HTML
-
Kashin-Beck disease (KBD) is a chronic, deforming endemic osteoarticular disease. More than 645, 000 patients with KBD were reported from an oblique geographic area running from the northeast to the southwest of China at the end of 2012 (Statistical Center of Ministry of Health, China, 2012). The clinical manifestations of KBD include arthritic pain, deformed and enlarged joints, shortened fingers, limited motion of extremity joints, and even dwarfism and disability in extreme cases[1]. Although research on KBD has been ongoing for 160 years, the pathogenesis of KBD has not yet been completely understood, and the disease is unlikely to be caused by a single factor or cause. The general presumption is that the etiology of KBD is a multifactorial combination of selenium (Se)-deficiency, mycotoxins, and genetic factors[2-4].
Chondrocyte death is a known feature of KBD, including the death of chondrocytes in the articular cartilage and growth plates of different peripheral joints, especially fingers[5]. Chondrocyte death plays an important role in the pathogenesis of KBD, based on the presence of red 'cell ghosts', hypocellularity, and a large number of empty lacunae, particularly in regions close to the subchondral bone[5]. Previous studies have shown that progressive chondral necrosis and destruction in the deep zone of cartilage are associated with the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS)[6]and release of glycosaminoglycan via aggrecan catabolism by aggrecanase and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)[7]. Moreover, chondrocyte death through apoptosis[8-9]and necrosis[10] may lead to the loss of resident cells in the articular cartilage, resulting in unfavorable consequences such as impaired matrix remodeling and osteoarthritis (OA)[11]. Thus, it is necessary to clarify the role of chondrocyte apoptosis in the pathogenesis of KBD using studies of suitable animal models of KBD.
In addition, patients with KBD are often found in geographic areas of selenium deficiency, and selenium levels in the serum of patients with KBD were reported to be markedly lower than those in healthy individuals[12-13]. Furthermore, selenium supplements are capable of preventing exacerbation of KBD[14]. Therefore, severe Sedeficiency has been considered as a risk factor for KBD[15]. T-2 toxin contamination in grains and selenium deficiency in drinking water and grains have been found in KBD-endemic areas[16]. We hypothesized that T-2 toxin contamination in food under a Se-deficient nutritional status may be considered as one of the etiological factors contributing to the occurrence of KBD. Therefore, we employed a rat animal model of KBD by administering T-2 toxin to the animals maintained with low selenium nutrition diet. We successfully demonstrated that feeding T-2 toxin with Se-deficient nutrition to rats for 1 month induced chondrocyte death in the deep zone of articular cartilages similar to that in KBD[17].
We had earlier reported that chondrocyte apoptosis can be induced by exposure to T-2 toxin, which can be inhibited by treatment with selenium[18]. Apoptotic forms of cell death have been reported in osteoarthritic cartilage and KBD[19-20]. Moreover, the effect of T-2 toxin on human chondrocyte apoptosis may be mediated by the mitochondrial pathway, which is highly consistent with the chondrocyte changes in KBD[21]. Several studies have demonstrated significant correlations between increasing amounts of chondrocyte apoptosis and severity of OA in both in vitro and in vivo studies in animals[22]and humans[23]. Chondrocyte apoptosis can be induced by exposing normal cartilage explants or chondrocyte cultures to biological agents in vitro[24-26] [e.g., nitric oxide (NO), collagenase, and anti-CD95]. Therefore, chondrocyte apoptosis is largely responsible for cartilage destruction in the articular cartilage and may play an important role in cartilage death and KBD. Moreover, the important question of whether chondrocyte apoptosis is involved in KBD pathogenesis has to be addressed properly in a suitable model. Thus, there is an urgent need for studies using suitable animal models of KBD to clarify the role of chondrocyte apoptosis in the pathogenesis of KBD. In this study, chondrocyte apoptosis was verified by caspase-3 expression and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL). First, we detected the levels of TUNEL in the cartilages to confirm chondrocyte apoptosis as a form of death associated with KBD. Then, we demonstrated chondrocyte apoptosis in the articular cartilages of rats of an established rat anomaly model by TUNEL staining. The mRNA and protein levels of p53, Bax, and Bcl-2 in the cartilages of the established animal model were determined to delineate the association of these apoptosis-related proteins and the apoptosis marker caspase-3 with Se-deficient nutrition, T-2 toxin treatment, or both.
