Hainan (3.31%, 95% CI: 1.66% to 5.02%), Yunnan (3.05%, 95% CI: 1.46% to 4.75%), and Guangdong Province (2.84%, 95% CI: 1.24% to 4.41%). Conclusion This nationwide study demonstrated that exposure to heat waves significantly increased the mortality risk of CKD, and that women, older individuals, and people in mesic/cold regions are more susceptible to heat waves. Global warming will significantly increase the future CKD mortality burden attributed to heat waves, particularly in southeastern China. Our findings emphasize the need to address CKD in the context of ongoing climate change.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.119
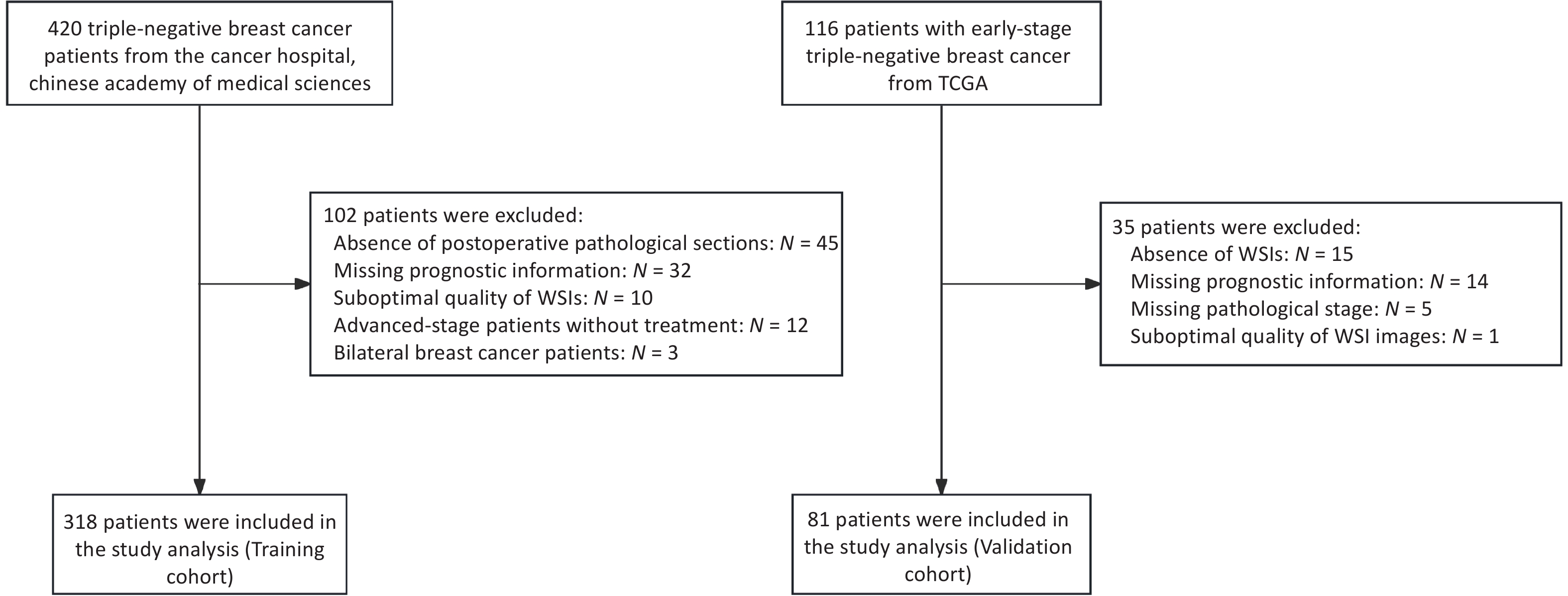
Objective To develop a prognostic prediction model for early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) using H&E-stained pathological images and to investigate its underlying biological interpretability. Methods A deep learning model was trained on 340 WSIs and externally validated using 81 TCGA cases. Image-derived features extracted through convolutional neural networks were integrated with clinicopathological variables. Model performance was assessed using ROC curve analysis, and interpretability was evaluated by correlating image features with mRNA-seq data and characteristics of the immune microenvironment. Results The model achieved AUCs of 0.86 and 0.75 in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. Analysis using HoVer-Net indicated that lymphocyte abundance was associated with recurrence risk. Texture-related features showed significant correlations with immune cell infiltration and prognostic gene expression profiles. Conclusion This study demonstrates that deep learning can enable accurate prognostic prediction in early-stage TNBC, with interpretable image features that reflect the tumor immune microenvironment and gene expression profiles.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.005
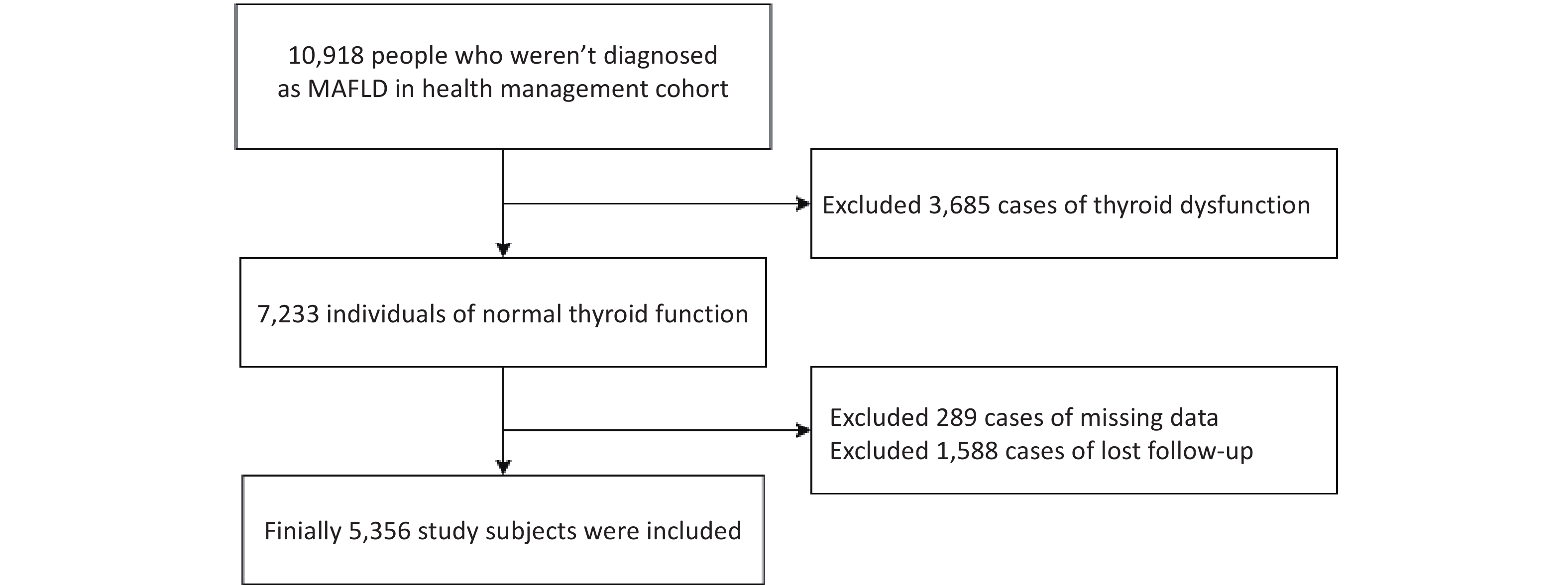
Objective To investigate the association between thyroid hormone sensitivity indices and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in euthyroid Chinese adults. Methods This cohort study included 5,356 euthyroid patients. The peripheral and central thyroid hormone sensitivity indices were calculated. Cox regression models were used to evaluate associations with MAFLD risk, and restricted cubic splines were used to assess potential nonlinearity. Mediation analyses based on an accelerated failure-time model were used to examine the role of the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index. Results MAFLD incidence in euthyroid participants was 18.26%. After adjustment, higher free thyroxine (FT4) levels were inversely associated with MAFLD (HR = 0.973, 95% CI: 0.948 to 0.999, P = 0.043), whereas higher free triiodothyronine (FT3) levels increased MAFLD risk (HR = 1.118, 95% CI: 1.000 to 1.250, P = 0.050). Enhanced thyroid hormone sensitivity, as reflected by elevated FT3/FT4 levels and lower thyrotrophic T4 resistance index (TT4RI), thyroid stimulating hormone index (TSHI), and thyroid feedback quantile-based index (TFQIFT4), was also associated with a higher incidence (all P < 0.05). Mediation analyses indicated that TyG partially mediated the FT3/FT4–MAFLD and TFQIFT4–MAFLD associations, with indirect effects of -96.27 (95% CI: -124.67 to -70.42) and -4.95 (95% CI: -8.29 to -2.10), respectively. Conclusion Increased FT3/FT4 and decreased TFQIFT4 levels were significantly associated with a higher MAFLD risk in euthyroid adults, with TyG acting as a partial mediator.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.162
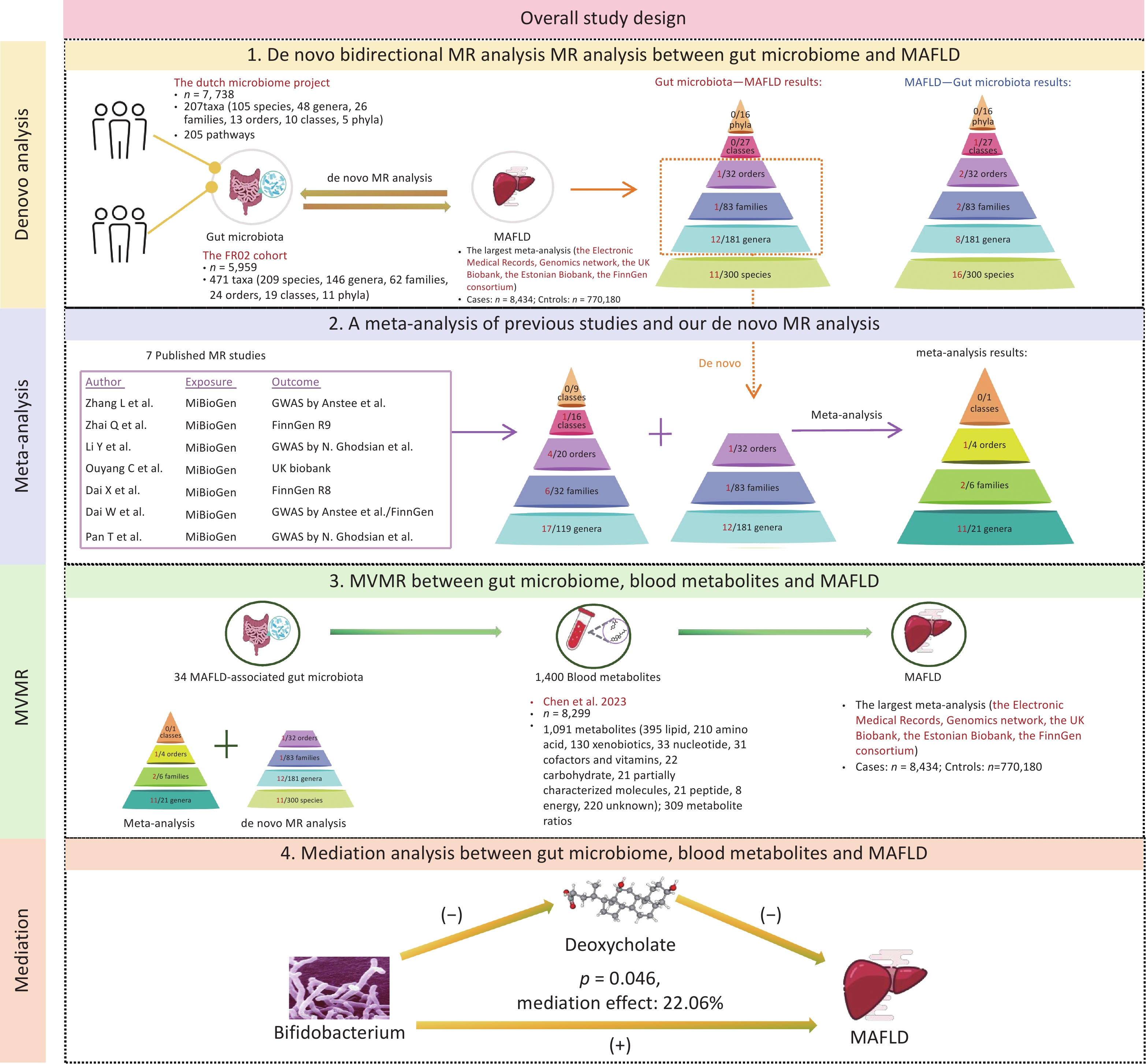
