2017 Vol. 30, No. 9
2017, 30(9): 623-631.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.083
2017, 30(9): 632-640.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.084
2017, 30(9): 641-648.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.085
2017, 30(9): 649-660.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.086
We assessed the prevalence of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) risk factors with a focus on their clustering among healthy adults in Shenzhen, China. Data from the 2011 China Health and Nutrition Survey, comprising a regionally representative sample of 806 healthy adults aged 35 years or older, were obtained to determine the prevalence of five risk factors for NCDs. The prevalence of current smoking, central obesity, impaired fasting glucose, borderline hypertension, and borderline high total cholesterol was 19.97%, 28.29%, 4.47%, 10.55%, and 36.10%, respectively. A total 63.77% of participants had at least one risk factor. Upon examination of risk factor clustering, we observed that 7.57% of participants had at least three risk factors. Using this threshold as a cutoff, clustering of risk factors was associated with sex [odds ratio (OR) = 3.336, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.782 to 6.246], physical activity (OR = 1.913, 95% CI: 1.009 to 3.628), and BMI (OR = 7.376, 95% CI: 3.812 to 14.270). The prevalence of risk factors for NCDs is fairly high among healthy adults in Shenzhen, with a clustering tendency.
2017, 30(9): 667-670.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.088
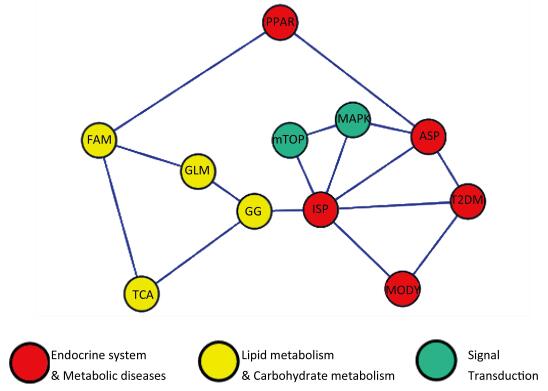
The study illustrate the inner correlation between global DNA methylation variation and different birth weights. Infant birth weight was used to identify cases and controls. Cord blood and placentas were collected. We performed DNA methylation profiling of bisulphite-converted DNA. We have identified many differentially methylated CpG sites in experimental groups; these sites involved in hundreds of signalings. Among these, more than ten pathways were referred to the glucose and lipid metabolism. Methylation changes in the insulin-signaling pathway (ISP), adipocytokine signaling pathway (ASP) and MAPK signaling pathway are involved in the fetal programming of diabetes.
We assessed the role of diabetes mellitus (DM) on treatment effects in drug-susceptible initial pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) patients. A prospective study was conducted in eight provinces of China from October 2008 to December 2010. We enrolled 1, 313 confirmed drug-susceptible initial PTB patients, and all subjects received the treatment regimen (2H3R3E3Z3/4H3R3) as recommended by the national guidelines. Of the 1, 313 PTB patients, 157 (11.9%) had DM; these patients had more sputum smear-positive rates at the end of the second month [adjusted odds ratios (aOR) 2.829, 95% confidence intervals (CI) 1.783-4.490], and higher treatment failure (aOR 2.120, 95% CI 1.565-3.477) and death rates (aOR 1.536, 95% CI 1.011-2.628). DM was a contributing factor for culture-positive rates at the end of the second month and treatment failure and death of PTB patients, thus playing an unfavorable role in treatment effects of PTB.
2017, 30(9): 676-680.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.090
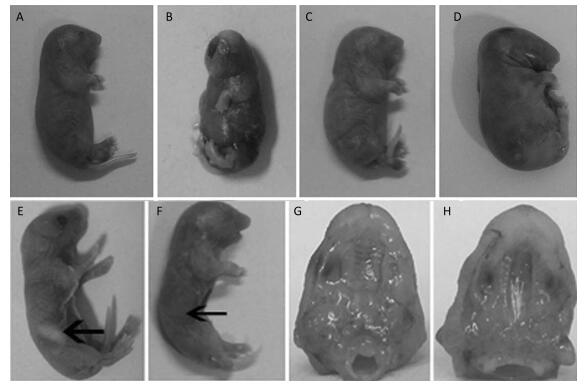
This study investigated the role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the development of the palatal tissues. Cleft palates in mice were induced by 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Expression levels of long non-coding RNA H19 (lncRNA H19) and insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) gene were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The rate of occurrence of cleft palate was found to be 100% by TCDD exposure, and TCDD could cause short upper limb, cerebral fissure, webbed neck, and short neck. The expression levels of lncRNA H19 and IGF2 gene specifically showed embryo age-related differences on E13, E14, and E15 in the palatal tissues. The expression levels of lncRNA H19 and IGF2 gene showed an inverse relationship on E13, E14, and E15. These findings demonstrated that lncRNA H19 and IGF2 can mediate the development of mouse cleft palate.
2017, 30(9): 681-684.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.091
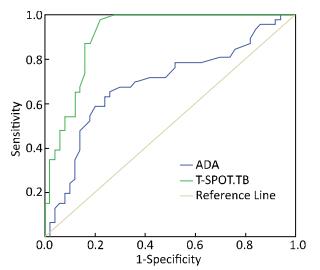
The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic value of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) T-SPOT.TB test for the diagnosis of TB meningitis (TBM). A retrospective analysis of 96 patients with manifested meningitis was conducted; T-SPOT.TB test was performed for diagnosing TBM to determine the diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV). A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was also drawn to assess the diagnostic accuracy. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of CSF T-SPOT.TB test were 97.8%, 78.0%, 80.3%, and 97.5%, respectively, for 52 patients (54.2%) of the 96 enrolled patients. The area under the curve (AUC) was 0.910, and the sensitivities of CSF T-SPOT.TB for patients with stages Ⅰ, Ⅱ, and Ⅲ of TBM were 96.7%, 97.2%, and 98.9%, respectively. CSF T-SPOT.TB test is a rapid and accurate diagnostic method with higher sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing TBM.
The gatekeeper policy has been implemented for approximately ten years on a pilot population in China. It is necessary to assess the satisfaction of patients utilizing community health service (CHS) under the gatekeeper system. Our study showed that the cognition of gatekeeper policy was associated with four dimensions including doctor-patient relationships, information and support, organization of care, and accessibility (P < 0.001). One or more factors such as gender and self-perceived health scores also affected their satisfaction. General practitioners must be prepared to focus on these aspects of information and support, organization of care, and accessibility as indicators of potential opportunities for improvement. Additionally, policymakers can improve patients' satisfaction with CHS by strengthening their awareness of the gatekeeper policy.
Nosocomial infections (NIs) are a critical issue affecting the quality of healthcare. In this study, we performed a retrospective study to explore the incidence rates, mortality rates, and microbial spectrum of NIs in Beijing Chest Hospital, a tuberculosis (TB) specialized hospital in China. Our data demonstrate that the overall incidence rate of inpatients with NIs slightly decreased from 2012 to 2016, which may be associated with the implementation of hand hygiene measures, while the mortality rates associated with NI did not significantly change. In addition, the species distribution of NIs was quite different from that presented in previous reports, and Klebsiella pneumoniae was the most frequently isolated microorganism.
2017, 30(9): 695-700.
doi: 10.3967/bes2017.094
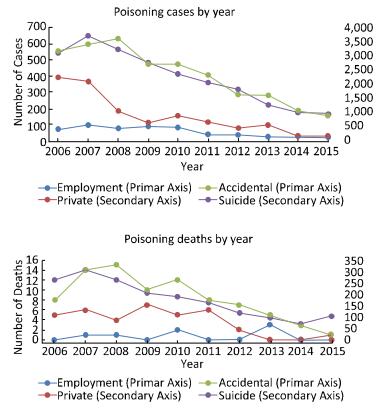
This study aimed to investigate the characteristics of pesticide poisoning in Jiangsu Province, China, and to provide a scientific basis for developing effective interventional measures and preventive strategies. From 2006 to 2015, a total of 35, 308 cases of pesticide poisoning were reported in Jiangsu Province. Non-occupational poisoning accounted for 73.79% of all poisoning cases. A comparison of the data collected before (2006) and after (2015) this study showed a decrease in non-occupational pesticide poisoning. Pesticide poisoning showed an age central tendency of 30 to 44 years, area central tendency for northern Jiangsu, and seasonal central tendency of occupational pesticide poisoning in autumn. Pesticide poisoning remains a major health concern in China. Government agencies together with scientists should focus their efforts on the prevention of potential threats to vulnerable groups such as the elderly, women, and children.


















 Quick Links
Quick Links