-
Cartilage samples were collected from the hand phalanges of five patients with KBD and five healthy children (aged 6-12 years)[6-7]. The control subjects were from non-KBD areas and included three boys and two girls who had died of nonrelated causes such as falling, road traffic accidents and acute diarrhea. The KBD subjects were from disease-prone areas and included two boys and three girls who had died of acute pneumonia, acute diarrhea, or road traffic accidents. Adults and children with KBD were evaluated based on the national diagnostic criteria of KBD in China (diagnostic code GB16395-1996)[27]using X-ray of the right hand and cartilage sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H & E). The health status of the control children was confirmed by histological examination of the cartilage sections after H & E staining.
-
Sprague-Dawley rats (all males) were purchased from the Experimental Animal Centre of Xi'an Jiaotong University. The experimental protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee, Medical School of Xi'an Jiaotong University. Use of animals in this study was in accordance with the National Institutes of Health publication 85-23 'Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals' (National Research Council, 1996).
To mimic the ages of human adolescents who are most susceptible to KBD, all the animals used in this study were initially 1-month-old and weighed 60-80 g. The rats were randomly divided into two groups and fed for 4 weeks with Se-deficient and normal diet, respectively. Blood selenium levels and serum glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activity levels were determined to confirm the selenium status in these rats as previously reported[28]. Each of the groups was then subdivided into two subgroups as shown in Figure 1. The final four groups were fed with normal diet (n = 20), Se-deficient diet (n = 20), normal diet plus T-2 toxin (200 ng/g body weight (BW)/day; n = 25), and Se-deficient diet plus T-2 toxin (200 ng/g BW/day; n = 25). The animals were then continuously fed with each specific diet (normal or low selenium) and T-2 toxin administered by the intragastric route for 4 weeks. Distilled water was accessible freely to all animals.
-
The normal and the Se-deficient diets were prepared as previously described[28]. The mineral mix and vitamin mix in the normal diet were prepared based on AIN-93G-MX and AIN-93-VX, respectively[28]. The mineral mix contained 0.15 mg selenium (0.35 mg Na2O4Se) per kilogram. In the Se-deficient diet, sodium selenite was omitted from the mineral mix. The selenium levels in the normal diet and Se-deficient diet were confirmed by analyses performed in the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention at the Medical School of Xi'an Jiaotong University. T-2 toxin was kindly provided by Professors YANG Jin Sheng and PENG Shuang Qin, Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Academy of Military Medical Sciences. Crystalline T-2 toxin was dissolved in absolute ethanol and diluted with 0.9% normal saline. T-2 toxin was administered to rats via the intragastric route at appropriate concentrations once a day for 4 weeks[17]. After 4 weeks of administration of T-2 toxin, blood samples were collected from the tail vein; then, the rats were sacrificed, and their knee joints were processed for histopathological evaluation.
-
The human hand phalanges and knee joints were fixed in 4% (w/v) paraformaldehyde for 2-3 days and decalcified in 10% (w/v) ethylenediaminete-traacetic acid for 4 weeks. The joints were dehydrated in a gradient ethanol series, cleared in xylene, and embedded in paraffin wax. Paraffinized 5-μm serial sections were cut in the coronal plane, stained with H & E, and examined microscopically. Some sections were mounted on slides, pretreated with 10% poly-L-lysine, and stored at room temperature until further use for immunohistochemistry of caspase-3 and apoptosis-related proteins.
-
Immunohistochemical staining of caspase-3 in the sections of five different cartilage tissues and hand phalanges of humans was performed using Vectastain 'Elite' ABC (rabbit) kits (Vector labs, Peterborough, UK) according to the manufacturer's protocols. For control sections, the primary antibody was omitted or irrelevant immunoglobulins were applied. For the positive control, the primary antibody used was MMP-13. Briefly, five paraffin-embedded sections (5 μm) from each group were dewaxed and dehydrated in an ethyl alcohol gradient. Endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with 0.3% hydrogen peroxide and 0.1% sodium azide in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Sections were blocked with 2.5% (v/v) normal goat serum for 1 h, followed by incubation with rabbit polyclonal caspase-3 (Cambridge, Abcam, UK) antibodies for 1 h at room temperature. Thereafter, the sections were incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rat HRP (1:500, Pierce Biotechnology, USA) in PBS/1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 30 min at room temperature. After washing, the sections were incubated with Vectastain ABC reagent for 30 min and visualized using the VectorNovaREDTM kit (Vector labs, Peterborough, UK) according to the manufacturer's protocol. After extensive washing, cell nuclei were counterstained with hemotoxylin. Sections were mounted using the Dibutyl phthalate (DPX) mounting medium. Representative regions were photographed using a Leica DMRB brightfield microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) equipped with digital image acquisition.
-
For the detection of in situ cell death, deparaffinized sections were permeabilized with proteinase K (20 μg/mL) and treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide to inhibit endogenous peroxidase activity. DNA strand breaks were then labeled using the in situ cell death detection kit-fluorescein (Roche Ltd, NY, USA) as per the manufacturer's protocol (TUNEL method). Biochemical controls were created as follows: positive control slides were treated with DNase, and negative control slides were treated with PBS instead of Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT). The TUNEL-positive cells were stained using DAB as a substrate for the peroxidase, and hematoxylin was used as a counterstain. This method permitted the end labeling of double-strand DNA breaks, which typically occur during apoptotic DNA fragmentation.
-
After surgery, the cartilage samples were collected into microfuge tubes and placed in liquid nitrogen. The snap-frozen samples were stored at -70 ℃. Tissues were pulverized using liquid nitrogen, and total RNA was extracted from the cartilage of experimental rats using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Life Technologies, Karlsruhe, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions, and the RNA concentration was determined spectrophotometrically at 260 nm. RNA preparations with 260:280 DNA ratio > 1.8 were used further. First-strand cDNAs were synthesized using the RevertAidTM first-strand synthesis kit (Fermentas, USA), which were then used as templates for real-time PCR. Real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR was carried out according to the manufacturer's instructions (SYBR® premix Ex TaqTM Ⅱ; Takara) using 2 μg of total RNA in an iQ5 cycler (Biorad, Munich, Germany). The temperature profile included an initial denaturation for 10 min at 95 ℃, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95 ℃ for 5 s, annealing at 60 ℃ for 15 s, elongation at 72 ℃ for 10 s, and fluorescence monitoring at 72 ℃. Each cDNA sample was analyzed for the expression of genes of interest, together with β-actin, using the fluorescent TaqMan 5'-nuclease assay, 2 × TaqMan master mix (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), 20 × assay-on-demand TaqMan primers, and probes in a total volume of 20 μL The following primer pairs were used: for p53: 5'-CACCTCCA CACCTCCACCTG-3' (forward) and 5'-TCCCGTCCCAG AAGATTCCC-3' (reverse); for caspase-3: 5'-TTGGAA CGAACGGACCTGTG-3' (forward) and 5'-CGGGTGCGG TAGAGTAAGC-3' (reverse); for Bcl-2: 5'-TCCTTCCAG CCTGAGAGCAAC-3' (forward) and 5'-GCGACGGTAG CGACGAGAG-3' (reverse); for Bax: 5'-ATGGGCTGG ACACTGGACTTC-3' (forward) and 5'-GAGCGAGGCG GTGAGGAC-3' (reverse); and for β-actin: 5'-ACTATCGGCAATGAGCGGTTCC-3' (forward) and 5'-CTGTGTTGGCATAGAGGTCTTTACG-3' (reverse). Each plate included a no-template control (NTC). The cycle of threshold (CT) for each sample was averaged and normalized to that of β-actin. The results were then analyzed using the comparative ΔΔCT method [2(-ΔΔCT)] for relative quantification of gene expression as follows:
$$ \Delta \Delta {\rm{CT = }}\Delta {\rm{CT}}\left( {{\rm{sample}}} \right)-\Delta {\rm{CT}}\left( {{\rm{control}}} \right) $$ (1) $$ \Delta {\rm{CT}}\left( {{\rm{sample}}} \right) = {\rm{CT}}\left( {{\rm{sample;target}}} \right)-{\rm{CT}}\left( {{\rm{sample}};{\rm{ \mathsf{ β} }}-{\rm{actin}}} \right) $$ (2) $$ \Delta {\rm{CT}}\left( {{\rm{control}}} \right) = {\rm{CT}}\left( {{\rm{control;target}}} \right)-{\rm{CT}}\left( {{\rm{control}};{\rm{ \mathsf{ β} }}-{\rm{actin}}} \right) $$ (3) -
Protein was obtained after extraction of total RNA from the articular cartilage using Trizol reagent according to the manufacturer's instructions. The levels of Bax, Bcl-2, p53, caspase-3, and β-actin were measured by Western blotting. Equal amounts of total proteins were size-fractionated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Immobilion; Millipore, USA). After blocking with Tween-20 plus Tris-buffered saline (TBST; 20 mmol/L, Tris-chloride pH 7.6, 150 mmol/L sodium chloride, and 0.05% (v/v) Tween-20) containing 5% (w/v) nonfat dry milk for 1 h at room temperature, the membrane was incubated with primary antibodies against Bax, Bcl-2, caspase-3, p53, or β-actin (Santa Cruz, CA, USA) for 30 min at 37 ℃ and then overnight at 4 ℃. After washing once for 10 min in TBST, the membrane was incubated with an appropriately diluted HRP-labeled secondary antibody in TBST for 1 h at room temperature. The membrane was washed twice, then reacted using the SuperSignal Ultra western blot chemiluminescence system with SuperSignal West pico chemiluminescent substrate (Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocol, and finally subjected to autoradiography. The intensity of the signal was analyzed by densitometry. The protein levels were standardized against β-actin.
-
Statistical analyses were performed independently by a nonclinical research assistant and an outside party to ensure objectivity using the SPSS version 16.0 software (SPSS Inc, USA). The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and were analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Results were considered statistically significant if the P value was < 0.05 for continuous variables.
Human Tissue Preparation
Experimental Animals
Diet and Administration of T-2 Toxin
Histology
Immunohistochemistry of Caspase-3
In Situ Cell Death Detection
RNA Preparation and Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Western Blot Analysis
Statistical Analysis
-
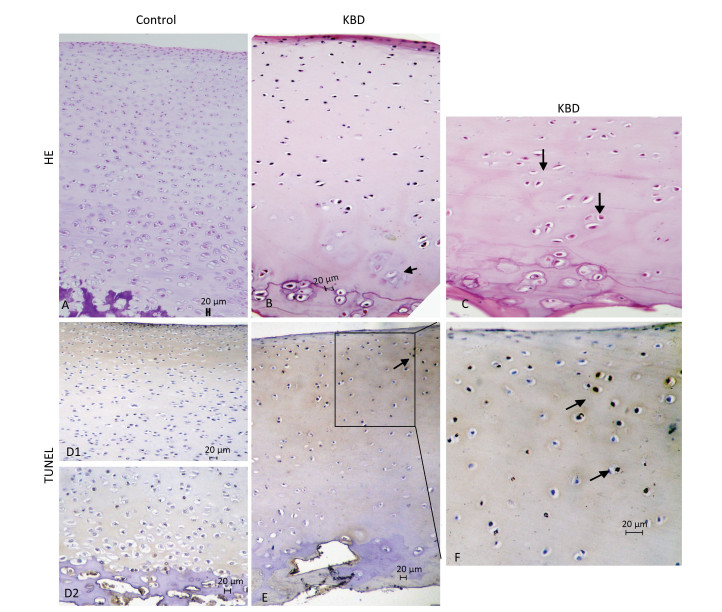
H & E staining results of cartilage from healthy individuals and patients with KBD are shown in Figure 2. Chondral necrosis occurred focally in patches or in band-like areas primarilyin the deep zone close to the bone edge of the articular cartilage from the diseased samples (Figure 2B). Chondral necrosis was indicated by the disappearance of cartilage cells, the presence of red nude nuclei-bearing cells (nuclei without cytoplasm) where only the red 'ghost' outlines of the chondrocytes remained (Figure 2B and 2C), and the loss of alkalinity in the matrix ground substance, which appeared as light blue color in the H & E sections.
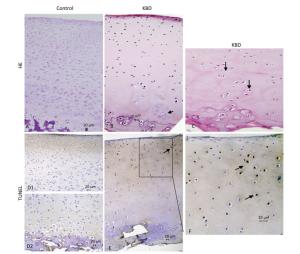
Figure 2. H & E and TUNEL staining of articular cartilage in fingers in normal and KBD child cartilage. Representative sections of articular cartilage from fingers of control and KBD patients. A to C: H & E staining. (A) Control cartilage shows no chondronecrosis. (B) KBD cartilage shows chondronecrosis with red 'ghost' outlines of the chondrocytes in the deep zone. (C) KBD deep zone cartilage shows large chondronecrotic areas where presence of red nude nucleus cells as red 'ghost' outlines of the chondrocytes (arrow) and loss of alkalinity in the ground substance without cells. D (D1 and D2) to F: TUNEL staining for apoptosis in which positive staining appears in brown color in nuclear of chondrocytes. (D) D1 and D2: Control cartilage shows lesser amounts of apoptotic cells throughout the depth of the normal child articular cartilage. (E) KBD cartilage shows an amounts of apoptotic cells from superficial to middle zone of chondrocytes with no TUNEL positive staining in the necrotic zone. The arrow in panels A-C points to chondrocyte necrosis and in panels D-F points to chondrocyte apoptotic cell. Scale bar: 20 μm.
Chondrocyte apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL staining on sections of finger joints from healthy individuals and patients with KBD. The TUNEL-positive cells showed brown staining and were easily visualized. TUNEL staining in the articular cartilage of the hand phalanges of children with KBD was higher than that of healthy children. TUNEL staining tended to be higher from the upper to the middle zones, which indicates that apoptotic chondrocytes were found mostly from the superficial to the middle zones (Figure 2E and 2F). Significantly more TUNEL staining was observed in the cartilage of children with KBD.
-
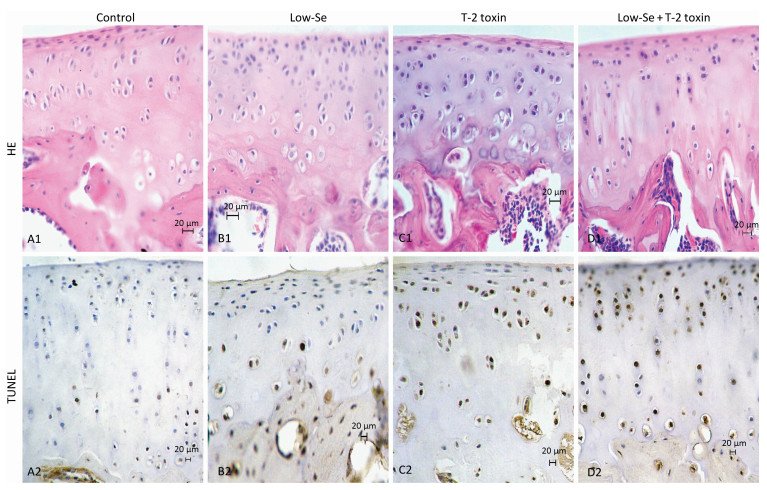
Histological examination of the articular cartilage of knee joints revealed no evidence of injury in rats fed with normal diet (Figure 3A1) or Se-deficient diet (Figure 3B1). Minimal injury, with minimum evidence of cell death, was noted in the articular cartilage of rats fed with normal diet plus T-2 toxin (Figure 3C1). In contrast, the articular cartilage of rats fed with T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet showed variable degrees of articular cartilage destruction in the deep zone (Figure 3D1). Cartilage destruction occurred focally in patches close to the bone edge (i.e., the deep zone of the cartilage), which was recognizable as a red 'cell ghost' where the cell disappeared and a vacant lacuna was left (i.e., a red area on the background due to the loss of alkalinity in H & E staining) (Figure 3D). This histological finding is similar to that found with chondrocyte necrosis in the deep zone of cartilage from the KBD samples (Figure 2E and 2F). Interestingly, no such histological abnormality was observed in the superficial zone of the rat articular cartilage (Figure 2E). Chondrocyte apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL staining on the paraffin sections of joints obtained from the model rats. The TUNEL-positive cells showed brown staining and were easily visualized. Significantly more TUNEL staining was observed in the cartilage of knee joints in the animals of the T-2 toxin plus normal diet and T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet groups compared to that in the normal diet group. Chondrocyte apoptosis within the cartilage increased by 50%-80% in the animals of the T-2 toxin or Se-deficient diet plus T-2 toxin groups compared to that observed in the normal diet group, indicating the presence of DNA breakage (Figures 3C2 and 3D2). Apoptotic chondrocytes were found mostly in the superficial to the middle zones; the presence of TUNEL-positive staining was similar to that found in apoptotic chondrocytes from the superficial to the middle zones of cartilage in the KBD samples (Figure 2E and 2F). No differences were observed between the sections from the groups that were administered Se-deficient diet and normal diet (Figures 3A2 and 3B2).
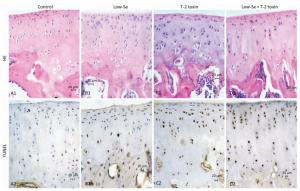
Figure 3. H & E and TUNEL staining in articular cartilage from SD rats fed the experimental diets. Representative H & E and TUNEL staining in the knee joints of rats. A1 to D1: H & E staining. A1-C1 show cartilages stained with H & E from control, selenium-deficient and T-2 toxin-treated rats, respectively. Panels D1 show cartilage from selenium-deficient plus T-2 toxin animals with chondrocyte necrosis and degeneration of cartilage. A2-D2: TUNEL staining for apoptosis in which positive staining appears in brown color in nuclear of chondrocytes. A2 and B2 showed stained with TUNEL from control and selenium-deficient rats with lesser amounts of apoptotic cells throughout the depth of the articular cartilage, C2 and D2 showed stained with TUNEL from normal diet plus T-2 toxin and selenium-deficient diet plus T-2 toxin rats with much number of apoptotic cells from superficial to middle zone of chondrocytes with fewer TUNEL positive staining cells in the necrotic zone. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
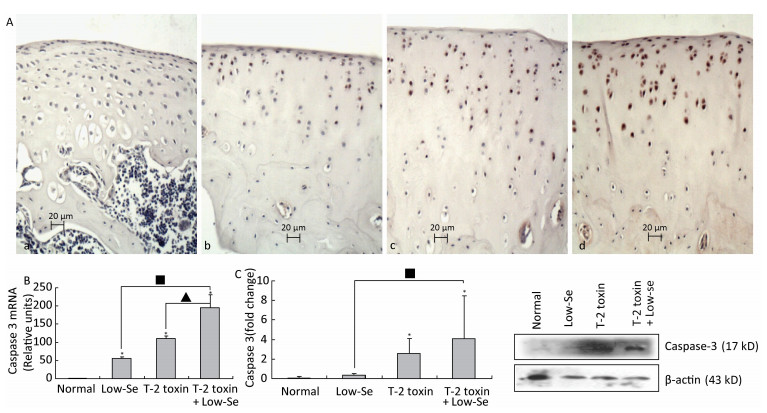
Caspase-3 is a key executioner of apoptosis, and activated caspase-3 cleaves several cellular substrates, ultimately causing cell death[17]. To provide further insight into the mechanisms of T-2 toxin or T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet on apoptosis in the articular cartilage, we examined caspase-3 expression at the site of the rat knee joint cartilage by immunohistochemical staining, real-time RT-PCR, and Western blot analysis (Figure 4). Caspase-3 staining increased in rats treated with T-2 toxin and increased further in rats fed with Se-deficient diet plus T-2 toxin. Caspase-3 staining tended to be higher in the middle and upper deep zones (Figure 4A), which was similar to that observed in the KBD articular cartilages[13]. Figures 4B and 4C depict the caspase-3 mRNA and protein levels in the knee joints of model rats byreal-time RT-PCR and western blot analysis. Both caspase-3 protein and mRNA levels increased significantly in the animals of the normal diet plus T-2 toxin and Se-deficient diet plus T-2 toxin groups compared to the levels in the normal diet group (P < 0.05). The percentage change of caspase-3 protein levels in the samples of T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet group was 20-fold more than that of the normal diet group, whereas it was approximately 2-fold higher when compared to that of the normal diet plus T-2 toxin group.
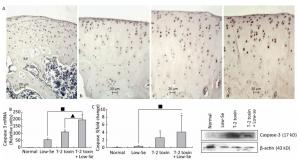
Figure 4. Caspase-3 expression in cartilage of rats. (A) Representative immunohistologic staining of caspase-3 expression in the knee joints of rats assessed by immunohistochemistry. Coronal sections of cartilage through the subchondral bone are shown from rats fed (a) normal diet, (b) selenium-deficient diet, (c) normal diet plus T-2 toxin treatment, and (d) selenium-deficient diet plus T-2 toxin treatment. Abundant expression of caspase-3 was observed in the knee joint in rats treated with T-2 toxin and especially in rats with T-2 toxin treatment plus selenium-deficient diet. Scale bar: 20 μm. (B) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of caspase-3 in cartilage of rats. Given are the log ratios of stimulation/control of five independent experiments each. Bars show the means and standard deviations (expression levels standardized to β-actin). (C) Western blot analysis for expression of protein levels of caspase-3 in cartilage of rats (for β-actin as a loading reference control of five independent experiments each). Bars show the means and standard deviations (expression levels standardized to β-actin). *P < 0.05 vs. control. ■P < 0.05 vs. selenium-deficient diet. ▲P < 0.05 vs. T-2 toxin.
-
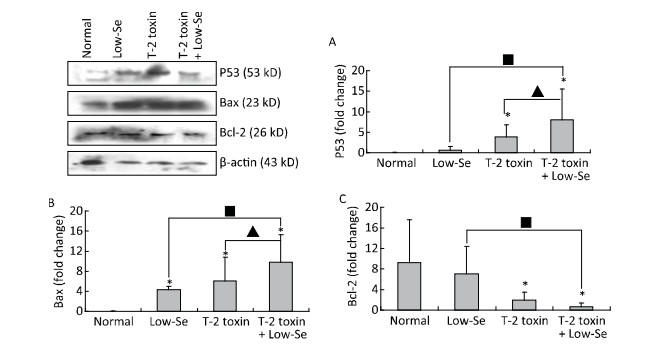
Cartilage samples were evaluated for protein levels of p53, Bax, and Bcl-2 using Western blot analysis (Figure 5). The levels of p53 and Bax were higher in the samples of Se-deficient, T-2 toxin, and T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet groups (Figure 5A and 5B) compared to those of the normal diet group. While Bcl-2 (Figure 5C) expression was reduced in the T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet group compared to that in other groups, the percentage changes of p53, Bax, and Bcl-2 levels in samples of T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet group were more than 20-fold higher than that in the normal diet group and were about 1.5-to 2-fold higher than that in the normal diet plus T-2 toxin group.
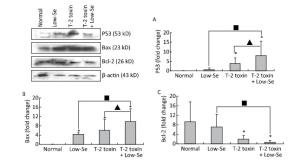
Figure 5. Western blot analysis for expression of protein levels of P-53 (A), Bax (B), and Bcl-2 (C) in cartilage of rats (for β-actin as a loading reference control of five independent experiments each). Bars show the means and standard deviations (expression levels standardized to β-actin).*P < 0.05 vs. control. ■P < 0.05 vs. selenium-deficient diet. ▲P < 0.05 vs. T-2 toxin.
-
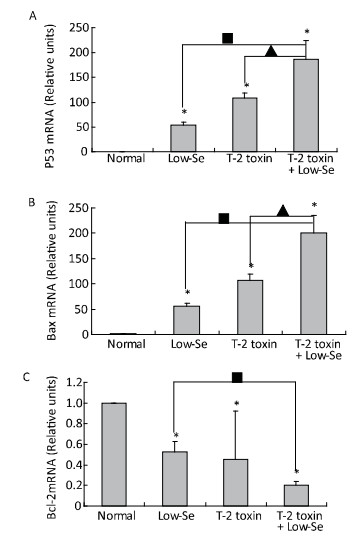
To determine whether alterations in the expression of p53, Bax, and Bcl-2 were associated with the deleterious effects of T-2 toxin and T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet, we evaluated the mRNA levels of p53, Bax, and Bcl-2 in the rat cartilage samples using quantitative real-time RT-PCR. p53 and Bax mRNA levels were significantly increased by T-2 toxin and T-2 toxin plusSe-deficient treatment (Figure 6A and 6B), whereas Bcl-2 levels were reduced in the samples of Se-deficient, T-2 toxin, and T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet groups compared to those in the normal diet group (Figure 6C). The percentage change in expression in the samples of the T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet group were approximately 2-fold higher for p53, Bax, and Bcl-2 compared to that of the T-2 toxin diet group samples.
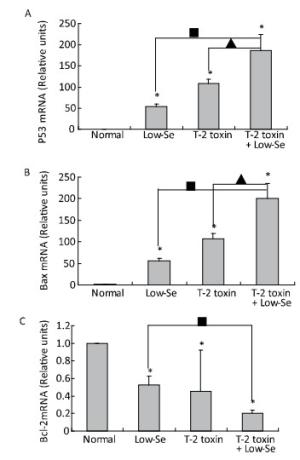
Figure 6. Real-time PCR analysis for expression of mRNA levels of P-53 (A), Bax (B) and Bcl-2 (C) in cartilage of rats. Given are the log ratios of stimulation/control of five independent experiments each). Bars show the means and standard deviations (expression levels standardized to β-actin). *P < 0.05 vs. control. ■P < 0.05 vs. selenium-deficient diet. ▲P < 0.05 vs. T-2 toxin.
Determination of Chondrocyte Apoptosis by the TUNEL Assay in the Articular Cartilage of KBD Samples
Chondrocyte Apoptosis in Model Rat Cartilage
Caspase-3 Expression in Model Rat Cartilage
Analysis of Apoptosis-related Proteins in Model Rat Cartilages
p53, Caspase-3, Bax, and Bcl-2 mRNA Levels in Model Rat Cartilages
-
Chondrocyte survival is important for the maintenance of proper cartilage matrix, and compromised chondrocyte function and survival causes articular cartilage failure. Progressive chondral death that causes destruction in the deep zone of cartilage is a common feature of KBD. In the present study, apoptosis of chondrocytes was observed from the superficial to the middle zones of the articular cartilage of children with KBD, which might result in matrix loss in KBD. Since KBD occurs principally in childhood, the breakdown of cartilage begins as early as in 2-or 3-year-old children. This study demonstrated that cartilage apoptosis occurred in the early stages of KBD. Since it is difficult to assess the relative contribution of chondrocyte apoptosis in KBD pathogenesis, any conclusion regarding the role of apoptotic chondrocyte death in KBD pathogenesis would be insufficient and oversimplified.
Results in this study demonstrated that both T-2 toxin and selenium deficiency increased the caspase-3 mRNA and protein levels, resulting in apoptosis in the superficial to middle zones of the articular cartilages, which is similar to the apoptotic death distribution pattern in KBD. Addition of T-2 toxin to selenium deficiency caused severe chondrocyte apoptosis, which might be involved in the disease pathogenesis as a result of chondral death in the articular cartilages. Therefore, damage caused by chondrocyte apoptosis may play a key role in the progression of KBD and KBD-like pathological processes in the rat model. The increase inchondrocyte apoptosis in animals fed with T-2 toxin plus Se-deficient diet supports this view.
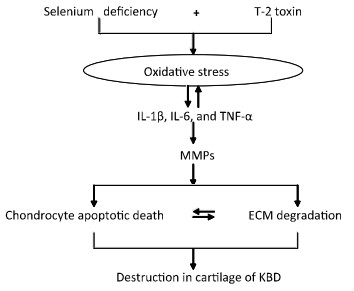
In our previous study, we had reported a number of important findings regarding the development and progression of KBD and had established a rat KBD model using T-2 toxin treatment under Se-deficient conditions[6, 29-31]. We found that oxidative damage of joint tissues in KBD and in the rat KBD model contributed to the pathological process of cartilage damage in KBD[6, 29]. T-2 toxin exposure under a Se-deficient nutritional status demonstrated increased IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α levels in serum and cartilages, which might account for the pathological mechanism underlying the cartilage damage in KBD[30]. Furthermore, the MMPs (MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13)/TIMP1 ratio in cartilage increased in KBD and in the rat KBD model[31]. Excessive levels of ROS initiate cell death through the activation of PKC-βI[32]. Collagen is particularly vulnerable to oxidative damage, which impairs its mechanical properties[33]. In addition, cytokines play important roles in articular cartilage degeneration[34]. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) play pivotal roles in the pathophysiology of RA. Moreover, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) induces cell death in chondrocytes in a NO-and ROS-dependent manner[35]. It is known that proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β produced by chondrocytes play pivotal roles in the progression of tissue degenerative changes, in part by stimulating the production of reactive nitrogen and ROS in an autocrine andparacrine manner[36]. Such reactive intermediates are regarded as causal or contributing factors for these diseases[37-38]. Taken together, we postulate that in patients with KBD and in rat KBD models, pathological changes in the cartilage initiate the development of KBD-like processes. This pathological change results from alterations in oxidative stress, cytokine levels (IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6), and MMP pathways by T-2 toxin and Se deficiency and may result in progressive chondrocyte apoptosis and cell death and extracellular matrix degradation and destruction in the deep zone of the cartilage. Our speculation regarding this process is summarized in Figure 7.
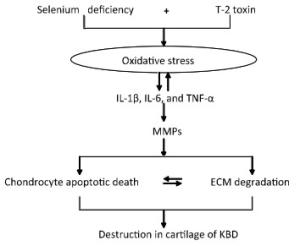
Figure 7. Schematic diagram of signal pathway of progressive chondrocyte apoptotic death in KBD and a rat Kashin-Beck disease model by employing T-2 toxin treatment under selenium deficient conditions.
The apoptosis pathway induced by T-2 toxin under Se-deficient conditions involves the upregulation of p53 and Bax and the downregulation of Bcl-2. p53, a highlyregulated transcription factor that induces cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in response to cellular stress such as DNA damage, plays an important role in mitochondrial membrane stability and promotes apoptosis[39-41]. Despite its central role in apoptosis, the mechanism of p53-mediated apoptosis after cellular stress remains unclear. A number of sites on p53 are phosphorylated after DNA damage, which increases the stability of p53 structure and enhances its activity[40, 42]. Moreover, evidence indicates that p53-mediated apoptosis transactivates target genes and directs signaling events, which may increase the expression of two sets of genes connected to stress signals[43-44], namely, p21/waf-1 and GADD45, which function in cell growth control[43], and Bax and Bcl-2, which are involved in apoptosis[45]. The T-2 toxin-induced activation of p53 affects the expression of its downstream effectors such as the Bcl-2 family of proteins[46]. It is well established that the Bcl-2 family proteins are central regulators of apoptosis; they act similar to checkpoints via which survival and death signals determine cell fate[45]. In our previous study, we reported that Bcl-2 and Bax levels were increased in KBD cartilage compared to those in normal cartilage[20]. In this study, we further demonstrated that chondrocyte apoptosis was present in the deep zone of the articular cartilage, which was associated with an increased expression of p53 and Bax and a decreased expression of Bcl-2 in rats fed with Se-deficient diet supplemented with T-2 toxin.
In conclusion, our data demonstrate the progression of chondrocyte apoptosis in the articular cartilage of rats fed with Se-deficient diet supplemented with T-2 toxin. Chondrocyte apoptosis is a key player in the vicious cycle of cartilage degradation, particularly in the cartilage of patients with KBD and in rats fed with T-2 toxin-supplemented Se-deficient diet. The results significantly advance our understanding of the pathogenesis of Kashin-Beck OA. Therefore, future development and use of intra-articular pharmacological inhibitors of apoptosis would be an interesting new treatment option for patients with KBD.








 Quick Links
Quick Links
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: