HTML
-
Inhalation of silica particles can result in the development of an inflammatory response and fibrosis in the lungs. Alveolar macrophages (AM) are the main target cells of silica dust. AM normally play a protective role in the lungs by clearing foreign materials[1-2]. Silicainduction leads to macrophage activation and phagocytosis, as well as the production of proinflammatory cytokines. Many studies have indicated that silica-induced activation of macrophages is associated with autophagy[3-4]. Silica exposure was shown to enhance autophagic activity in bone marrow-derived macrophages in vitro and in AM isolated from silica-exposed mice in vivo[5]. Autophagy, an alternative cell death pathway, is closely linked with apoptosis. Silica phagocytosis also causes apoptosis in AM[6-7]. There is substantial evidence that apoptosis of macrophages that take up silica particles plays a significant role in the etiology of silicosis[8-9]. AM apoptosis itself is an important event in silicosis and is associated with innate immune cell infiltration and increased collagen deposition[10]. However, the underlying regulation mechanism of silica-induced apoptosis remains unclear.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an intracellular organelle in which secretory and membrane proteins are assembled. The ER is also responsible for the quality control of protein folding and intracellular calcium homeostasis. Errors in protein folding in the ER lumen can lead to accumulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), which has been traditionally viewed as an adaptive mechanism and is also known as the unfolded protein response (UPR)[11]. Activation of the UPR pathway requires the activation of three sensor proteins: inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE-1), activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), and protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK)[12]. The UPR aims to remove the accumulated protein misfolding load, thus preventing further ERS. Prolonged ERS may activate downstream PERK-eukaryotic initiation factor 2/activating transcription factor 4/the CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP)-dependent pathway, which eventually cleaves caspase-3 to mediate cell apoptosis[13-15]. Although numerous situations can lead to protein misfolding in the ER, such as ischemia reperfusion injury, oxidative stress, calcium metabolism disorder, or simply increased secretary protein synthesis[16-18], silica-induced ERS in AM apoptosis is not well-understood.
In this study, we treated RAW264.7 cells with silica and explored the induction of apoptosis and ERS. Whether ERS mediates silica-induced apoptosis was determined.
-
Crystalline silica (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA, 0.1-10 µm in diameter) was prepared by washing with HCl to remove contaminating Fe2O3. Briefly, silica was boiled in 1 mol/L HCL, washed, and dried in an oven at 110 ℃ for 90 min. The particles were sterilized by heating at 180℃ for 6 h[19]. Before use, the particles were suspended in 1 mL of sterile saline and sonicated for 10 min.
-
RAW264.7 (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA, USA) cells were maintained in high-glucose DMEM (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) containing 10%-12% fetal bovine serum, penicillin (1000 IU/mL), and streptomycin (1000 IU/mL) overnight at 37 ℃ with 5% CO2. The cells were cultured in a 100-mL culture bottle until 60%-80% confluence, and then placed in dulbecco's modified eagle medium (DMEM) containing only 0.5% fetal bovine serum for 24 h before induction. Silica was prepared as 200 μg/mL samples in DMEM, and added to the cells.
-
Tunicamycin (Sigma), a reagent that strongly induces ERS by disrupting N-linked protein glycosylation[5], was prepared as a concentrated stock solution (10 mg/mL) in dimethyl sulfoxide. 4-Phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA, Sigma) was dissolved in DMEM at a concentration of 1000 mmol/L and diluted to the desired concentration directly in culture medium.
-
Cell viability was assayed using the MTT test. The cells were exposed to silica (200 μg/mL) for 0, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h. At the end of the experimental period, MTT (5 mg/mL) was added to the wells (20 μL/well). After 4-h incubation at 37 ℃, the media were removed and dimethyl sulfoxide was added (150 μL/well). The plates were shaken at room temperature for 10 min. The absorbance value of every well at a wavelength of 570 nm was quantified using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reader. Viable cells produced a dark blue formazan product, whereas no such staining occurred in dead cells.
-
The cells were incubated with silica (200 μg/mL) for the indicated periods. Next, the cells were fixed with 2% formaldehyde and 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 100 mmol/L phosphate buffer solution. Post-fixation was conducted with 1.0% osmium tetroxide in cacodylate buffer (pH 7.2), 0.8% potassium ferricyanide, and 5 mmol/L CaCl2, and then the cells were washed in 0.1 mol/L cacodylate buffer (pH 7.2). The cells were dehydrated in an acetone series and embedded in Spurr's resin. Thin sections (60-70 nm) were collected on 300 mesh copper grids, counterstained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and finally observed with an H500 Transmission Electron Microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan).