Objective Previous Mendelian randomization (MR) studies have suggested an association between the gut microbiome and metabolic - associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). However, the reliance on 16S rRNA sequencing data has led to inconsistent findings and limited species-level insights. To address this, we conducted a de novo MR analysis using species-level shotgun metagenomic data, combined it with a meta-analysis to consolidate the existing evidence, and explored metabolite-mediated pathways. Methods Bidirectional MR analyses were performed between 883 gut microbiota taxa (derived from shotgun metagenomic genome-wide association study) and MAFLD. Published MR studies (up to December 1, 2024) were identified using PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library for meta-analysis. Multivariable MR (MVMR) and mediation analyses were applied to assess the mediating effects of 1,400 blood metabolites. Results The de novo MR identified 25 MAFLD-associated microbial taxa. Integration with 7 published studies revealed 34 causal taxa, including 10 at the species level. Among the 1,400 metabolites, 53 showed causal links with MAFLD. MVMR and mediation analyses identified deoxycholate as a mediator of the effect of Bifidobacterium on MAFLD risk (22.06% mediation proportion). Conclusion This study elucidated the connections between species-level gut microbiota and MAFLD, highlighting the interplay between microbiota, metabolites, and disease pathogenesis. These findings provide novel insights into the potential therapeutic targets for MAFLD.
Weihua Cao,
Yaqin Zhang,
Ziyu Zhang,
Xinxin Li,
Wen Deng,
Shiyu Wang,
Xin Wei,
Linmei Yao,
Zixuan Gao,
Shuojie Wang,
Lu Zhang,
Yao Lu,
Ruyu Liu,
Shuling Wu,
Yuanjiao Gao,
Hongxiao Hao,
Yao Xie,
Minghui Li
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.161
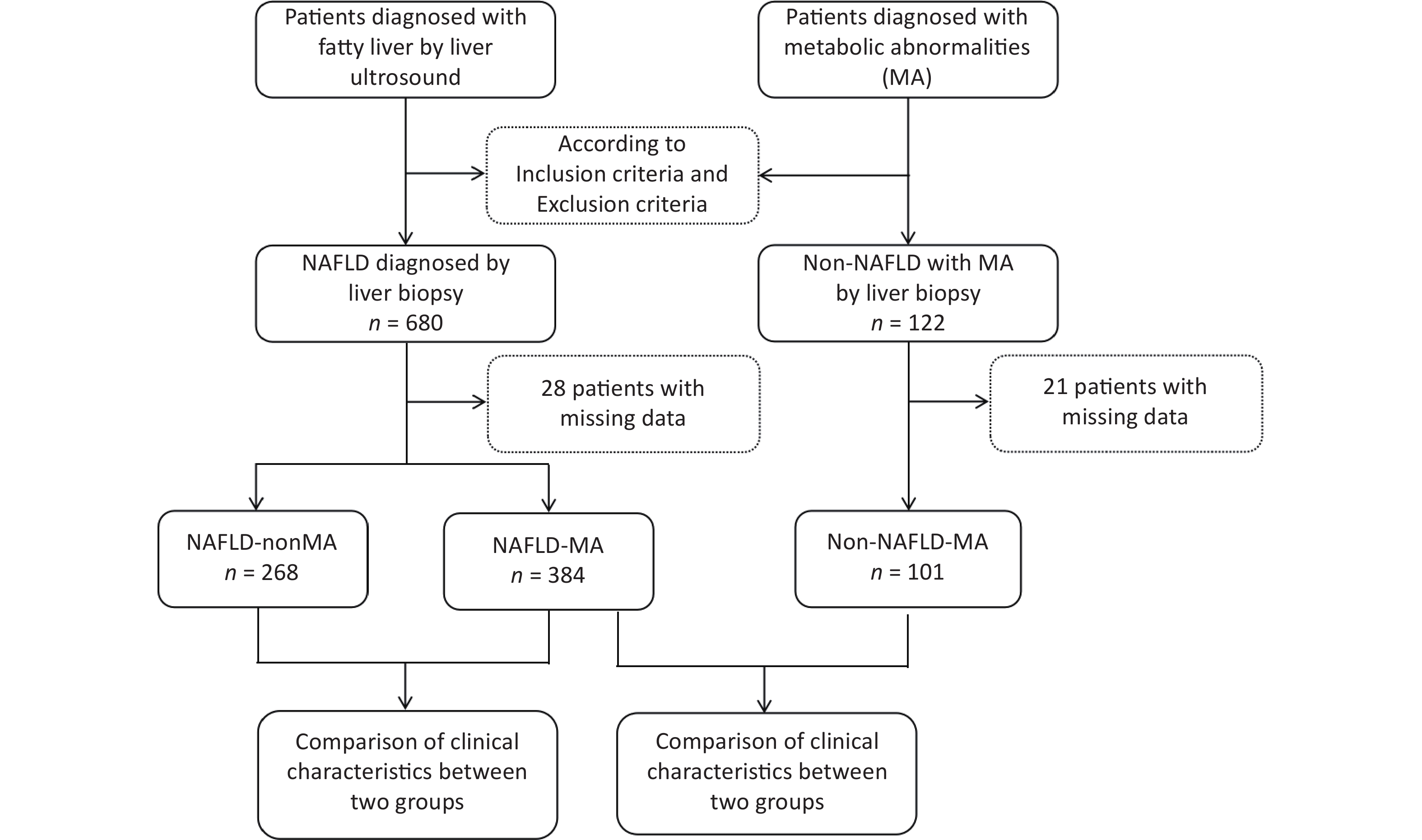
Objective To analyze the diagnostic efficacy of lipid-related insulin resistance (IR) markers in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic abnormalities (MA). Method Patients with NAFLD with MA, non-NAFLD patients with MA, and patients with NAFLD without MA underwent liver biopsy. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C), visceral obesity index (VAI), lipid accumulation product (LAP), and triglyceride glucose (TyG) index were analyzed. The diagnostic efficacy of these indicators of NAFLD was also evaluated. Results In the NAFLD-MA group, BMI, HOMA-IR, LAP, VAI, TyG index, and TG/HDL-C ratio were higher than those in the non-NAFLD-MA group (P < 0.001). Logistic regression indicated that BMI and TyG index were independent risk factors for NAFLD. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves analysis revealed that the Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) for TyG-BMI was 0.819, and the optimal cutoff for NAFLD was TyG-BMI 39.77. For patients with NAFLD with or without MA, logistic regression analysis suggested that age, TG level, and TyG index were independent risk factors. The area under the ROC curve showed that AUC for the TyG index was 0.724. The optimal cutoff for NAFLD-non MA was a TyG index of 1.580. Conclusion TyG index has diagnostic value in both types of NAFLD; however, TyG-BMI is better in patients with NAFLD with MA and may be an effective screening indicator alone in patients with NAFLD without MA.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.160
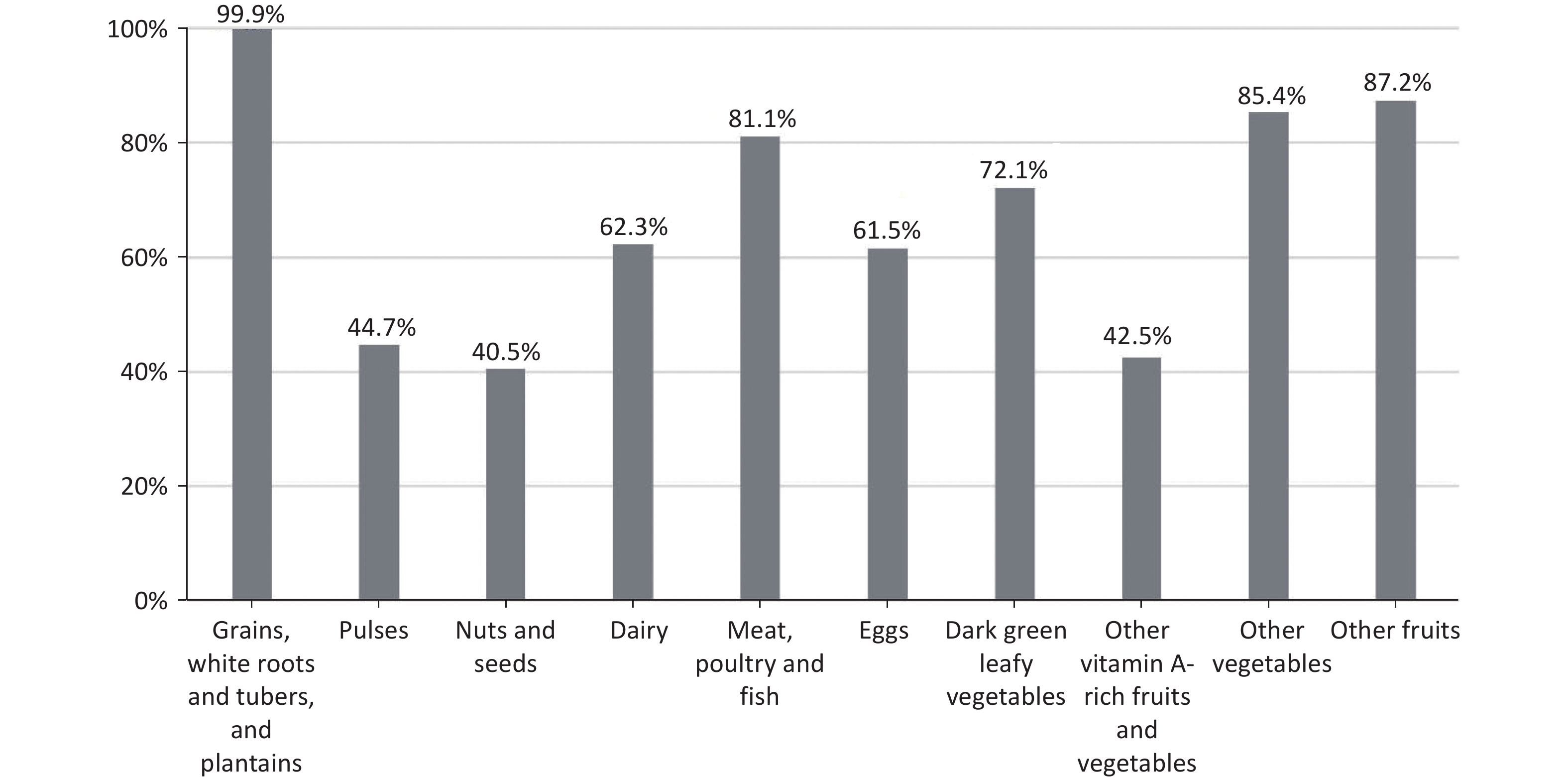
Objective The study aims to prospectively examine the association between the Minimum Dietary Diversity for Women (MDD-W) score and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Methods All participants were pregnant women enrolled in the Tongji Maternal and Child Health Cohort. Dietary intake was assessed using a food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) or 24-h dietary recall. The MDD-W score was constructed by categorizing all food items into 10 food groups, following the Food and Agriculture Organization guidelines. Oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) were conducted during 24-28 weeks of gestation to screen for GDM. Poisson regression models were used to assess the association between MDD-W scores and GDM risk. Results In total, 357 (11.8%) of the 3026 women were diagnosed with GDM. Compared with participants whose MDD-W score was ≥ 8, those with a score of 5-7 had an increased risk of GDM (relative risk (RR): 1.32; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.03, 1.69), and those with a score ≤ 4 had a significantly higher GDM risk (RR: 1.58; 95% CI: 1.12, 2.26). Furthermore, these findings indicate that pregnant women with MDD-W scores < 8, in conjunction with being overweight or obese before pregnancy and excessive gestational weight gain, have the highest risk of developing GDM. Conclusions These data suggest that a higher MDD-W score during pregnancy is independently associated with a lower GDM risk. Therefore, promoting dietary diversity and weight management is recommended to protect pregnant women from developing gestational diabetes.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.159
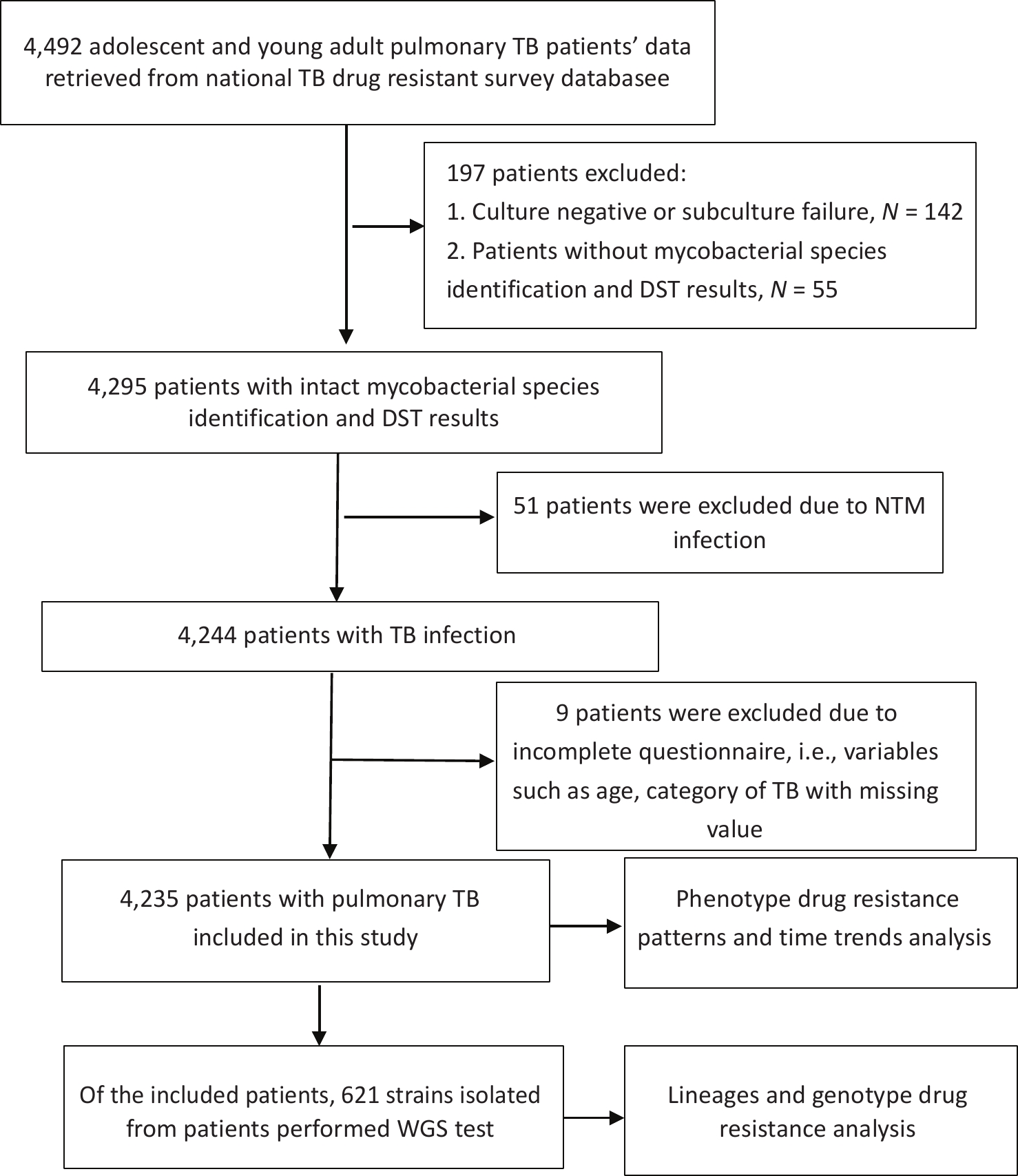
Objective To determine the proportions of drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB), its trends, and the drug resistance-conferring mutations among patients with pulmonary TB aged 10–24 years in China. Methods The data of patients with pulmonary TB were retrieved from a national drug-resistant TB survey for analysis. Joinpoint regression software was used to analyze time trends. We also used whole genome sequencing to analyze the lineages and drug resistance-conferring mutations of 621 isolates. Results Among 4,235 patients with pulmonary TB, the proportion of new cases of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) was 3.18% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.37–4.15) for adolescents and 3.76% (95% CI: 3.03–4.60) for young adults; for previously treated patients, MDR-TB accounted for 11.25% (95% CI: 5.28–20.28) of adolescents and 11.05% (95% CI: 6.88–16.55) of young adults. The proportion of patients with MDR-TB remained stable among both new and previously treated patients aged 10–24 years during the study period. Through whole genome sequencing, we found that the most common mutations in the MDR-TB strains were Ser315Thr in the katG gene (71.74%) and Ser450Leu in the rpoB gene (50.00%). Conclusion This study revealed a high proportion of MDR-TB among adolescents and young adults, indicating that urgent and comprehensive measures are needed to reduce the emergence and transmission of drug-resistant TB among this population in China.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.144
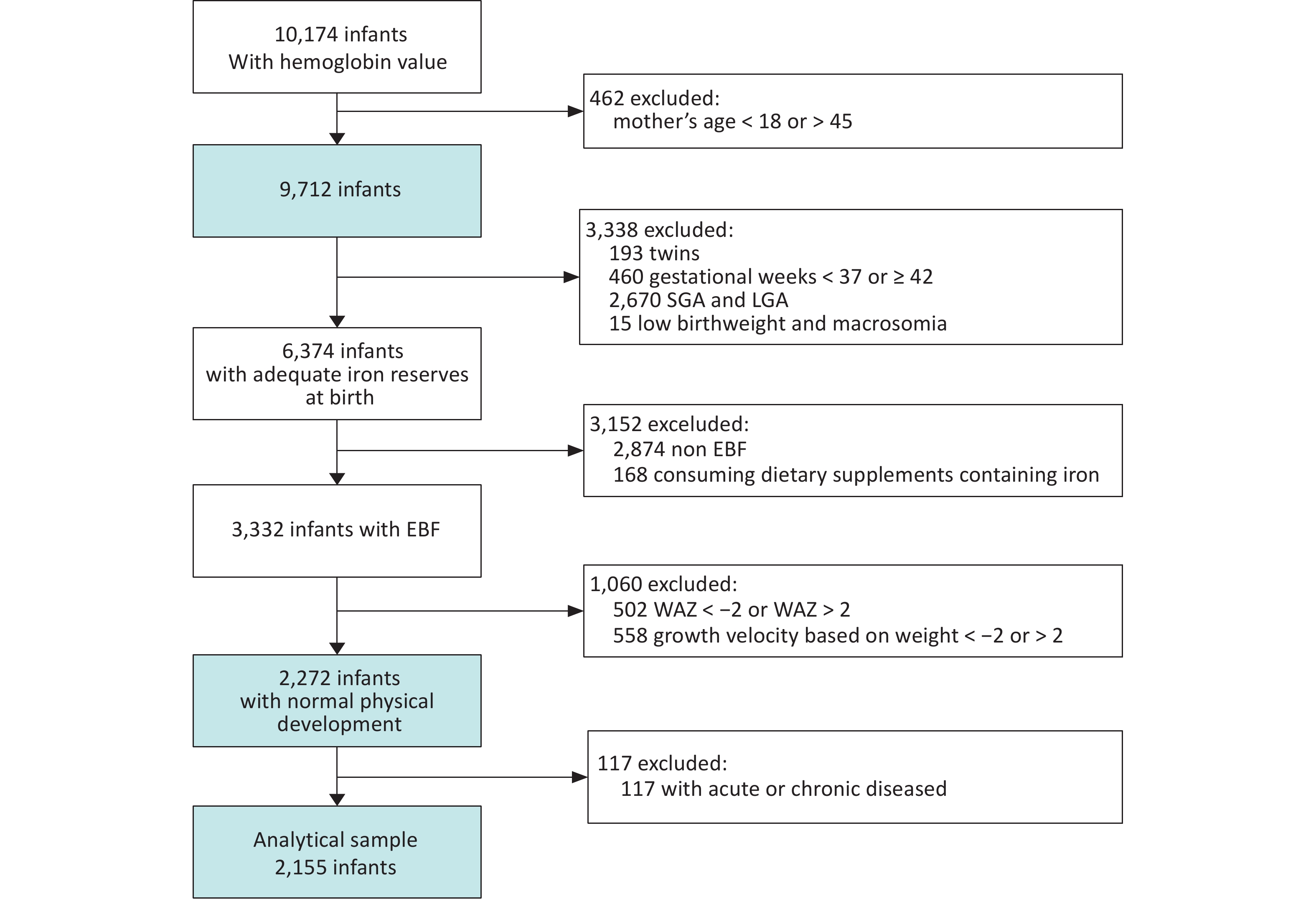
Objective To develop hemoglobin (Hb) percentiles and thresholds for defining anemia among infants aged 0–5 months in China. Methods The National Nutrition and Health Systematic Survey for children aged 0–17 years in China, a nationwide cross-sectional study, was conducted between 2019 and 2021. Hb levels were measured in infants using the HemoCue 201+ analyzer. Age- and sex-specific Hb distributions were constructed for “healthy infants,” defined as those with adequate iron reserves at birth, exclusive breastfeeding, normal weight-for-age Z-score and weight growth velocity, normal neuropsychological development, and absence of acute or chronic diseases. A generalized additive model for location, scale, and shape was applied to fit the Hb percentiles. The 5th percentile of the Hb distribution was defined as the threshold for anemia. Results A total of 10,174 infants aged 0–5 months participated in the study, among whom 2,155 healthy infants were included in the analysis. Hb levels peaked at birth, gradually decreased to a nadir around 60 days after birth, and then rose to a plateau. The Hb thresholds defining anemia were 102.7 g/L, 96.3 g/L, 92.8 g/L, 95.4 g/L, 97.1 g/L, and 95.8 g/L for the 0-, 1-, 2-, 3-, 4-, and 5-month age groups, respectively. Conclusion This study establishes hemoglobin thresholds for defining anemia in infants aged 0–5 months based on a nationwide, population-based dataset in China.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.141
Objective This study investigates the global, regional, and national cardiovascular disease (CVD) burden caused by household air pollution (HAP) from 1990 to 2021 across regions, time periods, sexes, and age groups. Methods The global CVD mortality and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) attributable to HAP are analyzed to assess their current status and historical trends. Quantitative methods are used to assess health inequalities. Projections up to the year 2040 are made using the Nordpred method. Results In 2021, 0.758 million deaths and 18.175 million DALYs were attributed to HAP-related CVD, with age-standardized rates (ASR) for mortality and DALYs of 8.950 and 210.354 per 100,000 individuals, respectively. The disease burden increased with age and was higher in men. While mortality and DALYs rates have decreased over the past three decades, with more significant reductions in low- and middle-income regions, health inequalities persist despite improvements. Projections indicate a slow increase in the CVD burden attributable to HAP by 2040, even as the per capita rates decline. Conclusion Although significant reductions in CVD attributable to HAP have occurred globally, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, disparities persist. Health inequalities have improved but remain significant. As the global population grows and ages, total cases will increase, highlighting the need for continued, targeted interventions.
Milan Jia,
Chenxia Zhou,
Hui Li,
Jing Lan,
Wenbo Zhao,
Lingyun Jia,
Sijie Li,
Changhong Ren,
Chen Zhou,
Lu Liu,
Xunming Ji
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.118
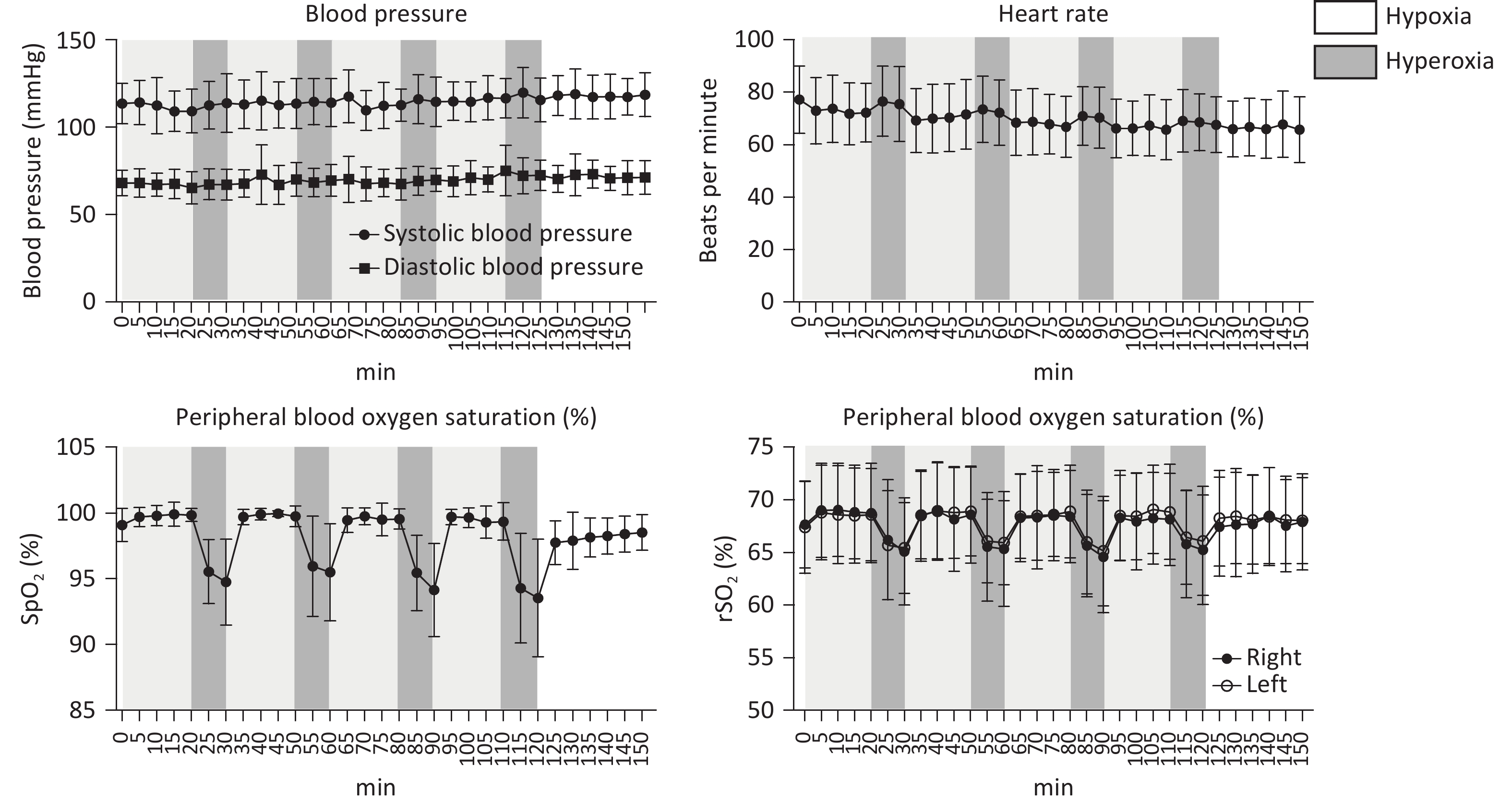
Objective Cerebral venous outflow disorders (CVOD) can impair cerebral perfusion and produce diverse, often debilitating symptoms, substantially reducing quality of life. Intermittent hypoxia–hyperoxia training (IHHT) has demonstrated therapeutic potential across various pathologies and may represent a promising non-pharmacological approach for CVOD management. Methods Patients with imaging-confirmed CVOD underwent 14 IHHT sessions, each comprising four cycles of 10-minute hypoxia (11% O2) stimulation and 20-minute hyperoxia (38% O2). Physiological parameters and adverse events were monitored throughout the intervention. Clinical scales, 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure, blood tests, jugular ultrasound, and perfusion imaging were assessed pre- and post-intervention. Results No participants experienced intolerable discomfort or severe adverse events; vital signs remained within normal ranges. No significant changes were observed in 24-hour blood pressure, blood cell counts, lipid profiles, or other blood markers. Notably, 60% of patients (n = 12) reported overall symptom improvement on the Patient Global Impression of Change scale. Headache severity, as measured by the visual analogue scale, significantly decreased (6.33 ± 1.22 vs. 4.89 ± 2.03, P = 0.016). In patients with internal jugular vein (IJV) stenosis, significant improvements were observed in regional cerebral blood flow (including the insula, occipital lobe, internal capsule, and lenticula) and left J3-segment IJV flow volume (107.27 [47.50, 160.00] vs. 140.83 [55.00, 210.00] mL/min, P = 0.011). Conclusion The current IHHT protocol is safe and well-tolerated in patients with CVOD. IHHT may alleviate CVOD-related symptoms by improving oxygen saturation, cerebral perfusion, and venous outflow pattern, supporting its potential as a non-invasive therapeutic strategy.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.117
Objective The aim of this study was to analyze the correlation between the levels of 12 cytokines in the cervical microenvironment and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in patients with high-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV) infection. Methods Female patients (n = 73) with HR-HPV infection were enrolled and divided into a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) group (n = 33) and a non-HSIL (N-HSIL) group (n = 40), which include low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and inflammation. Healthy screening subjects (n = 31) with negative HR-HPV results were enrolled as a control group. We examined contemporaneous plasma and secretory cytokines from 25 study subjects to investigate the difference between systemic cytokine profiles and the local microenvironment immunity using the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. The 12 cytokines from cervical secretions were compared between the three groups using the Mann-Whitney test, and logistic regression was used to analyze HSIL and N-HSIL. Results There were statistical differences in eight cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-12p70, IFN-α, and IL-8) between cervical secretion and plasma of the same patient, and seven cytokines were statistically different between the control and other two groups. We selected four independent variables (TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-12p70, and IFN-α) commonly identified by univariate regression analysis and non-parametric tests for multivariate logistic regression analysis. Based on this model, HSIL could be predicted in patients with HR-HPV infection, with the area under the curve being 0.76. Conclusion The systemic cytokine profile cannot reflect the local microenvironment immunity, and the occurrence of HSIL is related to the cytokine levels in the cervical microenvironment.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.094
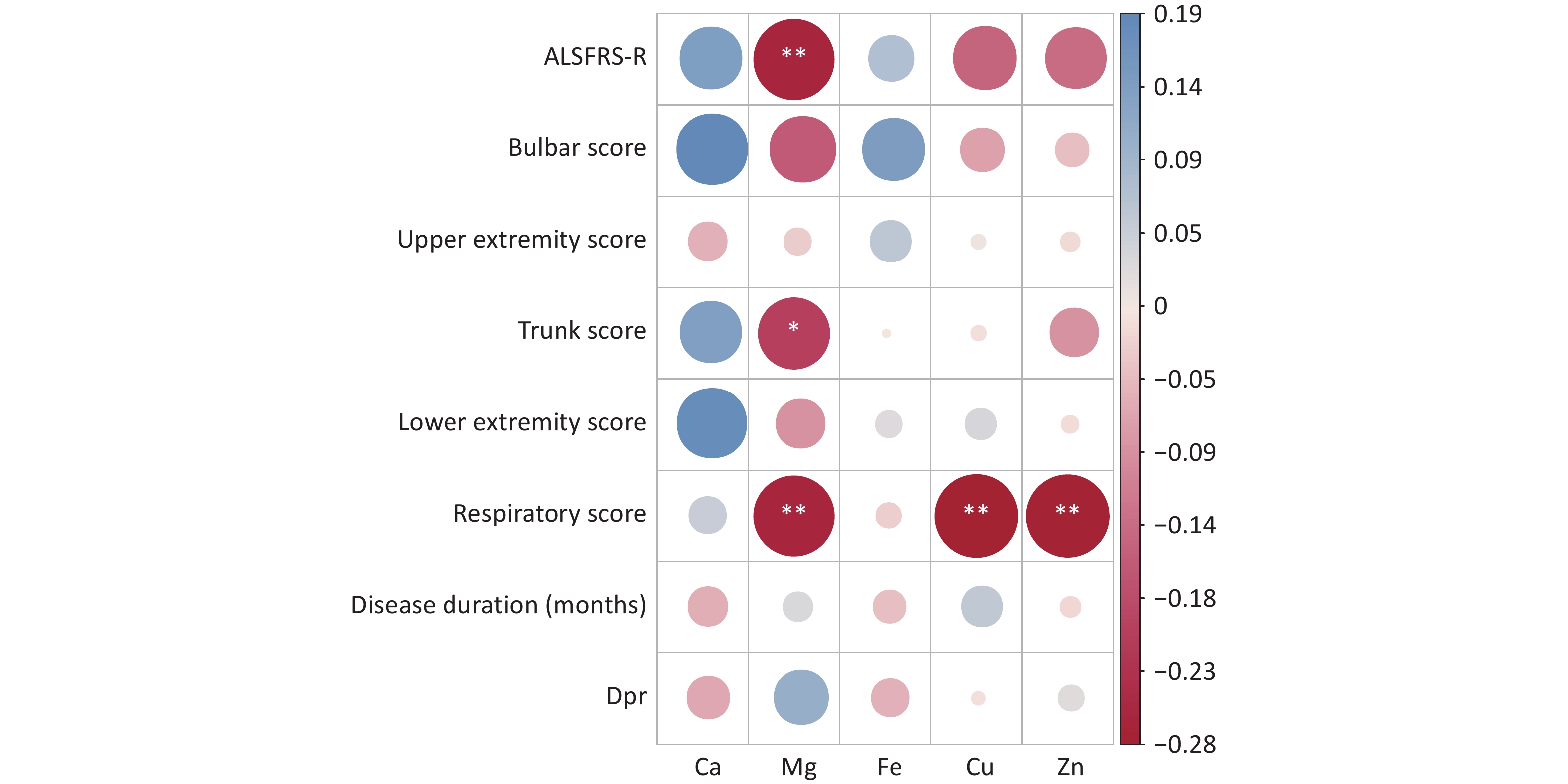
Objective The associations of serum trace element levels with disease progression and survival duration were assessed in individuals diagnosed with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (sALS) in China. Methods Clinical data, including diagnostic indicators, clinical characteristics, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale-Revised (ALSFRS-R) scores, and serum concentrations of calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn), were collected for hospitalized patients with sALS between 2018 and 2021. Correlation analysis, random forest analysis, and the Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test were used to evaluate the relations between serum trace element levels, disease progression, and survival duration. Results Lower serum Ca levels and higher Mg levels were observed in patients with ALSFRS-R scores < 39. Serum Mg was significantly negatively correlated with ALSFRS-R, trunk, and respiratory scores. Serum Cu and Zn also showed significant negative correlations with the respiratory score, whereas Ca and Fe were not significantly correlated with the ALSFRS-R score. The serum levels of Ca, Mg, Cu, Zn, and Fe remained consistent regardless of the site of disease onset. ALSFRS-R analysis revealed that serum Ca and Mg had a substantial effect on the total ALSFRS-R score, with serum Mg significantly influencing the course of the disease. Notably, low serum Mg levels were associated with extended survival times in patients with sALS. Conclusion Serum levels of Ca and Mg play critical roles in the progression of sALS, and a reduced serum Mg level is related to an extended survival time.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.016
Objective To investigate the association between occupational high-temperature exposure and accelerated biological aging. Methods A total of 140 male workers exposed to occupational high-temperatures and 207 male non-exposed control workers were selected as study subjects. Questionnaire surveys and health examinations were conducted. Biological age and organ-specific biological age were calculated using the Klemera–Doubal method. Generalized linear models were used to analyze the effects of occupational high-temperature exposure, body mass index (BMI), smoking, alcohol consumption, and sleep duration on biological age (BA) acceleration and organ-specific biological age. Results Significant differences were observed between the exposed and control groups in length of service, systolic blood pressure, red blood cell count, albumin levels, urea, creatinine, BA acceleration, and liver–kidney BA acceleration (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, which showed a BA acceleration of 0.04 ± 1.34 years, the exposed group demonstrated significantly higher BA acceleration of 0.62 ± 1.31 years. After adjustment for covariates, workers exposed to high-temperatures exhibited significantly higher BA acceleration and liver–kidney BA acceleration than controls (P < 0.001). High-temperature exposure and BMI were associated with BA acceleration, with a significant interaction between the two factors (P < 0.05). High- temperature exposure, BMI, and smoking were identified as risk factors for BA acceleration, whereas sleep duration was a protective factor (P < 0.05). Conclusion Occupational high-temperature exposure may accelerate biological aging. An interaction exists between occupational high-temperature exposure and BMI in relation to BA acceleration.
Queyun Sun,
Cheng Cui,
Weiting Cai,
Lin Jiang,
Jingjing Xu,
Yi Yao,
Na Xu,
Xiaozeng Wang,
Zhenyu Liu,
Zheng Zhang,
Yongzhen Zhang,
Xiaogang Guo,
Zhifang Wang,
Yingqing Feng,
Qingsheng Wang,
Jianxin Li,
Xueyan Zhao,
Jue Chen,
Runlin Gao,
Lei Song,
Yaling Han,
Jinqing Yuan,
Ying Song
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.015
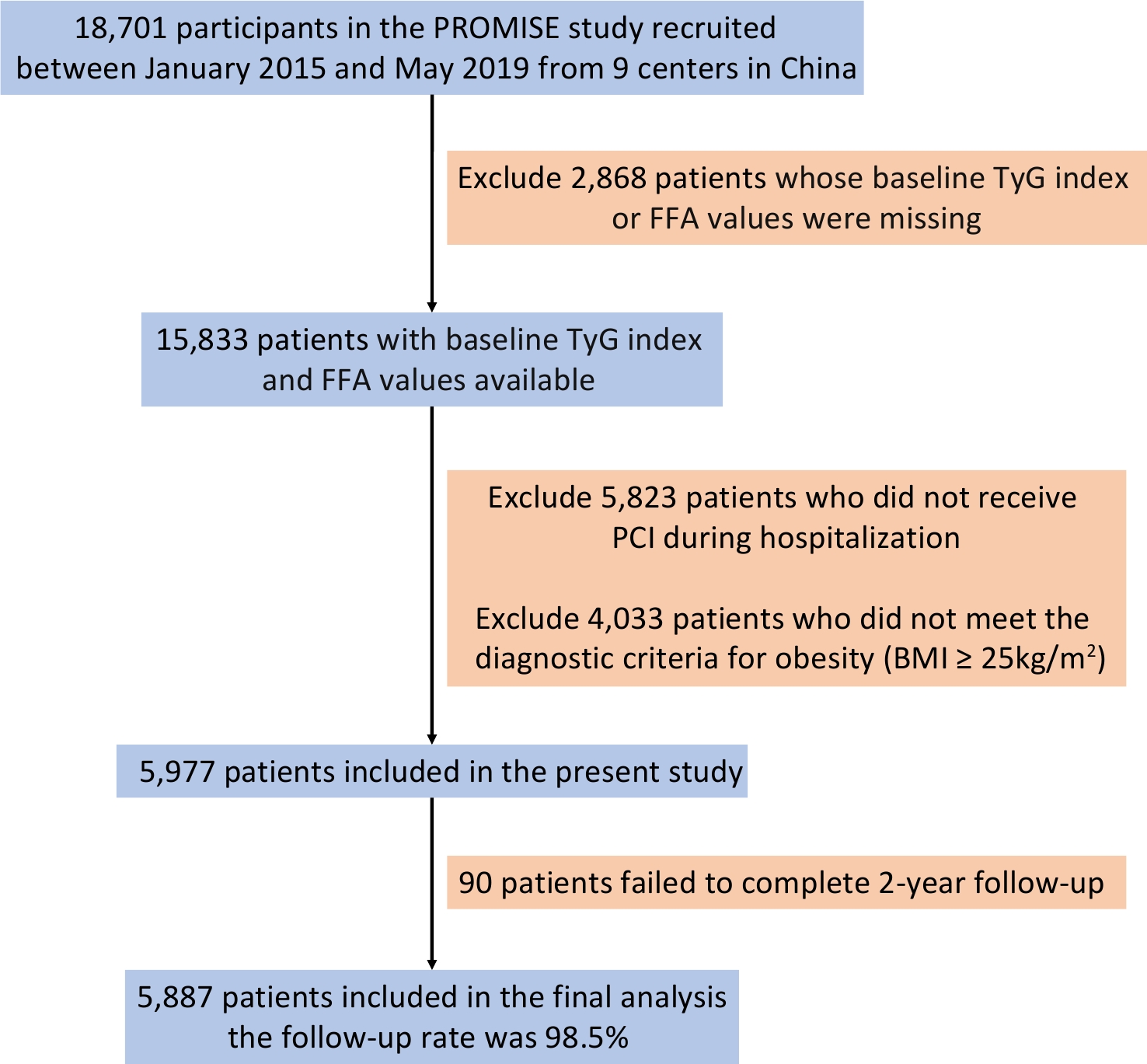
Objective To investigate the joint effect of free fatty acid (FFA) and the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index on the prognosis of overweight and obese coronary artery disease (CAD) patients. Methods A total of 5,887 patients were enrolled in this study. Restricted cubic spline analyses were used to assess the dose-response relationship of FFA and TyG with major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCE). Mediation analysis was used to examine whether TyG mediated the association between FFA and MACCE. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were used to compare the cumulative incidence of events. Multivariable Cox models were used to explore the independent association between Low-/High-FFA and Low-/High-TyG on outcomes. Results FFA and TyG were independent predictors of MACCE. TyG mediated 10.7% of the association between FFA and MACCE. Patients with high FFA and TyG levels exhibited a markedly higher MACCE risk (adjusted hazard ratio: 1.951, 95% confidence interval: 1.533–2.484; P < 0.001), with a significant interaction between FFA and TyG. Among patients with elevated FFA levels, MACCE increased progressively across higher TyG tertiles (P for trend = 0.001). Conclusions FFA and the TyG index independently predict adverse outcomes in overweight or obese CAD patients, with the TyG index mediating the relationship between FFA and MACCE. Their combined assessment enhances the risk stratification in this population.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.012
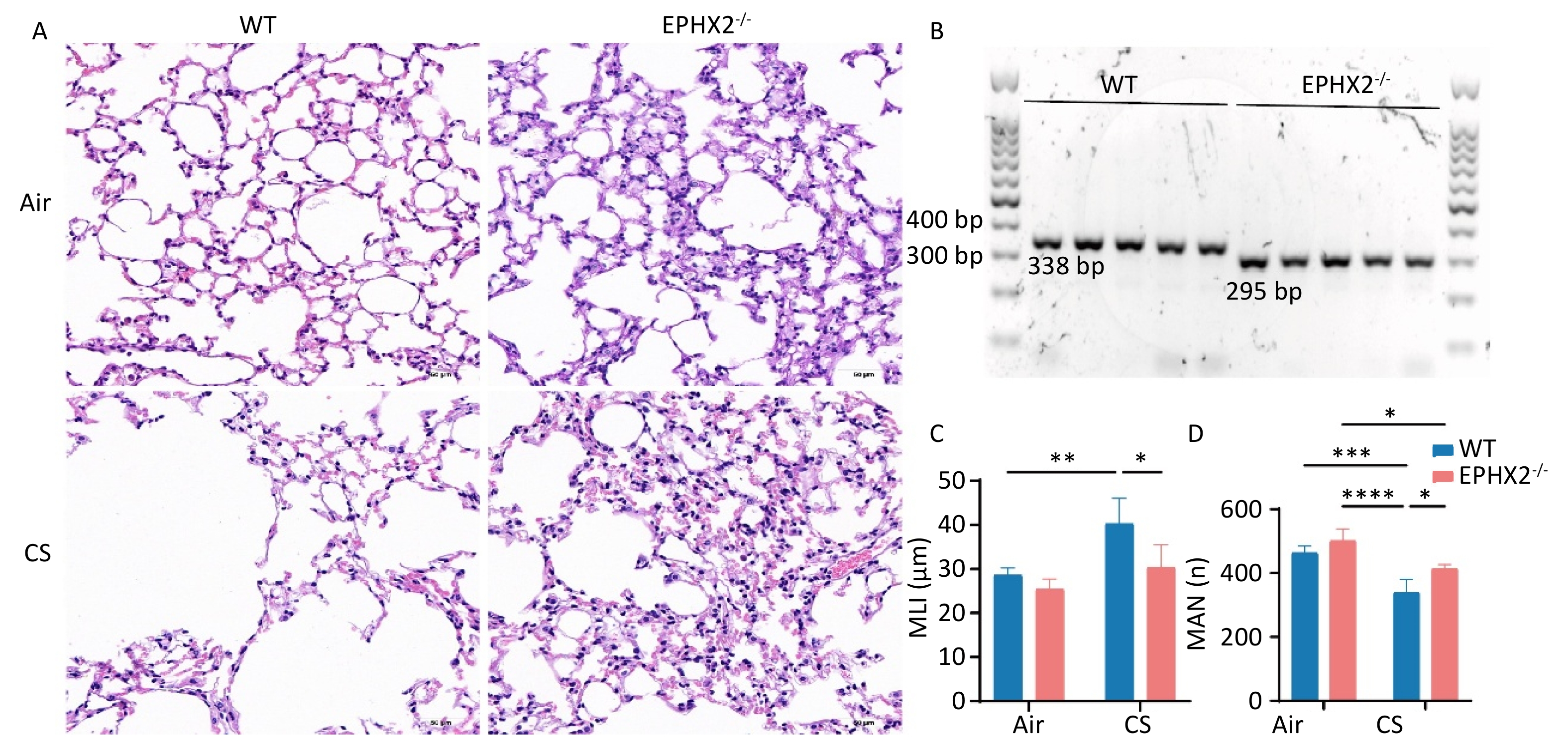
Objective This study investigated the effect of reducing soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH, encoded by the Ephx2 gene) on the mediation of EETs metabolism during ferroptosis in emphysema in vivo. Methods Male C57BL/6J wild-type (WT) and Ephx2-/- mice received whole-body exposure to either cigarette smoke (CS) or air for 16 weeks. The alveolar structure, pulmonary function, lung tissue morphology, cell death, and ferroptosis levels were assessed following exposure. Results CS exposure caused emphysema, reduced pulmonary function, and induced ferroptosis in mice compared with exposure to air. In contrast, following CS exposure, Ephx2-/- mice exhibited significantly lower levels of emphysema, impaired lung function, lung cell death, intracellular iron, lipid reactive oxygen species, cyclooxygenase-2, 4-hydroxynonenal, and malondialdehyde levels than those of WT mice. However, Ephx2-/- mice exhibited higher levels of glutathione and ferritin heavy/chain 1 than those of WT mice. SLC7A11 expression was significantly reduced, whereas glutathione peroxidase 4 expression was markedly increased in Ephx2-/- mice compared with WT mice. Statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) were observed. Conclusion These results suggest that Ephx2 deficiency inhibits ferroptosis to alleviate CS-induced emphysema, primarily by mitigating its inhibitory effect on the cystine/glutathione/glutathione peroxidase 4 axis. Therefore, Ephx2 represents an effective therapeutic target in CS-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.011
Objective Adaptive immune responses play a critical role in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In this study, we investigated the functional mechanisms of T cell subtypes and assessed the causal links between CD4+ cytotoxic T cell-related genes and ALS risk. Methods Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients with ALS and healthy controls (HC) was used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in CD4+ cytotoxic T cells. Comprehensive analyses of CD4+ cytotoxic T cells, including pseudotemporal trajectory, intercellular communication, and metabolic pathway analysis, were performed. Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis evaluated the causal effects of DEGs on ALS risk, with validation using independent genome-wide association study (GWAS) data. Expression patterns of the causal genes were further verified using scRNA-seq, bulk-seq, and clinical samples. Results CD4+ cytotoxic T cells were significantly expanded in patients with ALS. The upregulated genes S100A6, SERPINB6, SMAD7, and TPST2 were positively correlated with ALS susceptibility, whereas DIP2A showed a protective association. Conclusion S100A6, SERPINB6, SMAD7, TPST2, and DIP2A were identified as causal genes and potential therapeutic targets in ALS, implicating CD4+ cytotoxic T cells in the disease mechanisms. Further studies targeting these genes and neuroinflammatory pathways are warranted.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.151
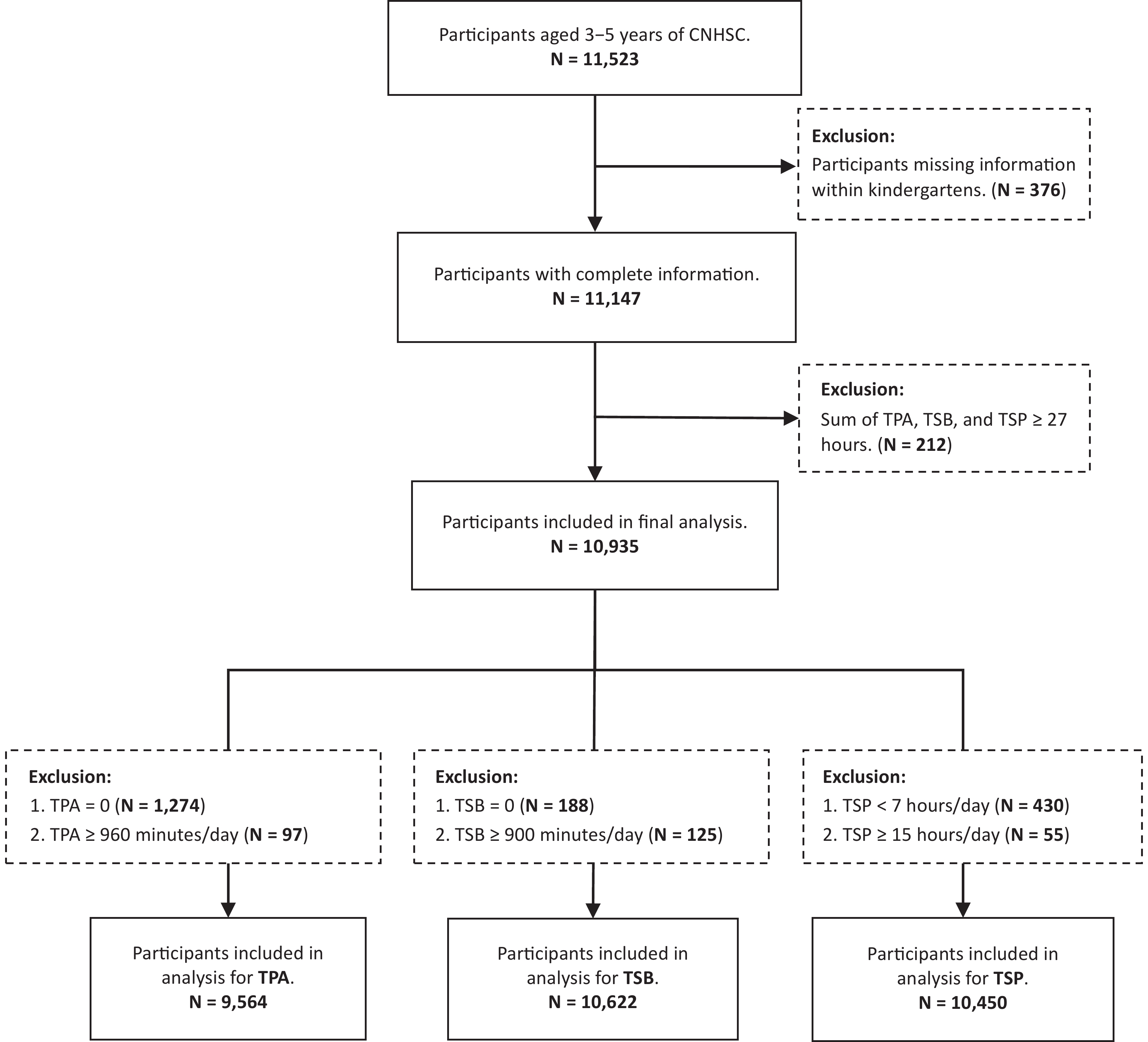
Objective This study aimed to describe 24-hour movement behaviors, including physical activity, sedentary behavior, and sleep period, among Chinese preschoolers using nationally representative data, and examine disparities by age, gender, and residence. Methods A cross-sectional analysis was conducted using data from the China National Nutrition and Health Systematic Survey for Children (2019–2021), including 10,935 children aged 3–5 years. Daily total time of physical activity (TPA), total time of sedentary behaviors (TSB), and total sleep period (TSP) was collected via validated structured questionnaires. Physical inactivity was defined as < 180 minutes of TPA per day. Results Median TPA was 121.4 (IQR: 71.4-209.6) minutes/day, and TSB was 231.4 (IQR: 175.0-304.3) minutes/day, with (11.46 ± 1.00) hours/day average TSP. Overall, 68.8% were physically inactive, with higher prevalence in rural (73.3%) versus urban areas (64.8%, P < 0.001). TPA and TSB increased with age, while TSP decreased (all P < 0.001). No significant gender differences were observed. Conclusion Most Chinese preschoolers exhibit insufficient physical activity and excessive sedentary behaviors, with notable urban–rural disparities and an escalating trend of ageing. Continuous monitoring and targeted interventions, especially in rural areas, are urgently needed.
Qiaoqiao Zhao,
Yanjie Zhao,
Jing Ju,
Liming Zhang,
Xueqing Jia,
Duoduo Fu,
Jiening Yu,
Kaili Sun,
Liying Chen,
Xiaoting Liu,
Zuyun Liu,
Yan Zhang,
Yangzhen Lu,
Xuan Ge
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.166
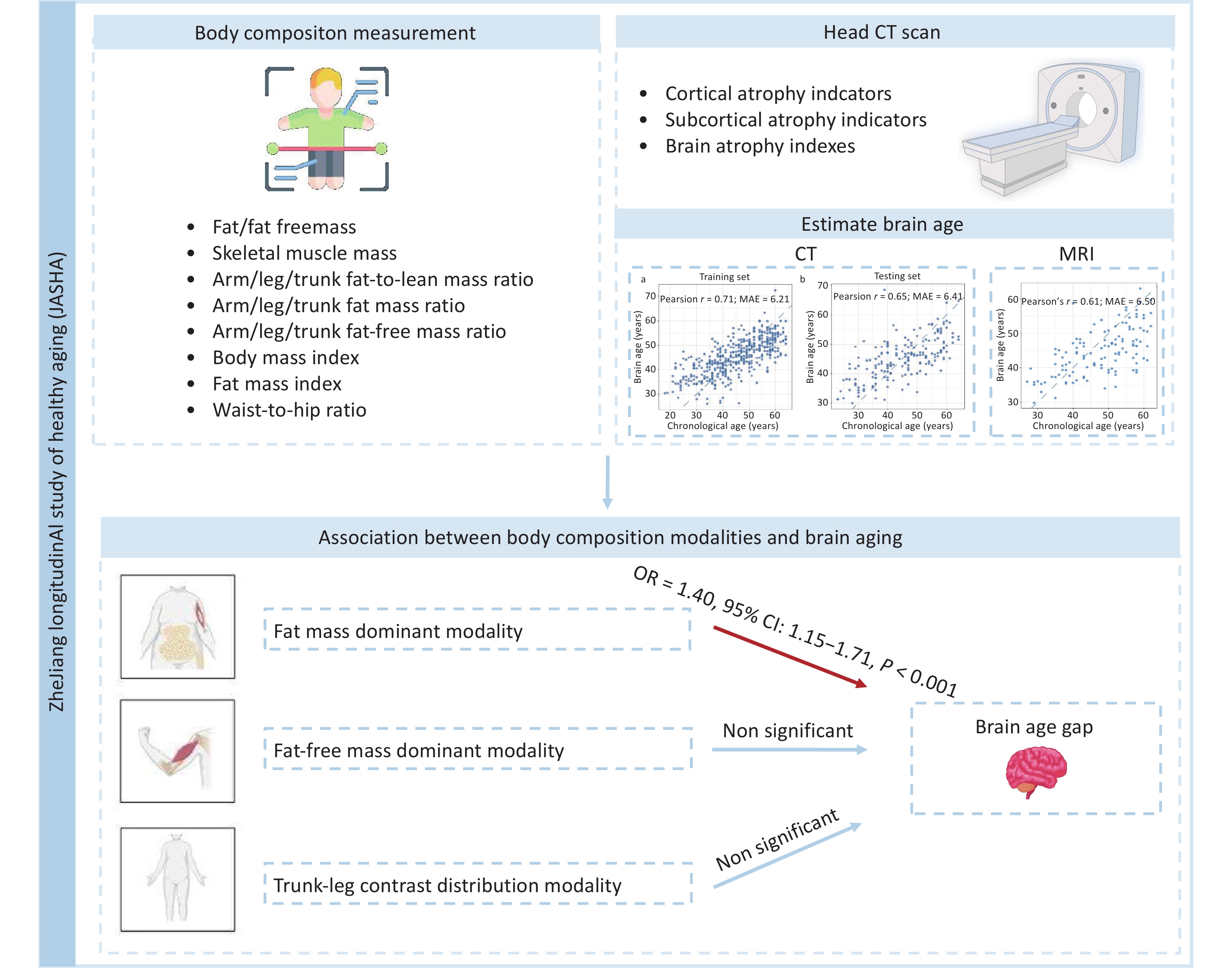
Objective This study examined the associations between multidimensional body composition modalities and brain aging in Chinese adults. Methods Brain age was estimated using ridge regression based on 24 head computed tomography-derived neuroanatomical indicators in a Chinese cohort (n = 557). Brain age gap (BAG), the deviation between the predicted brain age and chronological age (CA), was categorized into brain age acceleration (BAG > 0) and deceleration (BAG < 0) groups. Principal component analysis of 22 correlation-independent body composition indicators identified different body composition modalities. Logistic regression was used to examine the associations between these modalities and the BAG groups. Results The mean absolute error of brain age in predicting CA was 6.41 years. Three body composition modalities were identified: fat mass dominant (characterized by high loading coefficients of body fat mass, fat mass index, visceral fat level, and fat-to-lean mass ratio); fat-free mass dominant; and trunk-leg contrast distribution. The fat mass dominant modality was significantly associated with brain age acceleration (odds ratio [OR] = 1.40, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.15‒1.71), and the association was robust in sensitivity analyses. Conclusion The fat mass dominant modality was significantly associated with accelerated brain aging. This study suggests integrating deep body composition indicators into clinical and community health screening could aid in targeted prevention of brain aging.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.163
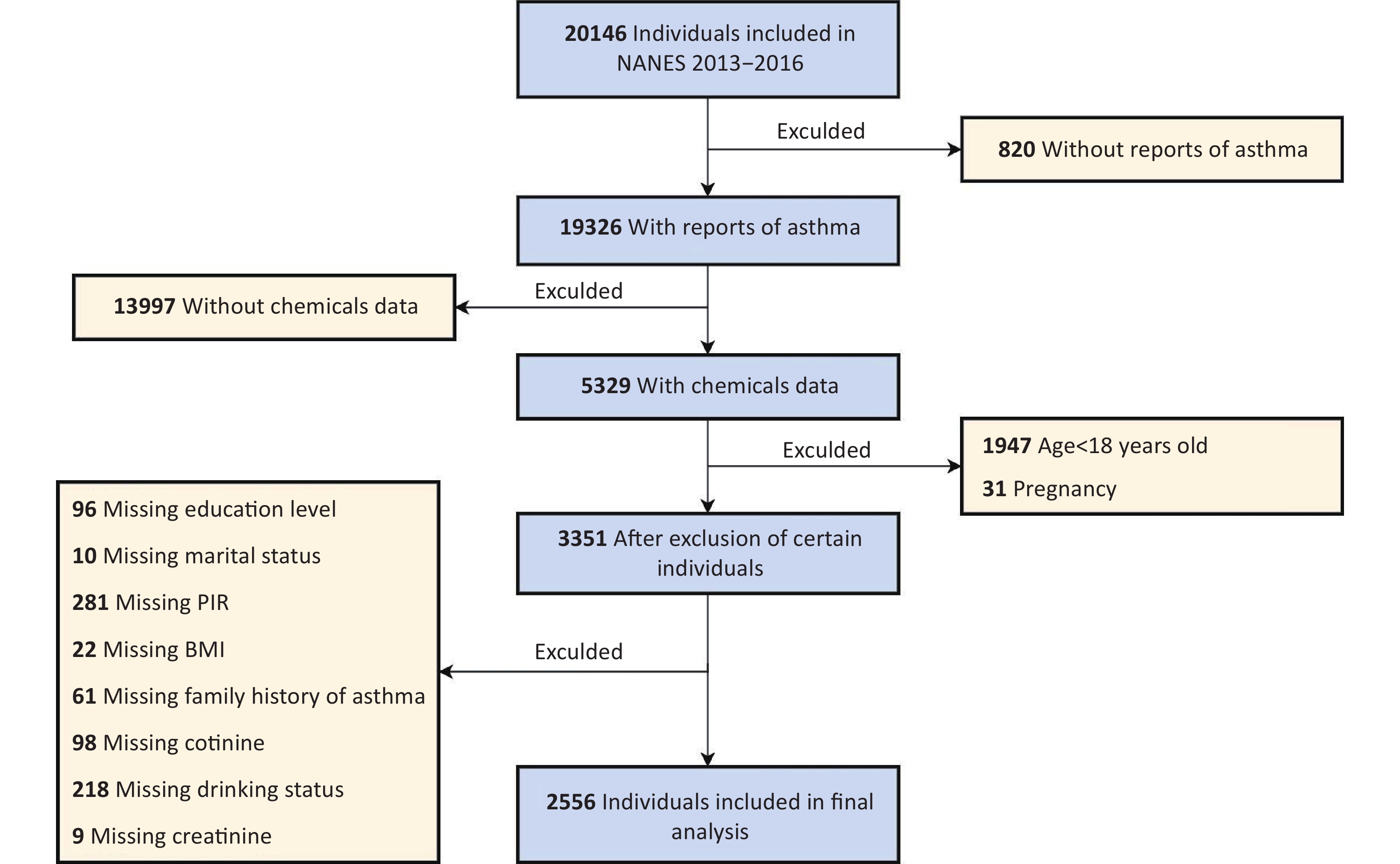
Objective Exposure to mixtures of environmental chemicals may influence asthma outcomes; however, the evidence remains equivocal. This study aimed to assess the association between mixed exposure to phenols and parabens and asthma outcomes in adults and to explore the mediating role of body mass index (BMI). Methods Based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES, 2013–2016), this study used multivariate generalized linear regression and weighted quantile sum (WQS) regression models to evaluate the associations between individual and joint exposure to phenols and parabens and asthma outcomes. These associations were further analyzed and stratified according to age and BMI. A mediation effect analysis was used to assess the role of BMI in this association. Results This study included 2,556 adults, of whom 400 (15.7%) were diagnosed with asthma. After adjusting for all covariates, a significant positive correlation was observed between the chemical mixture and asthma, with an odds ratio of 1.33 (95% confidence interval, 1.06–1.68). Among the eight phenols and parabens, bisphenol F (BPF), propylparaben (PrP), and bisphenol S (BPS) were the major contributors. Additionally, BMI mediated 15.5% of the association between BPF exposure and asthma. Conclusion In this cross-sectional study, mixed exposure to phenols and parabens was significantly associated with asthma outcomes, with BPF, PrP, and BPS identified as the primary contributing chemicals. This study provides valuable insights into the association between mixed chemical exposure and asthma as well as potential control pathways.
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.006
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.007
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.170
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.167
Xin Liu,
Xin Huang,
Jingya Zhang,
Haoran Li,
Ning Zhang,
Yingying Su,
Yang Wang,
Tongyan Liu,
Rengyu Wu,
Jincai Wei,
Bin Zhu
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.150
Minghui Zhang,
Yuanfang Qin,
Na zhang,
Yuqiao Liu,
Jun Yang,
Xiaonuo Xu,
Pengcheng Yu,
Shuqing Liu,
Qian Liu,
Xiaoyan Tao,
Wuyang Zhu
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.145
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.143
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.142
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2026.010
, Available online , doi: 10.3967/bes2025.164
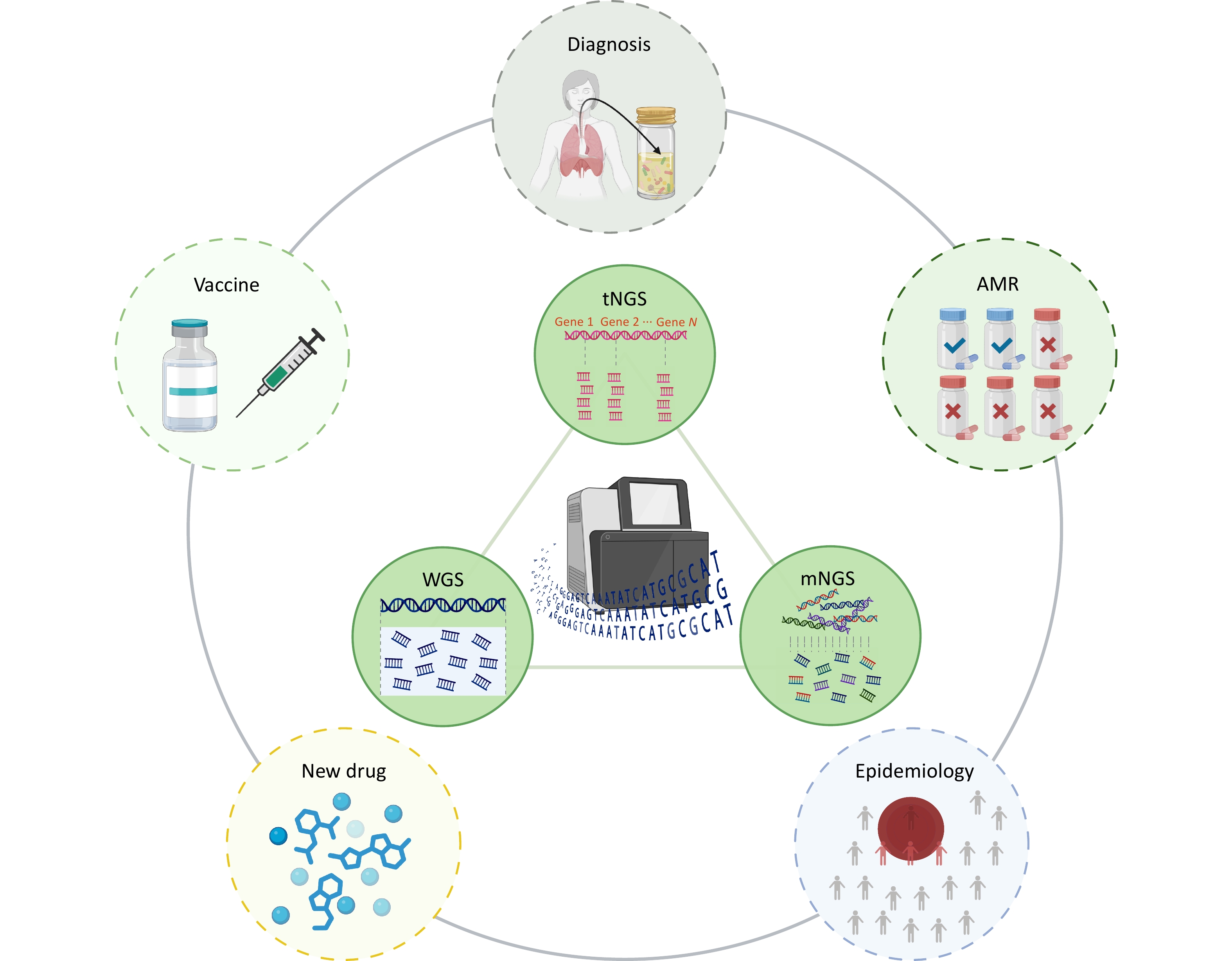
Tuberculosis (TB) continues to pose a significant threat to global public health, necessitating rapid and precise diagnostic methods and comprehensive detection of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to facilitate timely clinical management. Traditional diagnostic techniques suffer from extended turnaround times and limited ability to comprehensively profile AMR, often resulting in delayed therapeutic interventions. High-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies have revolutionized pathogen research by significantly improving diagnostic speed and accuracy. In the context of TB, diverse sequencing strategies and platforms are being employed to fulfill specific research goals, ranging from elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying AMR to characterizing the genomic diversity among clinical isolates. This review systematically examines current progress in the application of HTS for rapid pathogen identification, comprehensive AMR profiling, epidemiological studies, advances in novel drugs, and vaccine development. Furthermore, we address existing technological limitations and bioinformatics challenges and explore the future directions necessary for effectively integrating HTS-based methodologies into global TB control efforts.





















 Quick Links
Quick Links