-
Briefly, total cellular RNA was prepared using Trizol reagent according to the manufacturer instructions (TaKaRa, Shiga, Japan). Total RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using a random primer (TaKaRa). The forward primer for PCR amplification of BiP mRNA was 5'-GAACACTG TGGTACCCACCAAGAA-3' and the reverse primer was 5'-TCCAGTCAGATCAAATGTACCCAGA-3'. The forward primer of CHOP was 5'-AATAACAGCCGGAACC TGAGGA-3' and the reverse primer was 5'-ACTCAG CTGCCATGACTGCAC-3'. For real-time PCR analysis, the reaction mixture containing cDNA template, primers, and SYBR Green premix (TaKaRa) was amplified in the ABI 7500 Fast Real-time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Fold-changes in mRNA levels were determined after normalization to the RNA levels of the internal control, β-actin.
-
The cells were incubated with silica (200 µg/mL) for different times. After treatment for the indicated times, the cells were harvested and total protein was extracted. Equal amounts of cell proteins, quantified with a BCA protein assay kit (Pierce Biootechnology, Rockford, IL, USA) were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat milk for 2 h and then incubated with various antibodies for 18 h at room temperature. After incubation with the secondary antibody at room temperature for 2 h, immunoreactive bands were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence reactions. The rabbit polyclonal anti-GRP78/BiP, anti-CHOP, and anti-caspase-3 antibodies were obtained from Cell Signaling (Danvers, MA, USA), and anti-β-actin was from Proteintech (USA).
-
4, 6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, KeyGEN Biotech, Nanjing, China), a DNA-specific dye, was used to detect apoptosis. Cultured cells were mixed with 500 µL DAPI for 30 min at room temperature. The excitation wavelength was 340 nm and emission fluorescence was detected with a 380-nm filter. Morphological changes of the cells were observed under the a fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
-
Analysis of apoptosis was performed with a Annexin-V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Samples from different groups were collected by trypsinization and washed twice with cold phosphate-buffered saline. Analyses were performed on a Cytomics FC500 (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA). Cells were resuspended in 400 μL Annexin-V binding buffer, mixed with 5 μL Annexin-V-FITC, incubated at 2-8 ℃ for 15 min, and then mixed with 10 μL propidium iodide followed by incubation at 2-8 ℃ for 5 min in the dark.
-
All experiments were performed at least three times. A P value < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance and determined by one-way analysis of variance. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
Preparation of Crystalline Silica
Cell Culture
Reagents
MTT Assay
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Real-time PCR
Western Blot Analysis
DAPI Staining
Flow Cytometry Analysis
Statistics Analysis
-
To detect the effects of silica on the cell viability of RAW264.7 cells, the cells were incubated with silica (200 μg/mL) for 0, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h. After incubation, cell viability was evaluated using an MTT assay. The absorbance values derived from control or silica-exposed cells were compared. As shown in Table 1, silica decreased cell viability.
Time/OD Value (h) Control 200 μg/mL Silica Group 0 0.265 ± 0.041 0.265 ± 0.041 6 0.467 ± 0.050 0.275 ± 0.013* 12 0.594 ± 0.027 0.343 ± 0.032* 24 0.676 ± 0.016 0.431 ± 0.033* 48 0.865 ± 0.015 0.582 ± 0.029* Note.*: P < 0.05, compared with control. Table 1. Effect of Silica (200 μg/mL) on Cell Viability of RAW264.7 Cells
-
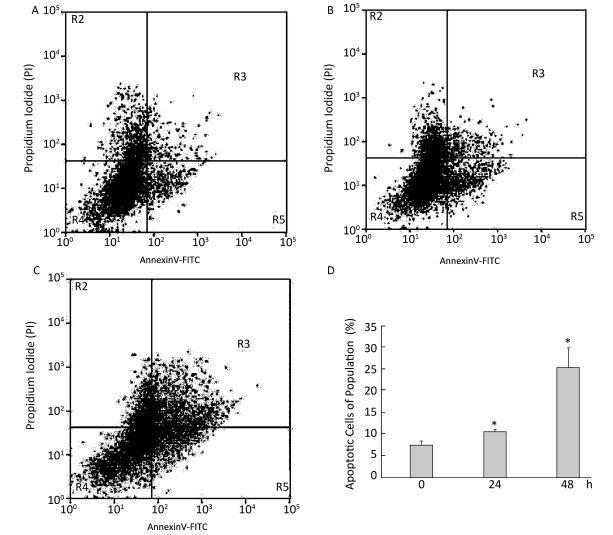
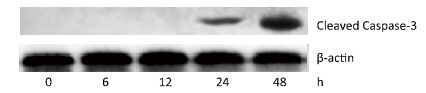
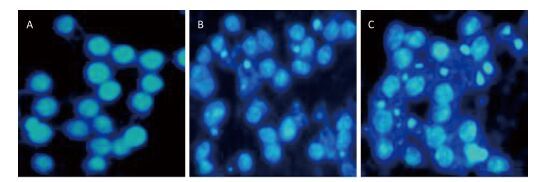
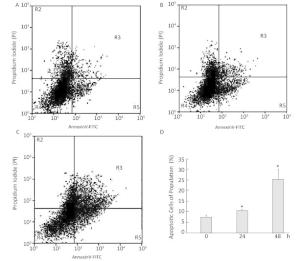
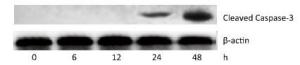
To investigate the effect of silica on the apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells, we detected apoptotic cells by fluorescent microscopy after DAPI staining. Silica induced prominent nuclear changes in treated cells (Figure 1). The nuclei were round, intact, and uniformly stained in control cells. However, at 24 and 48 h, silica exposure induced nuclear condensation, resulting in smaller nuclei that displayed membrane blebbing and fragmentation as the cells died. Nuclear changes were not significant at 6 and 12 h (data not shown). Next, to quantify silica-induced apoptosis, we performed flow cytometry. As shown in Figure 2, apoptotic cells were increased time-dependently by silica exposure. Furthermore, the level of cleaved caspase-3, which induces apoptosis, was detected in silica-treated cells. The expression of caspase-3 increased at 24 h and peaked at 48 h after silica exposure (Figure 3).
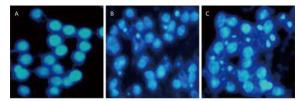
Figure 1. Silica treatment induced nuclear changes in RAW264.7 cells. Cells were treated with silica (200 μg/mL) for 0 h (A), 24 h (B), and 48 h (C) (magnification × 400). Morphological changes of cells nuclei were observed by DAPI staining under a fluorescence microscope.
-
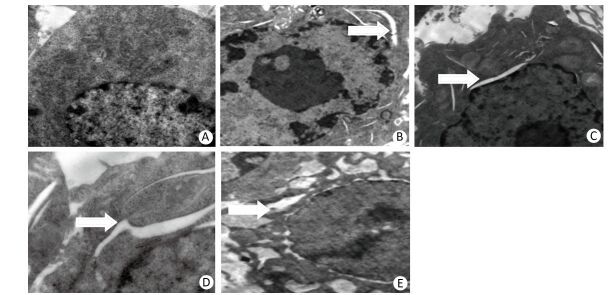
We performed transmission electron microscopy to observe the endoplasmic reticulum of silica-induced RAW264.7 cells. ER expansion was observed at 6 h after silica treatment and the extent of ER expansion increased gradually in a time-dependent manner in silica-treated cells (Figure 4).
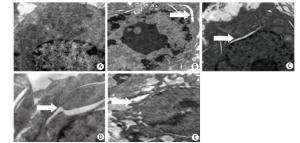
Figure 4. Silica treatment induced endoplasmic reticulum expansion of RAW264.7 cells. Cells were treated with silica (200 μg/mL) for 0 h (A), 6 h (B), 12 h (C), 24 h (D), and 48 h (E). Morphological changes of the endoplasmic reticulum were observed by transmission electron microscopy (magnification × 10, 000). White arrows show expanded endoplasmic reticulum.
-
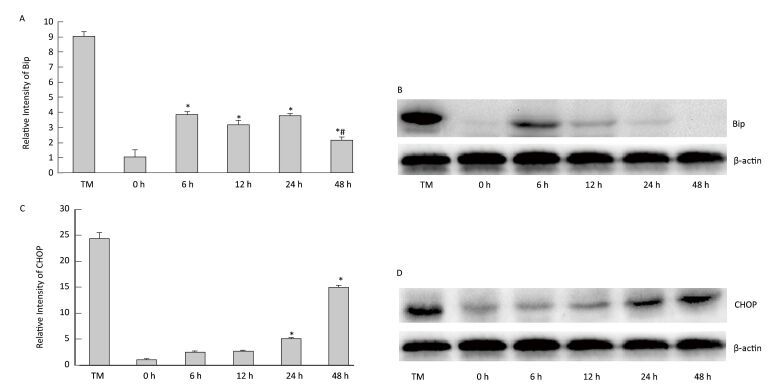
To determine the effect of silica on ERS, we examined the expression of ER stress markers GRP78/BiP and CHOP. As shown inFigure 5, silica caused a notable increase in the expression of Bip mRNA and protein. Maximum induction was observed at 6 h. Additionally, silica induced CHOP expression, which was increased in a time-dependent manner (Figure 5).
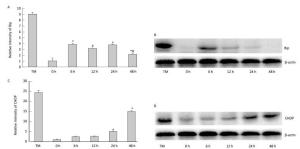
Figure 5. Silica treatment induced endoplasmic reticulum stress of RAW264.7 cells. Cells were treated with silica (200 μg/mL) for 0, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h. The expression of BiP and CHOP mRNA was determined by real-time PCR (A, C); *: P < 0.05, compared with 0 h group, #: P < 0.05, compared with 24 h group. The expression of BiP and CHOP proteins was determined by Western blotting (B, D).
-
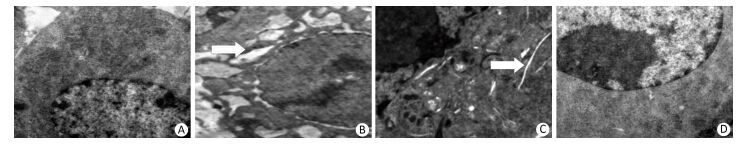
To identify the role of ERS in silica-induced apoptosis in RAW264.7 cells, we selected 4-PBA as an ERS inhibitor. First, we detected the effect of 4-PBA on endoplasmic reticulum expansion. The results showed that 4-PBA inhibited silica-induced endoplasmic reticulum expansion (Figure 6).
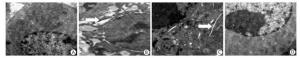
Figure 6. 4-PBA inhibited silica-induced endoplasmic reticulum expansion of RAW264.7 cells. Cells were pre-incubated with 20 μmol/L 4-PBA for 1 h and then stimulated with silica (200 μg/mL) for 48 h. Morphological changes of the endoplasmic reticulum were observed by transmission electron microscopy (magnification × 10, 000). White arrows show expanded endoplasmic reticulum. (A) without silica and 4-PBA group, (B) silica group, (C) silica and 4-PBA group, (D) 4-PBA group.
-
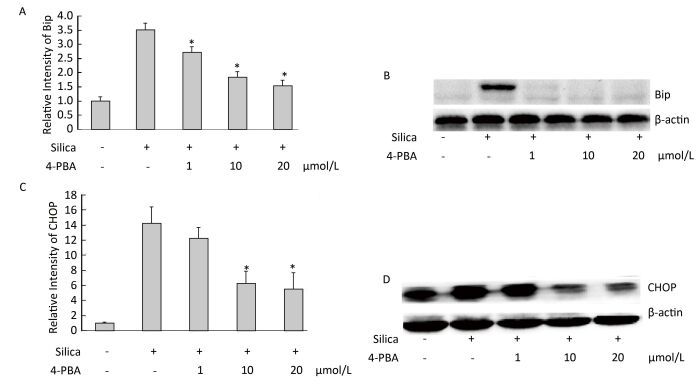
Next, we examined the effect of 4-PBA on the expression of ER stress markers BiP and CHOP in silica-stimulated cells. The results showed that 4-PBA (1, 10, 20 μmol/L) inhibited silica-induced mRNA and protein expression of Bip (Figure 7). In addition, pretreatment with 4-PBA (10, 20 μmol/L) decreased the mRNA and protein expression of CHOP (Figure 7).
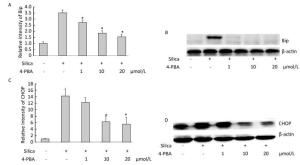
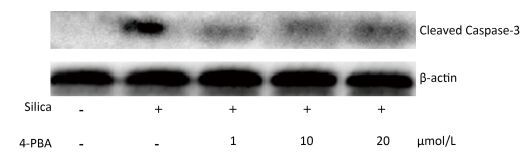
Figure 7. 4-PBA inhibited silica-induced ERS of RAW264.7 cells. Cells were pre-incubated with 1, 10, and 20 μmol/L 4-PBA for 1 h and then stimulated with silica (200 μg/mL) for the indicated times. Expression of Bip and CHOP mRNA was determined by real-time PCR (A, C); Expression of Bip and CHOP proteins was determined by Western blotting (B, D). *: P < 0.05, compared with silica-stimulated group.
-
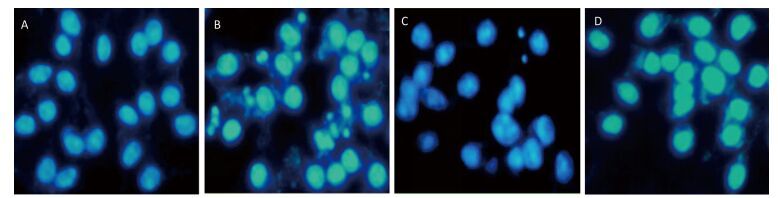
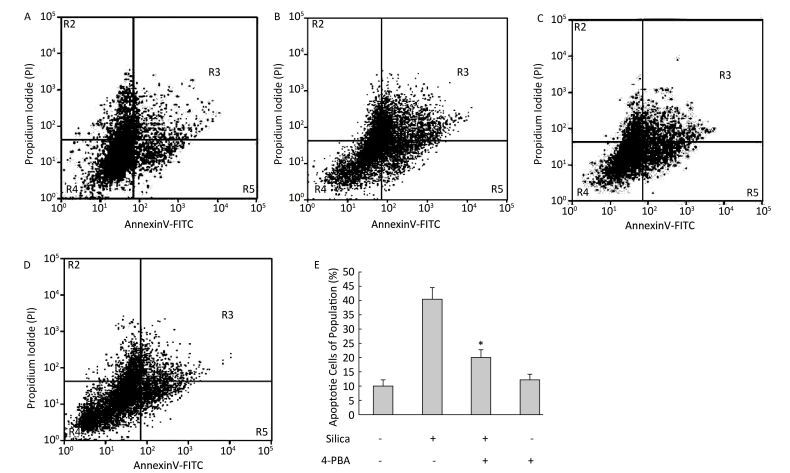
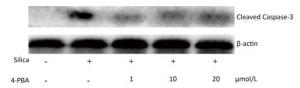
Next, we investigated the effect of 4-PBA on apoptosis induction by silica. DAPI staining showed that pretreatment with 4-PBA attenuated nuclear condensation in silica-stimulated cells (Figure 8). In addition, flow cytometry analysis demonstrated that 4-PBA prevented silica-induced apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells (Figure 9). The expression of cleaved caspase-3 was also decreased by 4-PBA in silica-treated cells (Figure 10).
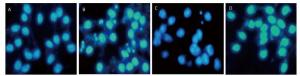
Figure 8. 4-PBA attenuated nuclear condensation in silica-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Cells were pre-incubated with or without 10 μmol/L 4-PBA for 1 h and then stimulated with or without silica (200 μg/mL) for 48 h. Morphological changes of cell nuclei were observed by DAPI staining under a fluorescence microscope (magnification × 400). (A) without silica and 4-PBA group, (B) silica group, (C) silica and 4-PBA group, (D) 4-PBA group.
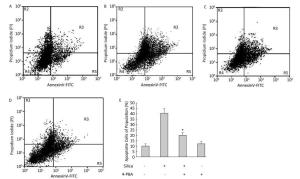
Figure 9. 4-PBA inhibited silica-induced apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells. Cells were pre-incubated with or without 10 μmol/L 4-PBA for 1 h and then stimulated with or without silica (200 μg/mL) for 48 h. Apoptotic cells were observed by flow cytometry. (A) without silica and 4-PBA group, (B) silica group, (C) silica and 4-PBA group, (D) 4-PBA group, (E) all histograms show the apoptotic cell populations (%), *: P < 0.05, compared with silica-stimulated group.
Silica Treatment Decreases Cell Viability of RAW264.7 Cells
Silica Treatment Induces Apoptosis of RAW264.7 Cells
Silica Treatment Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Expansion in RAW264.7 Cells
Silica Treatment Induces ERS in RAW264.7 Cells
4-PBA Inhibits Silica-induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Expansion of RAW264.7 Cells
4-PBA Inhibits Silica-induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress of RAW264.7 Cells
4-PBA Inhibits Silica-induced Apoptosis of RAW264.7 Cells
-
Silicosis is a progressive, disabling, and fatal disease that eventually causes pulmonary fibrosis. Once silicon particles arrive inside the alveoli, they are taken up by AM, which play an important role in the recognition, uptake, and clearance of particles from the lung[20].Phagocytosis of silica results in phagosome formation, lysosomal membrane permeabilization, and release of cathepsins into the cytosol, contributing to inflammasome activation and apoptosis signaling[21-22]. RAW264.7 cells, derived from a mouse peritoneal macrophage cell line, have the same characteristics as AM[23]. In the present study, silica induced the apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells. The results agree with those of previous reports[2, 8]. However, the specific mechanisms of silica-induced apoptosis have not been elucidated.
ER is the major site of protein synthesis, protein folding, and secretion as well as calcium storage, which are required for normal cellular function. Recent studies suggested that ERS pathways mediate apoptosis in lung diseases induced by particles and pathogens[24-25]. Therefore, we evaluated the influence of silica on ERS in RAW264.7 cells. Electron microscopy analysis revealed a massive expansion of the ER in RAW264.7 cells after silica treatment.
Next, we examined the marker molecules of ERS in silica-treated RAW264.7 cells. Any changes in homeostasis of the ER can activate a conserved signal transduction pathway, known as the UPR or ERS response. IRE1, PERK, and ATF6 are the three transmembrane proteins that transmit the unfolded protein signal across the ER. BiP and CHOP are used as UPR markers for ERS under pathological conditions. BiP is sequestered by binding to unfolded or misfolded proteins, leading to the release from IRE1/PERK/ATF6 and activation of ER-stress sensors[12], and is currently considered a marker of ERS because of its key role in regulation of ERS sensor activation and ERS initiation[26-27]. CHOP appears to be a crucial proapoptotic factor found at the convergence point in the regulatory network used to initiate apoptosis caused by persistent ERS[28-30]. Therefore, in this study, the expression of BiP and CHOP in silica-treated RAW264.7 cells was studied. We found that silica upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of BiP and CHOP. These results suggest that silica treatment induced ERS in RAW264.7 cells.
4-PBA is commonly used to alleviate ER stress and strongly inhibits activation of the IRE1 and ATF6 pathways and downstream pathogenic targets, including nuclear factor-κB and Akt in ERS-exposed cells[13]. 4-BPA can interact with hydrophobic domains of misfolded proteins and prevent their aggregation, providing the opportunity for the protein to fold into the proper conformation[31-32]. We used 4-PBA as an ERS inhibitor to investigate the correlation between ERS and apoptosis in RAW264.7 cells induced by silica. We found that 4-PBA inhibited silica-induced endoplasmic reticulum expansion and BiP and CHOP expression in RAW264.7 cells. Moreover, 4-PBA attenuated nuclear condensation, reduced apoptotic cells, and decreased the expression of activated caspase-3 in silica-stimulated cells. In addition, following preteatment with 4-PBA, the viability of silica-stimulated cells increased (data not shown). Thus, ERS may regulate silica-induced apoptosis in RAW264.7 cells.
This is an advanced study to show that ERS plays an important role in silica-induced apoptosis in AM. These findings provide insight into the molecular mechanisms involved in silica-induced pulmonary disease and the understanding and possible prevention of silicosis.
-
We are most grateful to the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions for this paper. We would like to extend our sincere thanks to all colleagues and participates involved in this work.
-
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.







 Quick Links
Quick Links
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: