-
Bitter melon (Momordica Charania L.), a member of the Cucurbitaceae family, is widely distributed across tropical and subtropical regions. Saponin, an important functional component of bitter melon, has been proven to exert hypoglycemic effects similarly to insulin, and also possesses lipid-lowering properties inhibiting preadipocyte differentiation and fat synthesis[1]. As bitter melon saponin extract (BMSE) consists of compounds assembled in various diverse structures, it is necessary to conduct systematic and comprehensive research to screen its active ingredients and targets. In this study, we aimed to rapidly assess saponin compounds possessing lipid-lowering activity by combining LC/Q-TOF-MS/MS and network pharmacology. The bioactivity of screened saponins needs to be further verified in vivo, and the mechanisms underlying these behaviours must be assessed.
Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), a form of nematode worms, is a species of eukaryotic animal with a short life cycle, and this species has attracted extensive attention for providing an intuitive way to evaluate fat accumulation, due to possessing homologous pathways of lipid metabolism with those of mammals. Accordingly, the intestinal tract of C. elegans is responsible for lipid uptake, synthesis, storage and mobilization. Oil Red O (ORO) staining and a triglyceride (TG) assay are typically applied to assess the influence of active compounds on lipid accumulation. One of our previous studies has shown that BMSE could significantly relieve fat deposition, both in C. elegans and in HepG2, possibly through lipophagy[2]. Lipid droplets (LDs) are multifunctional organelles present in eukaryotic cells that store triglycerides, cholesterol esters and other neutral lipids. The process of LDs being encapsulated by the autophagosome and hydrolyzed by lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) in the autolysosome is recognized as lipophagy. During lipophagy, adenosine 5‘-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) connect the signaling axes of the autophagosome, Transcription Factor EB (TFEB) and Forkhead Box O1 (FoxO1) transcription factors, lysosome and autophagy associated proteins, where TFEB and FoxO1 directly induce the expression of LAL and promote β-oxidation. Whether the compounds we screened in BMSE can also decrease the accumulation of fat via lipophagy requires further investigation.
In the present study, we tried to screen potential active compounds with anti-obesity effects present in BMSE, through LC/Q-TOF-MS/MS and network pharmacology. Furthermore, we estimated the lipid-lowering effects of active compounds in C. elegans, and illustrated its potential mechanisms from the perspective of lipophagy, based on the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis.
BMSE was extracted from bitter melon juice using 80% ethanol (EtOH) and purified through use of AB-8 macroporous resin. The resulting concentration of BMSE was 9.26 mg/mL. The composition analysis of BMSE by LC/Q-TOF-MS/MS was followed by the determination of anti-obesity active components of saponins and their molecular mechanisms, using network pharmacology. Then, experimental studies were conducted in obese C. elegans, with the groups being divided into control, model, BMSE (25, 50, and 100 μg/mL), Momordicine I (25, 50, and 100 μg/mL), and Momordicine II (25, 50, and 100 μg/mL). We conducted growth index analysis, ORO staining, and TG assay to determine the lipid-reduction capacity of BMSE and its potential active ingredients in obese C. elegans. Furthermore, Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) fluorescent staining was applied to detect the formation of autophagosomes in C. elegans. The mRNA expression levels of daf-16/FoxO1, hlh-30/TFEB and lipophagy related genes of C. elegans were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The primers used in this study are laid out in Supplementary Table S1 (available in www.besjournal.com). All data were analyzed as means ± SEM and were analyzed using the statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS 26.0) IBM Statistics 20 software (SPSS 26.0, Inc.). A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using Tukey’s range test was performed to identify the differences between independent sample groups. GraphPad prism 9.5 was used for graphing. Different letters present in the columns indicate statistically significant (P < 0.05) values.
Genes Forward sequences (5’–3’) Reverse sequence (5’–3’) daf-16 CCAGACGGAAGGCTTAAACT ATTCGCATGAAACGAGAATG hlh-30 ATTCGCATGAAACGAGAATG AGAACGCGATGCGTGGTGGG aak-2 TCTTCCGCCATCCGCATATC CCTCTTCATCGGGTCTACGC lgg-1 AACAACTTTGAGAAGCGTCGTGCC ATCTTCTGGACGAAGTTGGATGCG lgg-2 CTGCAAATTCCTAGTACCCGAG CATAGAATTTGACACCATTGAGC lipl-2 AATACGAGTCAAATCATTGAA GTAACACTCGTTTTTCCATAA lipl-3 ATGGGCAGGCAAATCCACCA AGTTGTTCTGCGCAATTATA atg-18 AAATGGACATCGGCTCTTTG TGATAGCATCGAACCATCCA act-1 TCGGTATGGGACAGAAGGAC CATCCCAGTTGGTGACGATA Table S1. Primer sequences for the genes involved in lipid metabolism and lipophagy in C. elegans
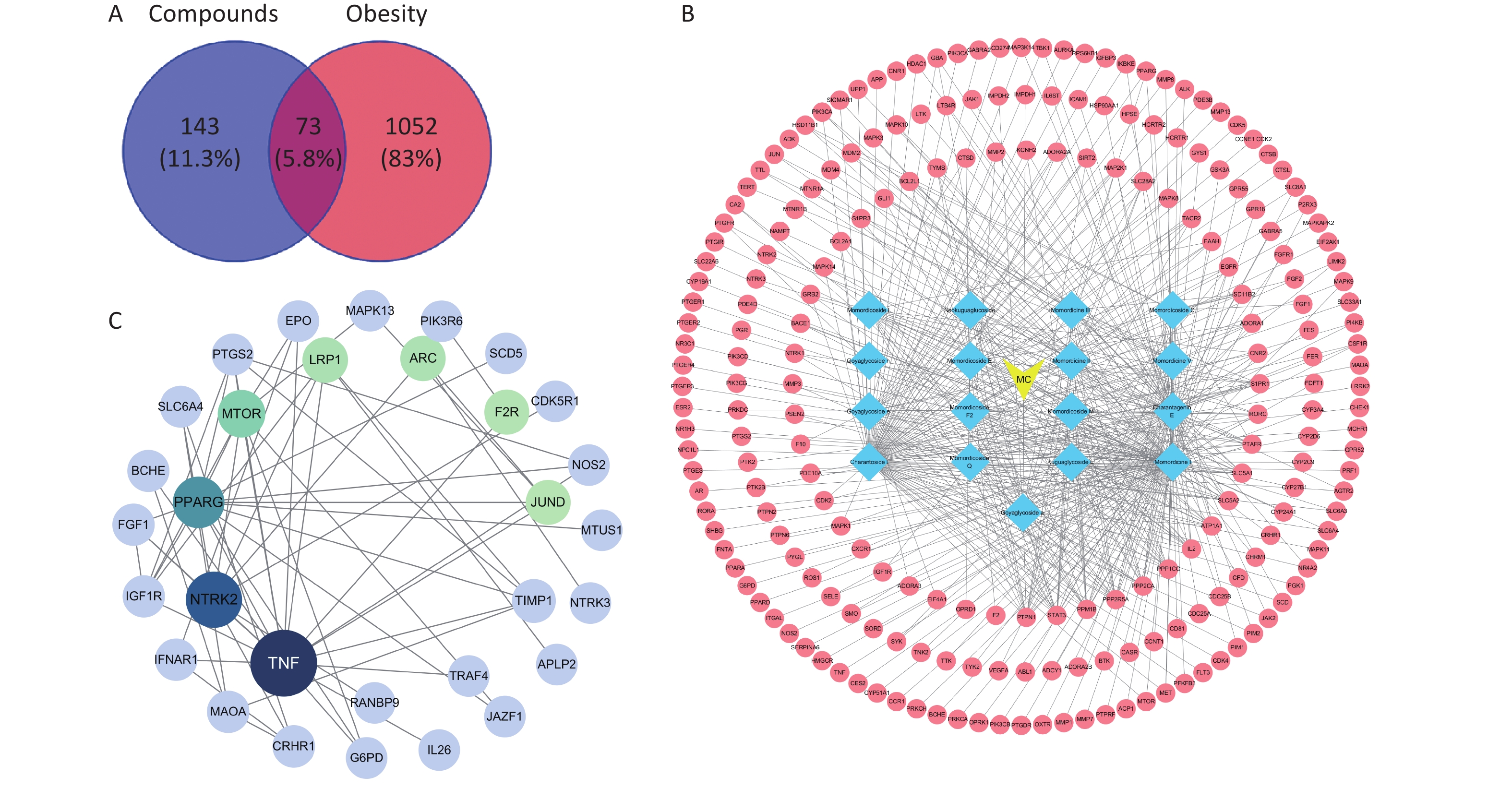
Supplementary Table S2 (available in www.besjournal.com) shows the compounds identified via LC/Q-TOF-MS/MS. To screen for saponins with good bioavailability, 17 saponins were filtrated based on their Gastrointestinal absorption rate, including Momordicoside M, Momordicine II, Momordicine V, Momordicoside F2, and Momordicine I. A total of 73 common potential targets were identified by Venn analysis, out of 216 screened component-related targets (Supplementary Table S3, available in www.besjournal.com) and 1,125 obesity-related targets. In a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network, TNF, NTRK2, PPARG, MTOR, LRP1, ARC, F2R, JUND, TIMP1, CRHR1 were the top ten targets with high degree values (Supplementary Figure S1, Supplementary Tables S4–S5, available in www.besjournal.com). A recent report has shown that caffeine and quercetin could activate autophagy by inhibiting the mTOR signaling pathway, thereby reducing fat deposition in mice with obesity induced by high-fat diet[3]. Thus, mTOR were considered highly likely to play an important role in the anti-obesity benefit of BMSE.
RT
(min)Molecular
formulaKey ion masses Adduct and fragmental ion exact masses [M − X]+ Tentatively identified compounds Relative content 1 5.52 C42H70O14 798.4766 [M+H]+ 821.4766 [M+Na]+
641.4116, 411.2465, 184.0775Kuguaglycoside E 0.25% 2 6.35 C42H68O14 796.4609 [M+H]+ 797.4732 [M+Na]+
639.3987, 455.3525, 439.3632, 391.3394Momordicoside M 2.93% 3 6.48 C42H70O15 814.4715 [M+H]+ 815.4846 [M+Na]+
455.3525, 425.2549, 353.2878, 335.2784Goyaglycoside h 1.44% 4 7.79 C36H60O10 652.4187 [M+H]+ 653.4296 [M+Na]+
349.1982, 335.2784, 187.1511Momordicoside Q 4.59% 5 8.48 C43H70O15 826.4715 [M+H]+ 849.4661 [M+Na]+
639.3898, 437.3442, 391.3394Momordicoside O 0.25% 6 8.6 C42H68O13 780.4660 [M+H]+ 781.4775 [M+Na]+
657.4031, 623.3918, 439.3558, 391.3394Goyaglycoside e 1.51% 7 9.04 C42H66O14 794.4453 [M+H]+ 795.4578 [M+Na]+
674.4048, 639.3898, 455.3525, 419.3315Neokuguaglucoside 1.40% 8 9.38 C43H70O14 810.4766 [M+H]+ 811.4872 [M+Na]+
657.4031, 439.3558, 421.3519, 391.3394Goyaglycoside g 5.18% 9 9.52 C37H60O12 696.4085 [M-H]- 695.3966 [M-H]-
513.3551, 314.9821, 146.9631Momordicoside E 7.54% 10 9.95 C37H58O8 630.4132 [M-H]- 675.4071 [M+HCOO]-
633.4081, 405.2952, 352.9889Charantoside I 1.15% 11 10.35 C36H56O10 648.3874 [M-H]- 647.3787 [M-H]-
326.9796, 264.9877, 240.9861Momordicine III 0.12% 12 10.38 C36H54O8 614.3819 [M+H]+ 615.3940 [M+H]+
477.3391, 419.3315, 3762607Charantosides Ⅶ 0.18% 13 10.4 C36H58O9 634.4081 [M+H]+ 657.4008 [M+Na]+
639.3898, 437.3442, 419.3315, 409.3449Momordicine II 22.02% 14 10.8 C39H60O12 720.4085 [M+H]+ 743.4030 [M+Na]+
657.4031, 477.3391, 391.3394Momordicine V 0.67% 15 10.83 C36H60O8 620.4288 [M+H]+ 621.4400 [M+Na]+
477.3391, 419.3315, 391.33943β,7β23-Trihydroxycucurbita-5,24-diene-7-O-β-D-glucoside 0.46% 16 11.47 C36H58O8 618.4132 [M+H]+ 619.4238 [M+Na]+
439.3558, 421.3519, 391.3394, 357.2881Momordicoside F2 6.67% 17 11.69 C30H48O3 456.3604 [M+H]+ 457.3700 [M+H]+
439.3558, 391.3394, 309.2590, 213.16943β-Hydroxy-7β,25-dimethoxy-cucurbita-5,23-dien-19-al 0.64% 18 11.69 C30H46O2 438.3498 [M+H]+ 439.3595 [M+H]+
421.3519, 409.3520, 391.3394, 357.27485β,19-Epoxy-cucurbita-6,22E,24-trien-3β-ol 1.59% 19 12.2 C30H44O2 436.3341 [M+H]+ 437.3436 [M+H]+
419.3387, 391.3394, 409.3520, 401.32383β-Hydroxycucurbita-5(10),6,22(E),24-tetraen-19-al 6.88% 20 12.2 C30H48O4 472.3553 [M+H]+ 495.3475 [M+Na]+
477.3391, 437.3442, 419.3315, 391.3394Momordicine I 2.76% 21 12.35 C37H60O9 648.4237 [M-H]- 693.4205 [M+HCOO]-
376.9863, 264.9877, 183.0082, 146.9631Goyaglycoside a 0.29% 22 12.44 C36H56O8 616.3975 [M+H]+ 617.4081 [M+Na]+
599.4000, 477.3391, 391.3394, 321.2765Momordicoside C 6.80% 23 13.14 C38H62O9 662.4394 [M+H]+ 685.4324 [M+Na]+
639.3987, 419.3387, 391.3464, 309.2652Momordicosides U 1.51% 24 13.34 C37H58O9 646.4081 [M+H]+ 669.3997 [M+Na]+
637.3712, 581.3309, 495.3455Karavilosides Ⅵ 0.66% 25 13.69 C38H64O8 648.4601 [M+H]+ 671.4531 [M+Na]+
405.3599, 391.3464, 349.2969Karavilosides Ⅰ 2.11% 26 15.75 C38H62O8 646.4445 [M+H]+ 647.4562 [M+Na]+
605.4295, 561.4016, 495.3455, 391.3394Charantosides Ⅴ 0.22% 27 17.27 C30H42O4 466.3083 [M-H]- 511.3030 [M+HCOO]-
326.986, 255.2324, 183.0129, 146.9631, 100.9326Kuguacins O 0.25% 28 19.11 C32H52O4 500.3866 [M+H]+ 523.3769 [M+Na]+
487.3723, 443.3338, 391.3394, 368.43045β,19-Epoxy-19-methoxy-cucurbita-6,23,25-trien-3-ol 1.41% 29 20.86 C33H54O4 514.4022 [M+H]+ 537.3960 [M+Na]+
522.6019, 495.2672, 439.20103β-Acetoxy-7β-methoxy-cucurbita-5,23(E)-dien-25-ol 18.49% Table S2. Identification of chemical constituents of BMSE by LC/Q-TOF-MS/MS
Compounds Targets 1 Kuguaglycoside E PTAFR, PTPN1, IL2, STAT3, PPP2CA, ATP1A1, PPP1CC, PPM1B, PPP2R5A, KCNH2, CXCR1, BACE1, SLC5A2, SLC5A1 2 Momordicoside M PTAFR, PPM1B, PPP1CC, PPP2CA, PPP2R5A, PTPN1, STAT3, RORC, ATP1A1, IL2 3 Goyaglycoside h STAT3 4 Momordicoside Q STAT3, PTAFR, PTPN1, ATP1A1, PPM1B, PPP2R5A, FAAH, CNR2, PPP1CC, PPP2CA, IL2, SLC5A2, SLC5A1, TACR2, IGF1R, ADORA1, S1PR1, NTRK1, MMP3, MMP2, CTSD, PSEN2, PSENEN, NCSTN, APH1A, PSEN1, APH1B 5 Goyaglycoside e STAT3, PTPN1, PPM1B, PPP2R5A, MAPK8, SLC28A2, SLC5A2, SLC5A1, ADORA3, MAP2K1, SIRT2, PPP2CA, TACR2, ADORA2A, TYMS, EIF4A1, ADORA1 6 Neokuguaglucoside PPM1B, PPP1CC, PPP2R5A, PTPN1, PTAFR, PPP2CA, STAT3, IL2, RORC, ATP1A1, OPRD1 7 Momordicoside E STAT3, PTPN1, IL2, HSD11B2, F2, BCL2L1, SLC5A2, SLC5A1, GLI1, F10, ADORA1, EGFR, TYMS, S1PR3, S1PR1, ADORA2A 8 Charantoside I PTPN1, PPM1B, PPP2R5A, MAPK8, STAT3, SIRT2, BCL2A1, PDE10A, CDK2, MAPK1, MAPK14, GRB2, TACR2, MTOR, MET, SLC5A2, ATP1A1, PFKFB3, FLT3, CDK4, RORC, PPP1CC, PPP2CA, PIM1, MAP2K1, PIM2, JAK2, S1PR3, S1PR1, SCD, PGK1, NR4A2, MAPK11, SLC6A4, SLC6A3, ADORA2A, ADORA1, AGTR2, PRF1, EGFR, GPR52, MCHR1, CHEK1, LRRK2, AOA, CSF1R, PI4KB, SLC33A1, MAPK9, SLC5A1, LIMK2, EIF2AK1, MAPKAPK2, P2RX3, SLC8A1, CTSL, CTSB, CCNE1 CDK2, CDK5, MMP13, PDE3B, MMP2, ALK, MMP8, PPARG, IKBKE, IGFBP3, RPS6KB1, AURKA, TBK1, MAP3K14, KCNH2, CD274, GABRA2, GABRB3, GABRG2, PIK3CA, PIK3R1, GBA, HDAC1, CNR1, APP, UPP1, SIGMAR1, PIK3CA 9 Momordicine III HSD11B2, IL2, TPN1, PM1B, PPP1CC, PPP2CA, PP2R5A, HSD11B1, SLC28A2, SLC5A2, SLC5A1, STAT3, ADK, GLI1, BCL2L1, S1PR1, PPARG 10 Momordicine II PTPN1, PPM1B, PPP1CC, PPP2CA, PPP2R5A, BCL2L1, HSD11B2, S1PR1, SLC28A2, STAT3, JUN, SLC5A2, SLC5A1, TTL 11 Momordicine V PPM1B, PPP1CC, PPP2R5A, JUN, PTPN1, PPP2CA, TTL, TERT, GLI1 12 Momordicoside F2 STAT3, ATP1A1, PTPN1, IL2, PTAFR, PPM1B, PPP1CC, PPP2R5A, CNR2, FAAH, GRB2, RORC, CTSD, SLC5A2, SLC5A1, CA2, S1PR1 13 Momordicine I PTGFR, PTGIR, SLC22A6, CYP19A1, PTGER1, PTGER2, NR3C1, PTGER4, PTGER3, ESR2, R1H3, PTPN1, NPC1L1, PPARG, PTGES, AR, RORC, RORA, SHBG, FNTA, PPARA, G6PD, PPARD, SLC6A4, ITGAL, HSD11B1, NOS2, SERPINA6, HMGCR, TNF, CES2, CYP51A1, CCR1, PRKCH, BACE1, BCHE, PRKCA, OPRK1, PIK3CB, PTGDR, MAPK8, OXTR, MMP3, MMP1, MMP2, MMP7, MAPK14, PTPRF, ACP1, PGR, GPR55, GPR18, CNR2, PIK3CD, PIK3CG, PIK3CA, CYP24A1, MAPK3, SIGMAR1, PDE10A, PSEN2, CYP27B1, PTPN6, PTGS2, IL6ST, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, CYP3A4, HSD11B2, PYGL, MAPK10, MAPK9, PTPN2, P2RX3, CDC25B, MTNR1A, MTNR1B, F10, MET, MMP8, MDM2, CASR, EGFR, HCRTR2, HCRTR1, SORD, GSK3A, FDFT1, CFD, MDM4, PDE4D, CRHR1, CD81, LTB4R, SLC6A3, CDC25A, ADCY1, SMO, HSP90AA1 14 Goyaglycoside a STAT3, PPM1B, PPP2R5A, PTPN1, ATP1A1, CNR2, PPP2CA, SIRT2, EGFR, BCL2A1, SYK, MAP2K1, IMPDH1, IMPDH2, RORC, LIMK2, TYMS, PTAFR, GBA, TACR2, SLC28A2, CSF1R, PTGFR, IL2 15 Momordicoside C STAT3, IL2, PTAFR, PPM1B, PPP1CC, PPP2CA, PPP2R5A, HSD11B2, HSD11B1, VEGFA, FGF1FGF2, HPSE, ATP1A1, MDM2 16 Charantagenin E IL2, PTPN1, PTAFR, PPP1CC, PPP2CA, STAT3, PPM1B, PPP2R5A, S1PR3, S1PR1, ATP1A1, RORC, JAK2, ICAM1, SELE, SLC8A1, UPP1, FAAH, CNR2, PIM1, PIM2, MAPK14, IKBKE, TBK1, PRKDC, JAK1, TYK2, TTK, MAPK8, SLC5A2, SLC5A1, ADORA1, AGTR2, SIRT2, MAP3K14, MTOR, NR4A2, GABRA5, CSF1R, ABL1, CDK2, PIK3CA, MAPK1, EGFR, PI4KB, MAP2K1, BCL2A1, SCD, MAPK10, NAMPT, KCNH2, ADORA2A, ADORA2B, PTK2, SYK, HDAC1, BTK, PFKFB3, MET, GBA, FGFR1, GYS1, SMO, CCNT1, NTRK1, FER, ALK, TNK2, NTRK2, FES, PTK2B, ROS1, NTRK3, LTK 17 Momordicoside I STAT3, ATP1A1, PTPN1, IL2, PTAFR, PPM1B, PPP1CC, PPP2R5A, CNR2, FAAH, GRB2, RORC, CTSD, SLC5A2, SLC5A1, CA2, S1PR1 Table S3. Corresponding targets of active ingredients in BMSE
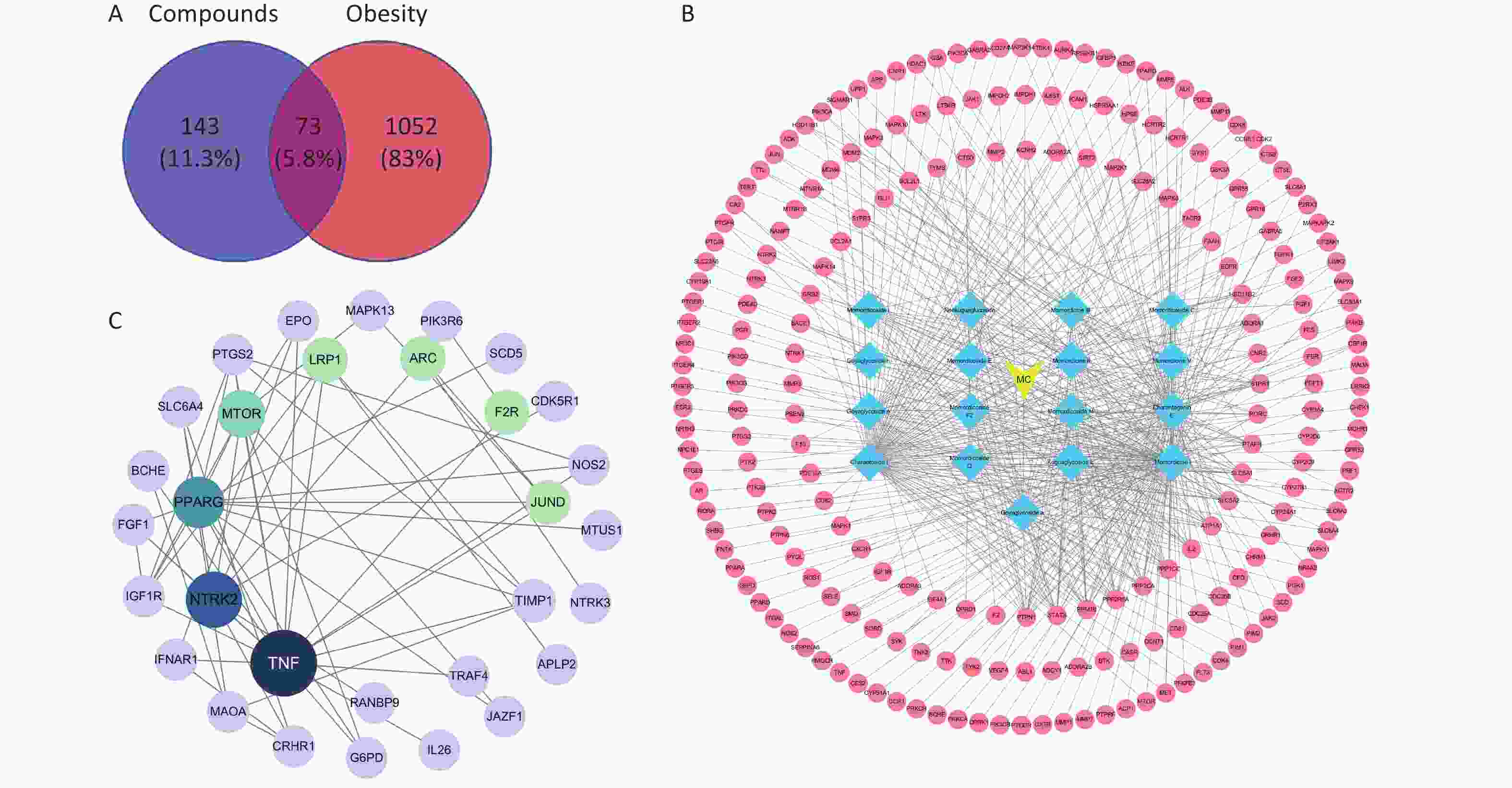
Figure S1. Network pharmacology was applied to screen the active saponins of bitter melon saponin extract (BMSE). (A) Venn diagram showing intersection of active saponins with obesity targets. (B) Diagram of bitter melon-active saponin-targets. (C) Diagram of protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of saponins for the treatment of obesity targets. MC, Momordica Charania.
Name Betweenness Degree Eccentricity Neighborhood connectivity Number of directed edges Radiality Stress MC 0.0775 17 2 28.06 17 0.7682 81058 Momordicoside I 0.0125 18 3 9.50 18 0.5558 28154 Charantagenin E 0.2841 75 3 3.89 75 0.6781 321464 Momordicoside C 0.0404 16 3 8.00 16 0.5515 34620 Goyaglycoside a 0.0405 25 3 6.88 25 0.5708 60992 Momordicine I 0.5609 101 3 1.79 101 0.7339 435226 Momordicoside F2 0.0125 18 3 9.50 18 0.5558 28154 Momordicine V 0.0171 10 3 9.20 10 0.5386 14494 Momordicine II 0.0167 15 3 9.53 15 0.5494 26186 Momordicine III 0.0233 18 3 8.89 18 0.5558 38228 Charantoside I 0.3458 83 3 3.46 83 0.6953 406470 Goyaglycoside e 0.0255 18 3 7.83 18 0.5558 31000 Momordicoside E 0.0243 17 3 7.06 17 0.5536 35178 Kuguaglycoside E 0.0144 15 3 10.33 15 0.5494 19582 Neokuguaglucoside 0.0103 12 3 11.50 12 0.5429 11902 Momordicoside Q 0.0295 23 3 8.22 23 0.5665 50976 Goyaglycoside h 0.0000 2 3 16.00 2 0.5215 154 Momordicoside M 0.0018 11 3 12.45 11 0.5408 6626 LTK 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 NTRK3 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 ROS1 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 PTK2B 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 FES 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 NTRK2 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 TNK2 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 FER 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 CCNT1 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 GYS1 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 FGFR1 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 BTK 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 PTK2 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 ADORA2B 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 NAMPT 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 ABL1 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 GABRA5 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 TTK 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 TYK2 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 JAK1 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 PRKDC 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 SELE 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 ICAM1 0.0000 1 4 75.00 1 0.4292 0 HPSE 0.0000 1 4 16.00 1 0.3026 0 FGF2 0.0000 1 4 16.00 1 0.3026 0 FGF1 0.0000 1 4 16.00 1 0.3026 0 VEGFA 0.0000 1 4 16.00 1 0.3026 0 IMPDH2 0.0000 1 4 25.00 1 0.3219 0 IMPDH1 0.0000 1 4 25.00 1 0.3219 0 SYK 0.0004 2 4 50.00 2 0.4464 764 HSP90AA1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 SMO 0.0099 2 4 88.00 2 0.6245 10986 ADCY1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CDC25A 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 LTB4R 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CD81 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CRHR1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PDE4D 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 MDM4 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CFD 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 FDFT1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 GSK3A 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 SORD 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 HCRTR1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 HCRTR2 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CASR 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 MDM2 0.0041 2 4 58.50 2 0.5129 2208 MTNR1B 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 MTNR1A 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CDC25B 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTPN2 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 MAPK10 0.0099 2 4 88.00 2 0.6245 10986 PYGL 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CYP3A4 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CYP2C9 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CYP2D6 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 IL6ST 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTGS2 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTPN6 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CYP27B1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 MAPK3 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CYP24A1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PIK3CG 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PIK3CD 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CHRM1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 GPR18 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 GPR55 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PGR 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 ACP1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTPRF 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 MMP7 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 MMP1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 OXTR 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTGDR 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PIK3CB 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 OPRK1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PRKCA 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 BCHE 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PRKCH 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CCR1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CYP51A1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CES2 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 TNF 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 HMGCR 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 SERPINA6 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 NOS2 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 ITGAL 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PPARD 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 G6PD 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PPARA 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 FNTA 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 SHBG 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 RORA 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 AR 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTGES 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 NPC1L1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 NR1H3 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 ESR2 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTGER3 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTGER4 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 NR3C1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTGER2 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTGER1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 CYP19A1 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 SLC22A6 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTGIR 0.0000 1 4 101.00 1 0.4850 0 PTGFR 0.0030 2 4 63.00 2 0.5279 3340 CA2 0.0000 2 4 18.00 2 0.3090 2 TERT 0.0000 1 4 10.00 1 0.2897 0 TTL 0.0000 2 4 12.50 2 0.3069 34 JUN 0.0000 2 4 12.50 2 0.3069 34 ADK 0.0000 1 4 18.00 1 0.3069 0 HSD11B1 0.0064 3 4 45.00 3 0.5300 4664 PIK3CA 0.0189 3 4 86.33 3 0.6910 24468 SIGMAR1 0.0081 2 4 92.00 2 0.6288 11014 UPP1 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 APP 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 CNR1 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 HDAC1 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 GBA 0.0017 3 4 61.00 3 0.5279 4266 PIK3CA 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 GABRA2 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 CD274 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 MAP3K14 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 TBK1 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 AURKA 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 RPS6KB1 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 IGFBP3 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 IKBKE 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 PPARG 0.0109 3 4 67.33 3 0.6416 14320 MMP8 0.0081 2 4 92.00 2 0.6288 11014 ALK 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 PDE3B 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 MMP13 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 CDK5 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 CCNE1 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 CTSB 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 CTSL 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 SLC8A1 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 P2RX3 0.0081 2 4 92.00 2 0.6288 11014 MAPKAPK2 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 EIF2AK1 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 LIMK2 0.0005 2 4 54.00 2 0.4678 1034 MAPK9 0.0081 2 4 92.00 2 0.6288 11014 SLC33A1 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 PI4KB 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 CSF1R 0.0017 3 4 61.00 3 0.5279 4266 MAOA 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 LRRK2 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 CHEK1 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 MCHR1 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 GPR52 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 PRF1 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 AGTR2 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 SLC6A3 0.0081 2 4 92.00 2 0.6288 11014 SLC6A4 0.0081 2 4 92.00 2 0.6288 11014 MAPK11 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 NR4A2 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 PGK1 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 SCD 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 JAK2 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 PIM2 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 PIM1 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 CDK4 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 FLT3 0.0000 1 4 83.00 1 0.4464 0 PFKFB3 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 MET 0.0189 3 4 86.33 3 0.6910 24468 MTOR 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 GRB2 0.0006 3 4 39.67 3 0.4635 1394 MAPK14 0.0189 3 4 86.33 3 0.6910 24468 MAPK1 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 CDK2 0.0009 2 4 79.00 2 0.5150 2468 PDE10A 0.0081 2 4 92.00 2 0.6288 11014 BCL2A1 0.0017 3 4 61.00 3 0.5279 4266 S1PR3 0.0020 3 4 58.33 3 0.5300 4284 EGFR 0.0263 5 4 60.20 5 0.7103 33870 F10 0.0023 2 4 59.00 2 0.5129 2198 GLI1 0.0002 3 4 15.00 3 0.3326 274 BCL2L1 0.0001 3 4 16.67 3 0.3305 206 F2 0.0000 1 4 17.00 1 0.3047 0 HSD11B2 0.0120 5 4 33.40 5 0.5494 9598 OPRD1 0.0000 1 4 12.00 1 0.2940 0 EIF4A1 0.0000 1 4 18.00 1 0.3069 0 TYMS 0.0003 3 4 20.00 3 0.3562 508 ADORA2A 0.0029 4 4 48.25 4 0.5386 5710 SIRT2 0.0027 4 4 50.25 4 0.5343 5690 MAP2K1 0.0027 4 4 50.25 4 0.5343 5690 ADORA3 0.0000 1 4 18.00 1 0.3069 0 SLC28A2 0.0004 4 4 19.00 4 0.3648 816 MAPK8 0.0237 4 4 69.25 4 0.7017 28432 PSEN2 0.0021 2 4 62.00 2 0.5236 2930 CTSD 0.0000 3 4 19.67 3 0.3283 102 MMP2 0.0107 3 4 69.00 3 0.6438 14932 MMP3 0.0021 2 4 62.00 2 0.5236 2930 NTRK1 0.0003 2 4 49.00 2 0.4442 658 S1PR1 0.0065 8 4 33.38 8 0.5622 13066 ADORA1 0.0039 5 4 43.20 5 0.5494 7702 IGF1R 0.0000 1 4 23.00 1 0.3176 0 TACR2 0.0017 4 4 37.25 4 0.4893 3184 CNR2 0.0203 6 4 43.33 6 0.6545 25062 FAAH 0.0008 4 4 33.50 4 0.4528 1592 RORC 0.0327 8 4 42.88 8 0.7167 41482 SLC5A1 0.0088 10 4 30.00 10 0.5751 16604 SLC5A2 0.0088 10 4 30.00 10 0.5751 16604 BACE1 0.0025 2 4 58.00 2 0.5129 2090 CXCR1 0.0000 1 4 15.00 1 0.3004 0 KCNH2 0.0016 3 4 57.67 3 0.5215 3378 PPP2R5A 0.0163 14 4 25.50 14 0.6009 24972 PPM1B 0.0163 14 4 25.50 14 0.6009 24972 PPP1CC 0.0127 12 4 26.17 12 0.5837 18862 ATP1A1 0.0091 10 4 29.60 10 0.5751 14684 PPP2CA 0.0144 12 4 26.75 12 0.5944 20874 STAT3 0.0185 15 4 24.40 15 0.6052 26538 IL2 0.0066 11 4 22.55 11 0.5150 10258 PTPN1 0.0636 15 4 30.60 15 0.7554 73762 PTAFR 0.0043 9 4 23.67 9 0.4979 6258 Note. MC, Momordica Charania. Table S4. Representative information of active compounds and targets
name Betweenness Degree Eccentricity Neighborhood connectivity Number of directed edges Radiality Stress TNF 420.7889 17 3 4.59 17 0.9067 690 NTRK2 242.4444 9 3 5.22 9 0.8400 458 PPARG 165.6778 12 3 5.08 12 0.8333 326 MTOR 99.6667 9 3 6.67 9 0.8333 236 LRP1 65.9667 5 3 7.60 5 0.7933 126 ARC 62.6667 3 4 4.67 3 0.7000 124 F2R 58.0000 2 4 9.00 2 0.7267 70 JUND 56.2667 4 3 8.50 4 0.7800 134 TIMP1 38.2111 5 4 8.80 5 0.7867 104 CRHR1 15.6222 4 4 4.75 4 0.7000 34 MAOA 12.8667 4 4 3.50 4 0.6733 26 IFNAR1 12.7667 3 4 8.00 3 0.7467 32 IGF1R 11.8333 6 4 8.83 6 0.7800 42 FGF1 11.7667 4 3 11.00 4 0.7933 44 BCHE 9.0778 2 4 10.50 2 0.7400 28 SLC6A4 5.9556 3 4 5.67 3 0.6867 16 PTGS2 5.4222 6 4 8.67 6 0.7800 22 EPO 2.3333 3 4 9.67 3 0.7467 6 MAPK13 0.6667 2 4 6.50 2 0.6667 2 APLP2 0 1 4 5.00 1 0.6000 0 NTRK3 0 1 5 3.00 1 0.5067 0 CDK5R1 0 1 4 9.00 1 0.6467 0 PIK3R6 0 1 5 2.00 1 0.5333 0 G6PD 0 3 4 12.67 3 0.7533 0 IL26 0 1 4 17.00 1 0.7133 0 JAZF1 0 2 4 10.50 2 0.6933 0 MTUS1 0 1 4 12.00 1 0.6400 0 NOS2 0 3 4 11.67 3 0.7467 0 RANBP9 0 1 4 9.00 1 0.6467 0 SCD5 0 1 4 12.00 1 0.6400 0 TRAF4 0 1 4 17.00 1 0.7133 0 Table S5. Representative information of protein-protein interaction (PPI) network
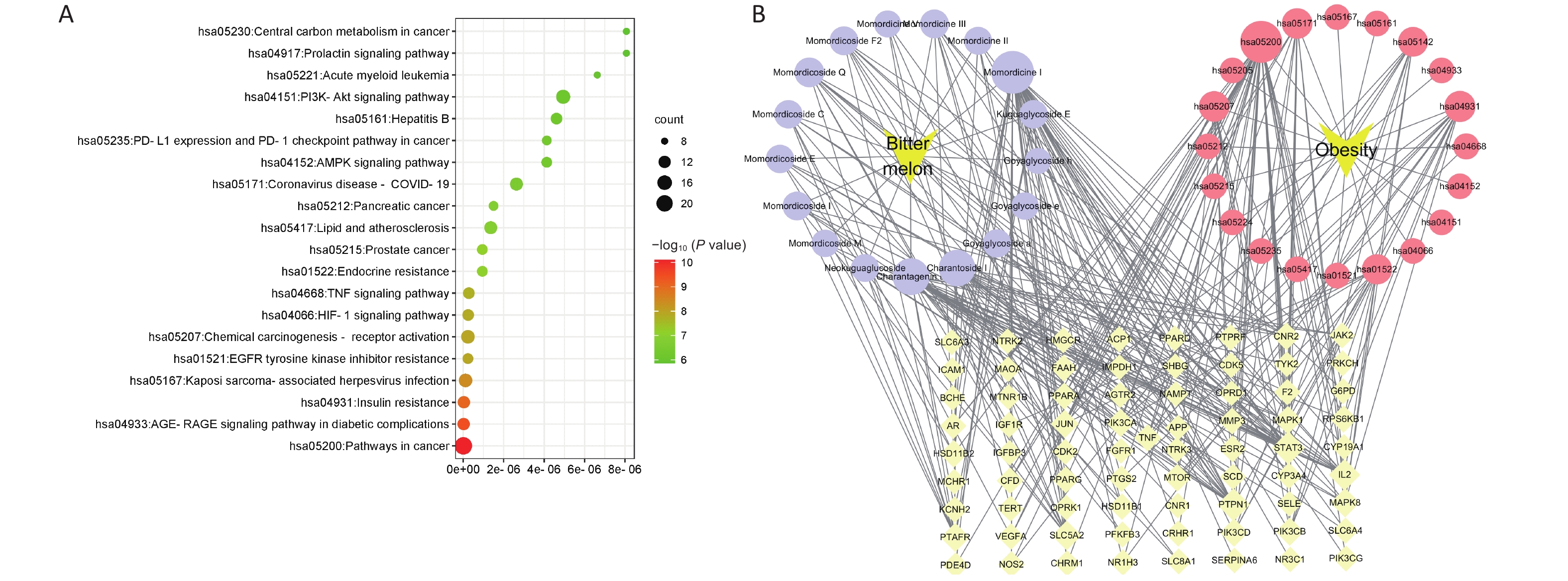
To further elaborate on the biological functions and signaling pathways involved in the anti-obesity processes of BMSE, KEGG enrichment analysis was employed. The top 20 main targets were screened by P-value, including the AMPK signaling pathway, the insulin resistance, lipid and atherosclerosis, AMPK signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and Type II diabetes mellitus (Figure 1A and Supplementary Table S6, available in www.besjournal.com). For the AMPK signaling pathway, a large amount of data showed that BMSE was a novel AMPK activator. Bitter melon derived triterpenoids could phosphorylate AMPK, and subsequently promote GLUT4 translocation to the cell membrane, thereby eliminating in vivo and in vitro hyperglycemia[4]. In addition, mTOR is a well-known key factor in the AMPK signaling pathway, regulating lipophagy by connecting autophagosome-TFEB and FoxO1 transcription factor-lysosome, in which TFEB and FoxO1 induce downstream targets including LAL, thereby promoting the β-oxidation of fatty acids[5]. However, there is little literature about how BMSE and its active compounds regulate lipophagy in vivo to inhibit fat accumulation.
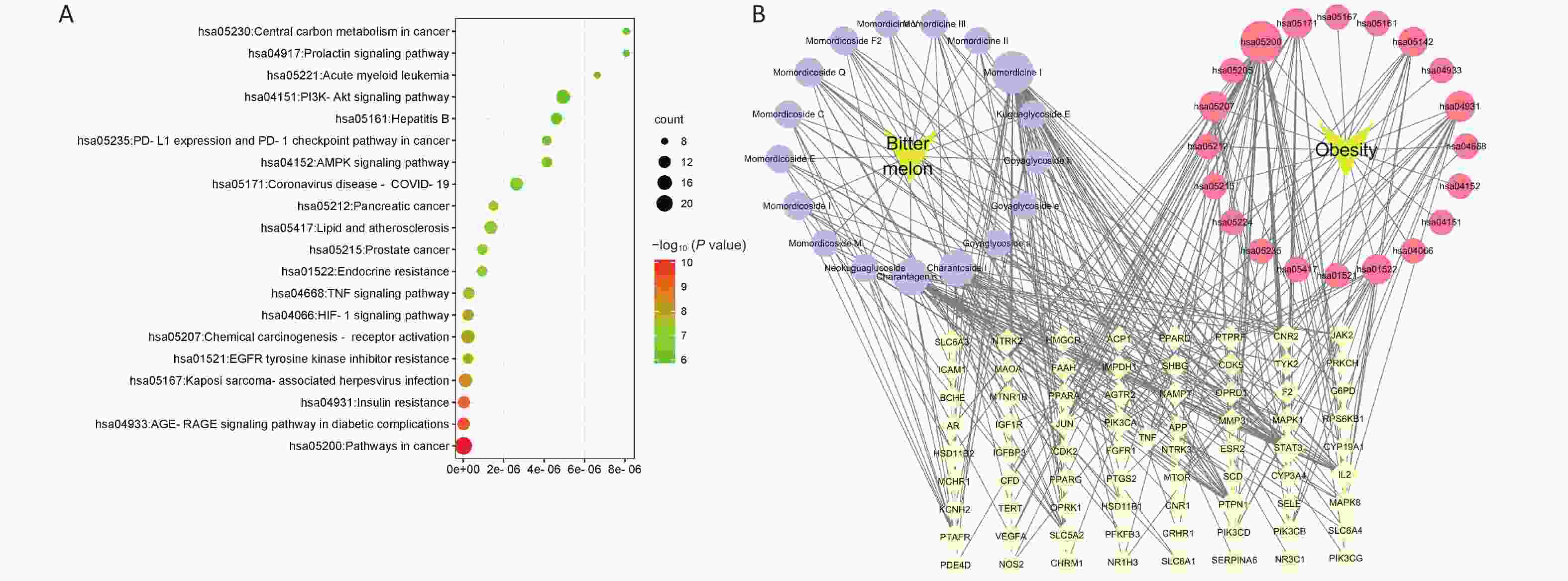
Figure 1. Screening the active saponins present in bitter melon saponin extract (BMSE) through Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis. (A) KEGG enrichment column of BMSE for potential targets of active ingredients associated with obesity. (B) Diagram of target pathway network of BMSE for the treatment of obesity. Values with different superscripts are significantly different (P < 0.05).
Based on the betweenness value in the ‘Compound-Target-disease-pathway’ network, we observed that Momordicine I in BMSE was most likely to be the core component in treating obesity. Combined with the results of LC/Q-TOF-MS/MS, the relative content percentage of Momordicine I and II in BMSE was found to be 2.76% and 22.02% respectively. The response value of Momordicine II was relatively high, as Momordicine II may also regulate insulin-resistance and thus play a role in anti-obesity (Figure 1B and Supplementary Table S7, available in www.besjournal.com). Consequently, we selected Momordicine I and Momordicine II for further studies on lipid-lowering activity and its potential mechanisms, from the perspective of lipophagy based on the KEGG enriched pathways.
Name Betweenness Degree Eccentricity Neighborhood connectivity Number of directed edges Radiality Stress MC 0.0000 17 2 10.59 17 0.7441 0 Obesity 0.0000 20 2 5.50 20 0.6721 0 Goyaglycoside a 0.0001 7 1 11.71 7 0.6324 6 Momordicoside I 0.0001 8 1 11.88 8 0.6360 7 Charantagenin E 0.0010 26 1 5.62 26 0.7081 25 Momordicoside C 0.0001 7 1 10.00 7 0.6360 6 Momordicine I 0.0026 39 1 3.85 39 0.7586 38 Momordicoside F2 0.0001 8 1 11.88 8 0.6360 7 Momordicine V 0.0001 4 1 10.75 4 0.6288 3 Momordicine II 0.0001 6 1 12.50 6 0.6360 5 Momordicine III 0.0001 8 1 11.13 8 0.6360 7 Charantoside I 0.0011 25 1 5.00 25 0.7045 24 Momordicoside E 0.0001 7 1 12.14 7 0.6324 6 Neokuguaglucoside 0.0001 6 1 12.67 6 0.6288 5 Goyaglycoside e 0.0000 5 1 14.20 5 0.6288 4 Momordicoside Q 0.0002 10 1 10.10 10 0.6468 9 Goyaglycoside h 0.0000 2 1 17.50 2 0.6108 1 Momordicoside M 0.0000 5 1 15.00 5 0.6252 4 Kuguaglycoside E 0.0001 7 1 12.57 7 0.6324 6 hsa05142 0.0002 10 1 8.60 10 0.6973 9 hsa05200 0.0017 37 1 5.35 37 0.7982 36 hsa05205 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa05224 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa05235 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa04152 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa05212 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa05161 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa01522 0.0002 11 1 7.36 11 0.6613 10 hsa05215 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa05171 0.0003 12 1 8.67 12 0.7081 11 hsa04151 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa05417 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa01521 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa04668 0.0000 2 1 11.50 2 0.5243 1 hsa04066 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa05207 0.0003 12 1 6.33 12 0.6613 11 hsa04931 0.0003 13 1 8.54 13 0.7117 12 hsa05167 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 hsa04933 0.0000 1 0 20.00 1 0.4739 0 NAMPT 0.0000 1 0 26.00 1 0.5099 0 IMPDH1 0.0000 1 0 7.00 1 0.4342 0 MTNR1B 0.0000 1 0 39.00 1 0.5604 0 OPRK1 0.0000 1 0 39.00 1 0.5604 0 BCHE 0.0000 1 0 39.00 1 0.5604 0 SERPINA6 0.0000 1 0 39.00 1 0.5604 0 SHBG 0.0000 1 0 39.00 1 0.5604 0 NR3C1 0.0000 1 0 39.00 1 0.5604 0 CYP19A1 0.0000 1 0 39.00 1 0.5604 0 HSD11B1 0.0000 3 0 18.00 3 0.5856 0 APP 0.0000 1 0 25.00 1 0.5063 0 SLC8A1 0.0000 2 0 25.50 2 0.5495 0 MAOA 0.0000 1 0 25.00 1 0.5063 0 MCHR1 0.0000 1 0 25.00 1 0.5063 0 AGTR2 0.0000 2 0 25.50 2 0.5495 0 SLC6A3 0.0000 2 0 32.00 2 0.6288 0 SLC6A4 0.0000 2 0 32.00 2 0.6288 0 CNR2 0.0000 6 0 16.33 6 0.6613 0 FAAH 0.0000 4 0 13.00 4 0.5279 0 SLC5A2 0.0000 10 0 11.00 10 0.6000 0 KCNH2 0.0000 3 0 19.33 3 0.5532 0 PTAFR 0.0000 9 0 9.33 9 0.5640 0 CDK5 0.0000 1 0 25.00 1 0.5063 0 PRKCH 0.0000 2 0 38.00 2 0.6468 0 CNR1 0.0000 1 0 25.00 1 0.5063 0 HSD11B2 0.0000 6 0 17.33 6 0.6685 0 OPRD1 0.0000 1 0 6.00 1 0.4306 0 ACP1 0.0000 2 0 38.00 2 0.6468 0 PDE4D 0.0000 2 0 38.00 2 0.6468 0 CRHR1 0.0000 2 0 38.00 2 0.6468 0 IGFBP3 0.0000 1 0 25.00 1 0.5063 0 NTRK3 0.0000 1 0 26.00 1 0.5099 0 G6PD 0.0000 2 0 38.00 2 0.6468 0 SCD 0.0000 2 0 25.50 2 0.5495 0 HMGCR 0.0000 2 0 38.00 2 0.6468 0 CFD 0.0000 3 0 29.33 3 0.6505 0 NTRK2 0.0000 1 0 26.00 1 0.5099 0 CHRM1 0.0000 2 0 38.00 2 0.6468 0 MMP3 0.0000 4 0 24.50 4 0.6685 0 PFKFB3 0.0000 2 0 25.50 2 0.5495 0 CYP3A4 0.0000 3 0 29.33 3 0.6505 0 NR1H3 0.0000 3 0 29.67 3 0.6505 0 PTPRF 0.0000 3 0 29.67 3 0.6505 0 PTPN1 0.0000 17 0 13.00 17 0.7946 0 PPARA 0.0000 4 0 25.25 4 0.6541 0 TYK2 0.0000 1 0 26.00 1 0.5099 0 PIK3CG 0.0000 2 0 38.00 2 0.6468 0 TNF 0.0000 5 0 22.20 5 0.6577 0 SELE 0.0000 1 0 26.00 1 0.5099 0 ICAM1 0.0000 1 0 26.00 1 0.5099 0 VEGFA 0.0000 3 0 18.67 3 0.6180 0 TERT 0.0000 2 0 20.50 2 0.6072 0 STAT3 0.0000 18 0 11.06 18 0.7730 0 RPS6KB1 0.0000 5 0 19.60 5 0.6793 0 PTGS2 0.0000 3 0 26.00 3 0.6505 0 MAPK8 0.0000 9 0 19.78 9 0.7586 0 MAPK1 0.0000 7 0 19.00 7 0.7225 0 PPARG 0.0000 4 0 27.25 4 0.7045 0 PPARD 0.0000 2 0 38.00 2 0.6468 0 PIK3CD 0.0000 7 0 19.14 7 0.6685 0 PIK3CB 0.0000 7 0 19.14 7 0.6685 0 PIK3CA 0.0000 7 0 23.00 7 0.7514 0 NOS2 0.0000 3 0 28.67 3 0.6505 0 JUN 0.0000 7 0 13.14 7 0.6324 0 JAK2 0.0000 2 0 25.50 2 0.5495 0 IL2 0.0000 14 0 11.29 14 0.7297 0 IGF1R 0.0000 2 0 10.50 2 0.5423 0 MTOR 0.0000 6 0 20.67 6 0.7189 0 FGFR1 0.0000 1 0 26.00 1 0.5099 0 F2 0.0000 3 0 18.67 3 0.6144 0 ESR2 0.0000 4 0 24.75 4 0.6577 0 CDK2 0.0000 2 0 25.50 2 0.5495 0 AR 0.0000 3 0 29.33 3 0.6505 0 Note. MC, Momordica Charania. Table S7. Representative information of target pathway network
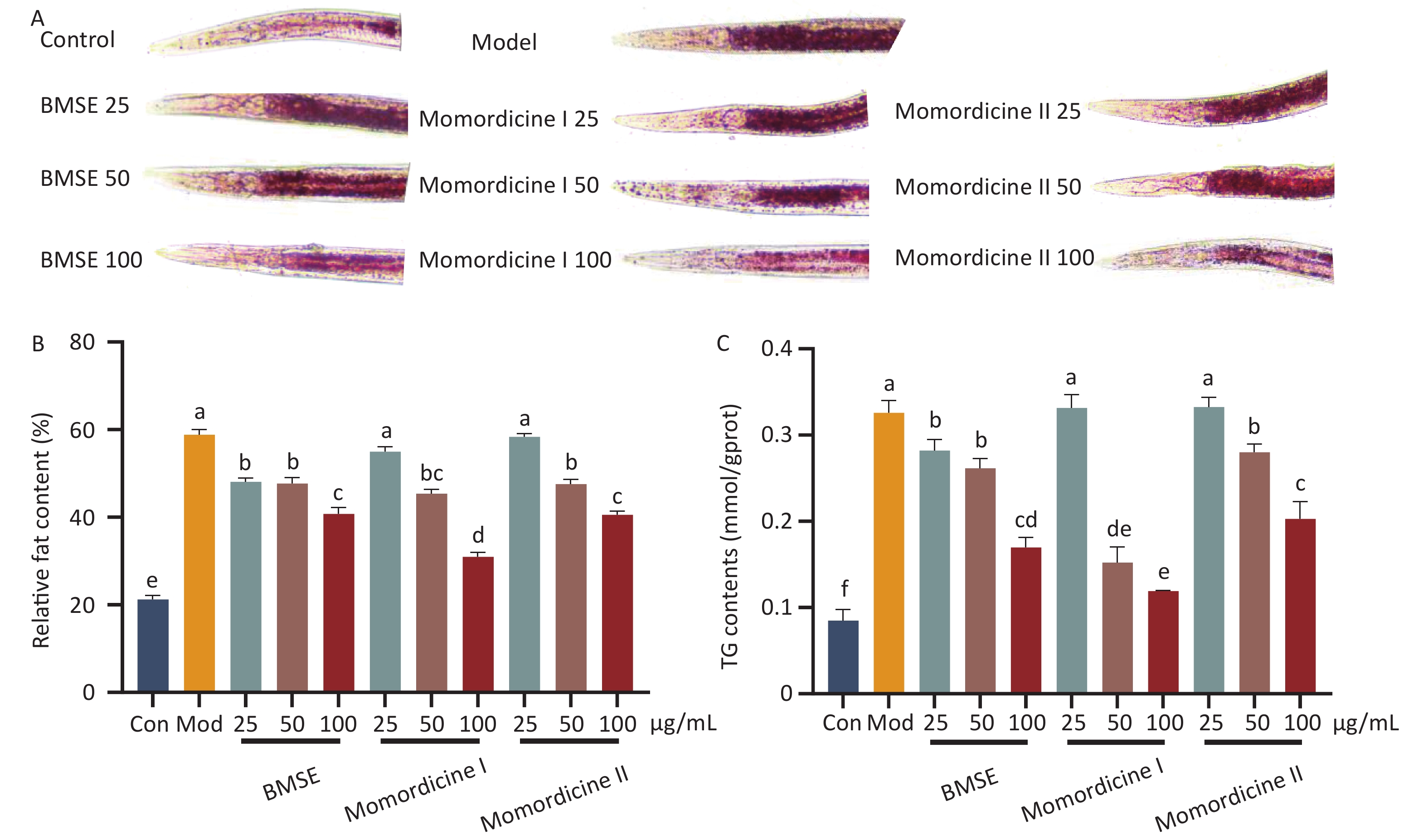
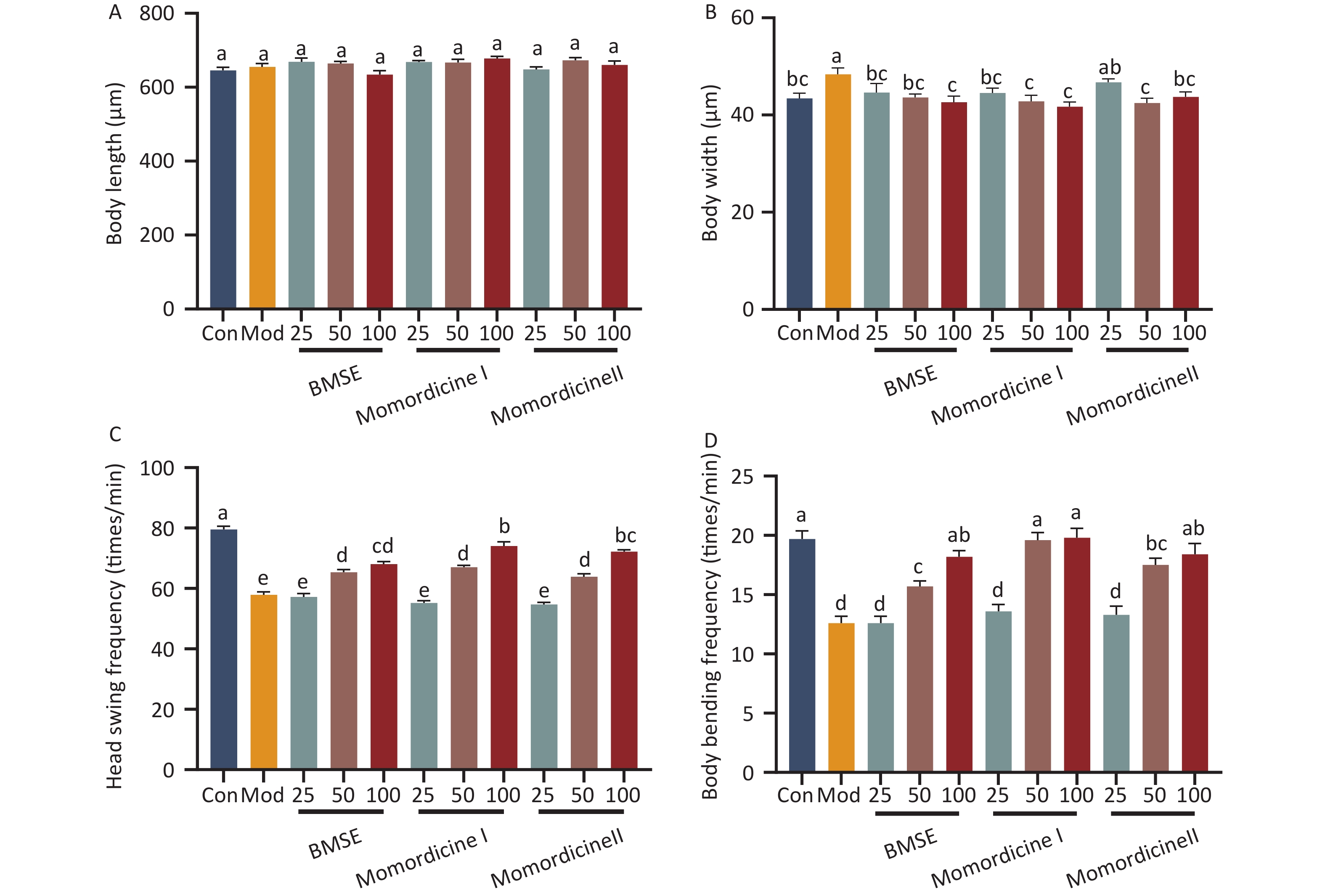
To verify the lipid-lowering effects of BMSE, Momordicine I and Momordicine II in vivo, an obese C. elegans model was established using high glucose. Supplementary Figure S2 (available in www.besjournal.com) shows that the concentrations of 25, 50, and 100 μg/mL of BMSE had no negative effects on the growth of nematodes. Lipids in C. elegans is mainly stored in the intestinal epithelial and intestine, in the form of TG. Compared with the model group, both BMSE, Momordicine I and Momordicine II were found to significantly reduce fat content in C. elegans, and the lipid-lowering effect was proportional to the dose concentration. 100 μg/mL Momordicine I degraded the fat content of C. elegans sharply in all treated groups (P < 0.05) (Figure 2). Lin et al. found that BMSE had a strong lipid-lowering benefit in both normal and high-fat C. elegans, as well as improved lifespan and healthspan. These data strongly confirm the lipid-reduction effects of BMSE and hint that Momordicine I played a leading role.
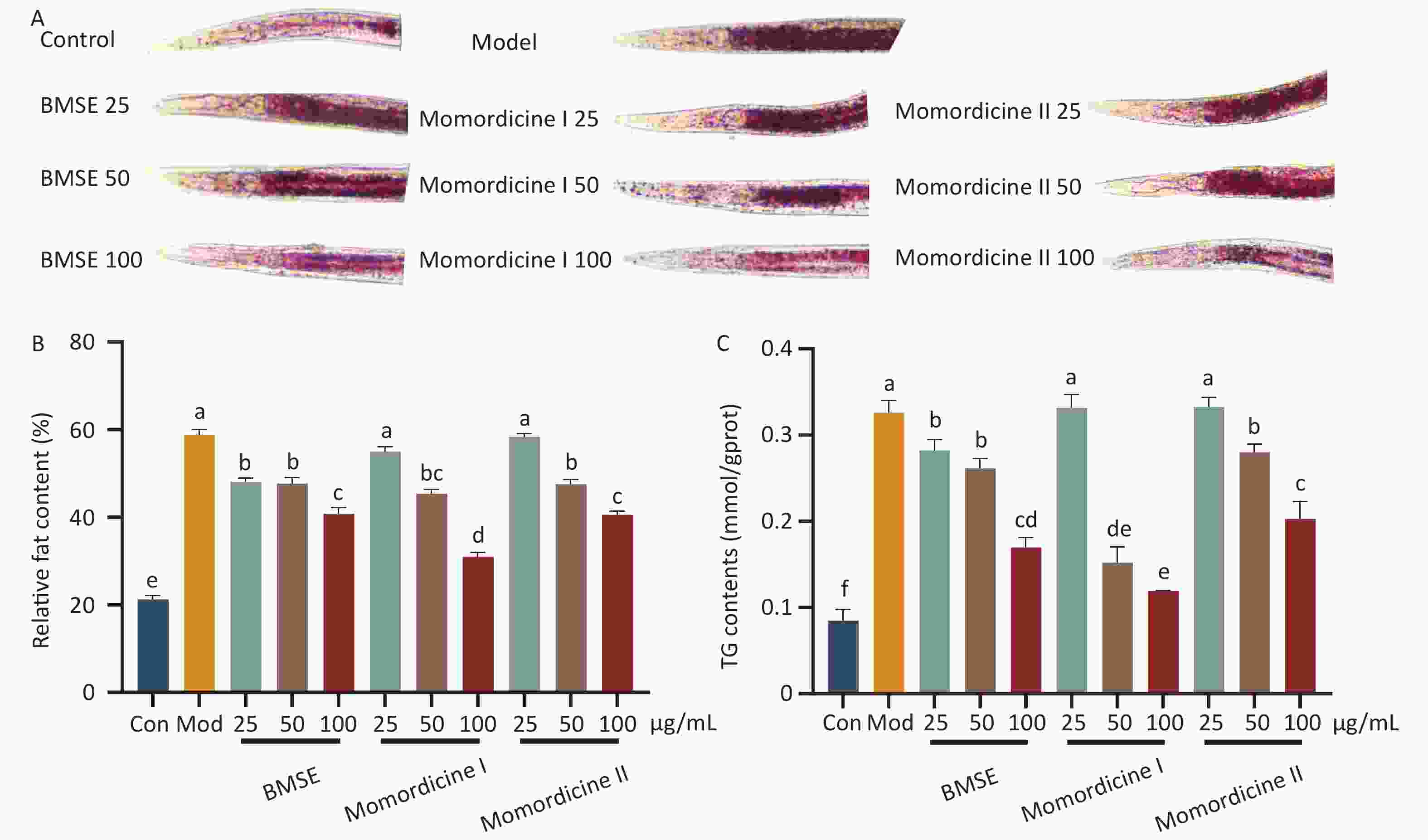
Figure 2. Effects of bitter melon saponin extract (BMSE) on lipid accumulation (overall fat and triglyceride content) of wild type (N2) Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). (A) and (B) C. elegans were treated from L1 to L4 stage for 48 h followed by Oil Red O (ORO) staining. The Fat intensities were quantitatively analyzed by Image J from 15 to 20 C. elegans. (C) The triglyceride (TG) content was determined by kits. Results are shown as mean ± SEM. Values with different superscripts are significantly different (P < 0.05).
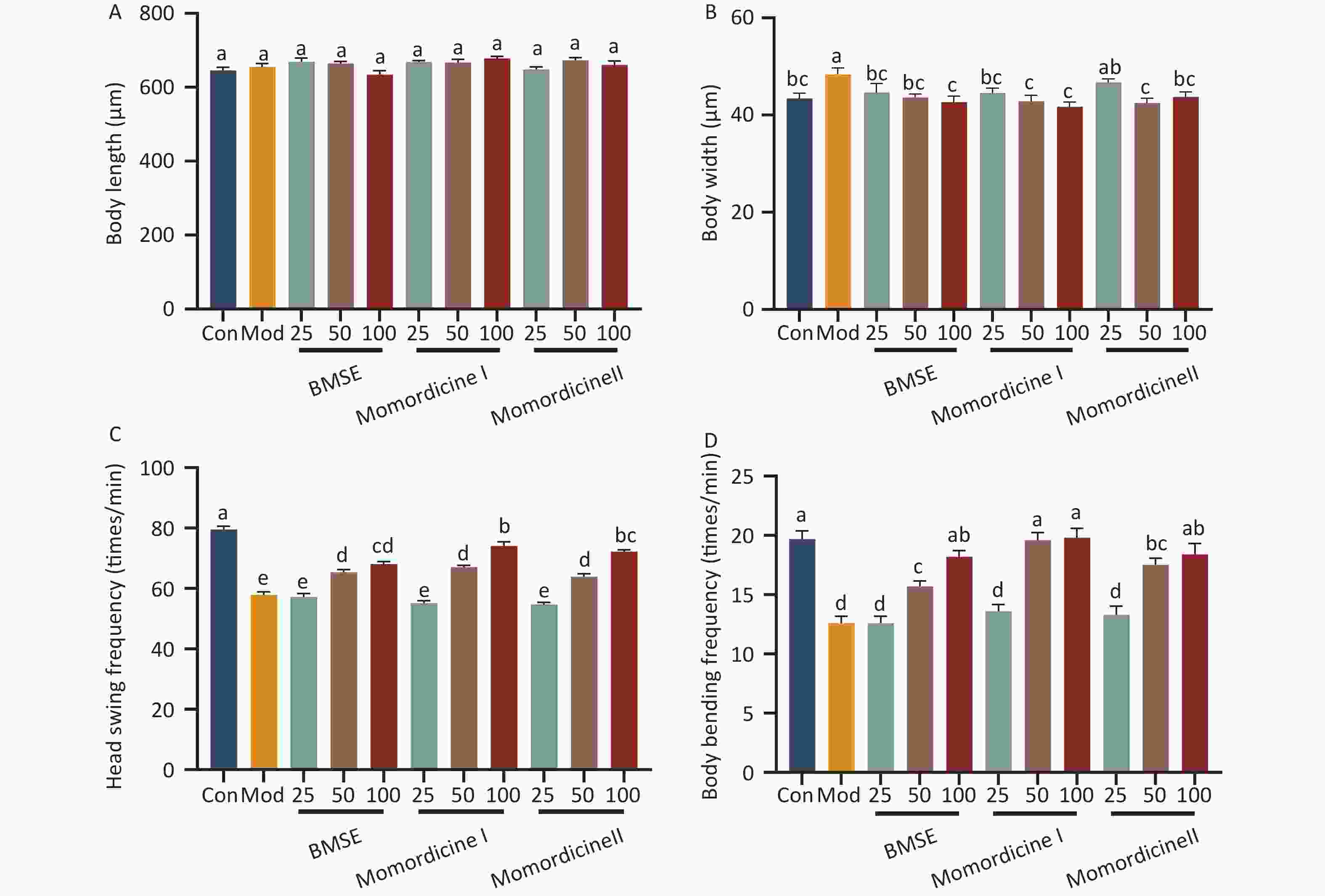
Figure S2. Effects of bitter melon saponin extract (BMSE) on worm size and locomotive activity. (A) Body length and (B) body width were analyzed using Image J software (n > 30 per group). (C) Head swing frequency and (D) body bending frequency were counted under a microscope for 1 min (n > 30 worms per group). Results are showed as mean ± SEM. Values with different superscripts are significantly different (P < 0.05).
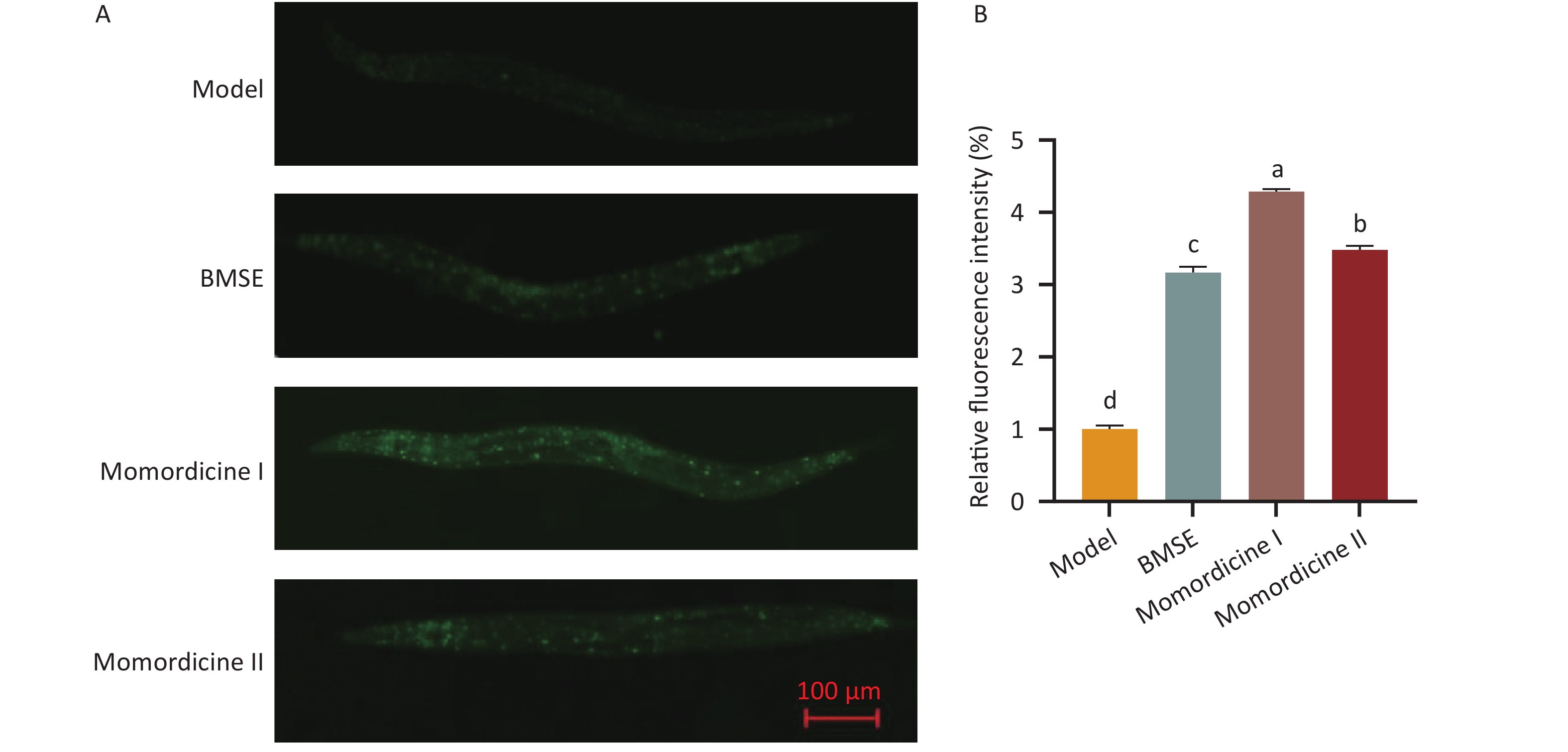
Based on the screening of anti-obesity targets of BMSE, mTOR is closely related to lipophagy with high degree values, and thus we speculated that BMSE may regulate lipid metabolism via lipophagy. Lipophagy is a form of selective autophagy, catabolizing the components of LDs through LAL, which is a significant fat-degradation pathway besides lipohydrolysis. MDC fluorescent staining was applied to detect the formation of autophagosomes in nematodes (Supplementary Figure S3, available in www.besjournal.com). The green fluorescence was significantly enhanced (P < 0.05) in all treated groups, indicating that the number of autophagosomes remarkably increased via treatment with BMSE. By contrast, Momordicine I and Momordicine II had better effects than BMSE on the autophagy flow of obese nematodes, with Momordicine I exerting the best effect. Liao et al. found that dihydromyricetin clearly attenuated high FBS-induced inhibition of autophagosome formation in LO2 cells, similar to our results[6]. Therefore, we confirmed that BMSE alleviated lipid accumulation in nematodes via lipophagy. Nevertheless, its molecular mechanism required further investigation.
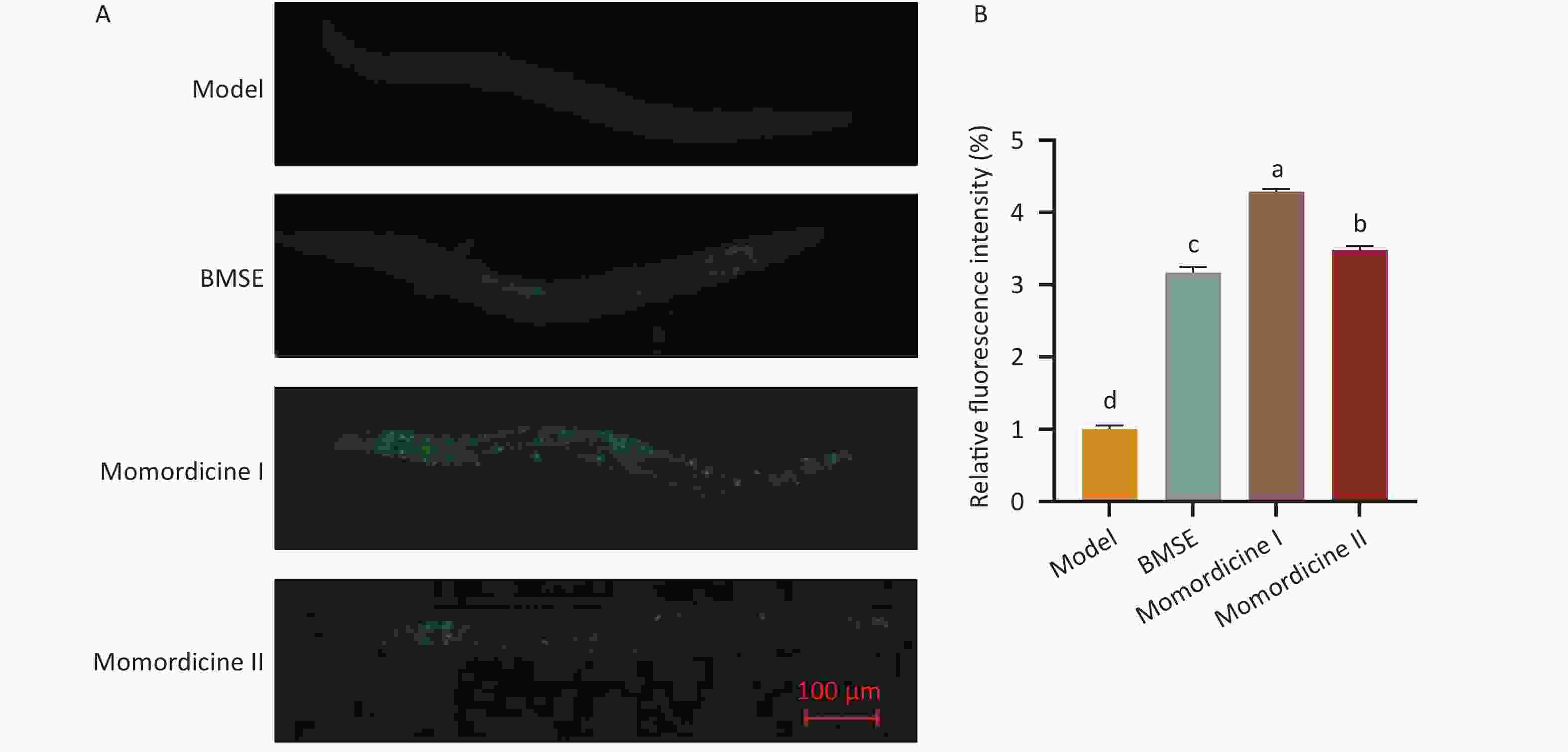
Figure S3. Effect of bitter melon saponin extract (BMSE) on autophagosome formation in obese nematodes. (A) and (B) Worms were treated from L1 to L4 stage for 48 h followed by Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) fluorescent staining. The relative fluorescence intensities were quantitatively analyzed by Image J for over 20 worms. Results are showed as mean ± SEM. Values with different superscripts being significantly different (P < 0.05).
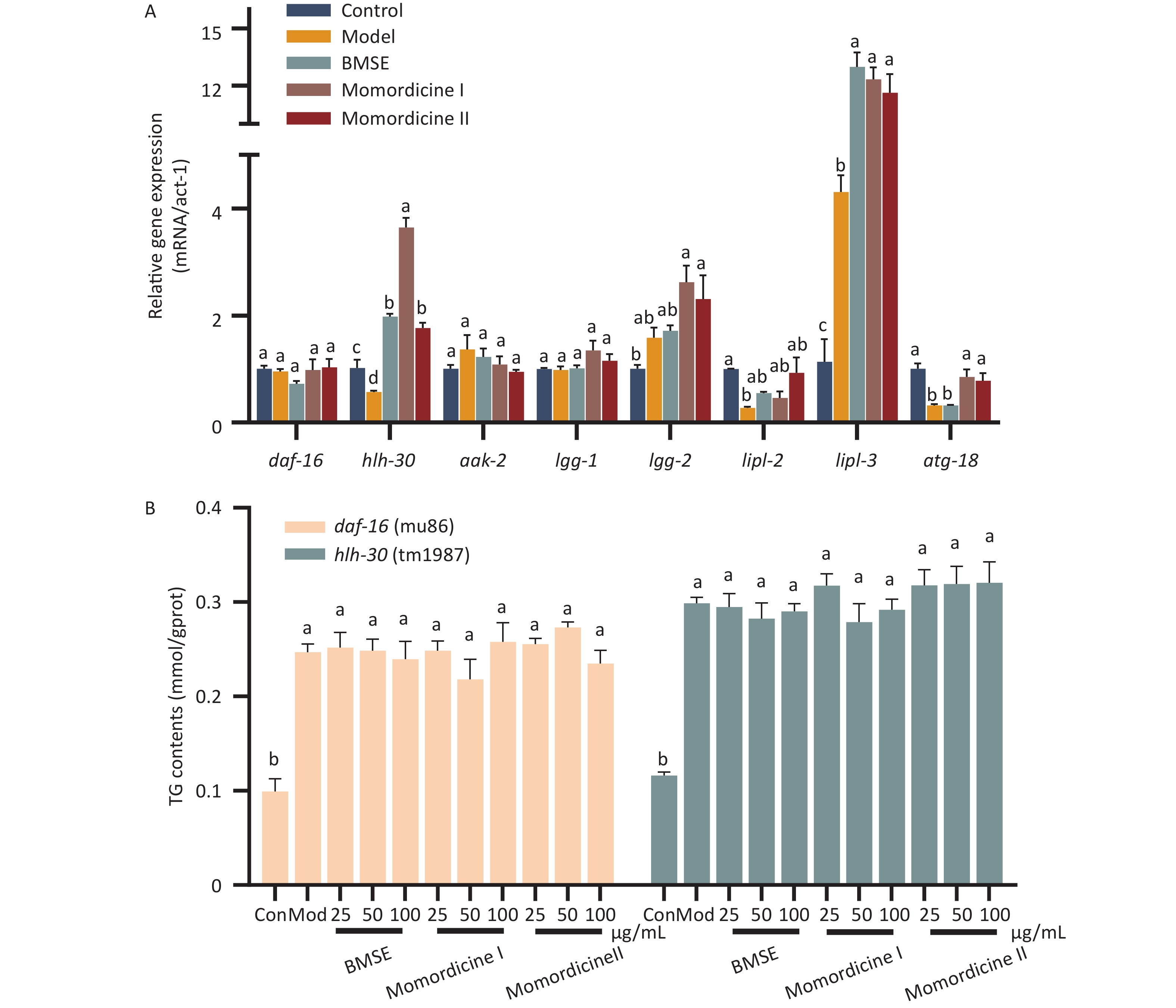
In order to study the mechanism by which BMSE and its constituent compounds regulate the lipid metabolism, the expression profile of lipophagy related genes was investigated by qRT-PCR (Figure 3A). The present study indicates that a high glucose diet inhibited hlh-30 (TFEB homolog) gene levels compared to the control group (P < 0.05), with BMSE, Momordicine I and Momordicine II treatments significantly counteracting this effect. Furthermore, lipl-3 (LAL homolog), and atg-18 (ATG-18 homolog) were markedly up-regulated in Momordicine I and Momordicine II groups, while other related genes including daf-16 (FoxO1 homolog) showed no notable alterations. ATG-18 promotes the formation of autophagosomes, and LAL is the key enzyme hydrolyzing TG and cholesterol in lysosomes, both of which would be regulated by daf-16 or hlh-30. No changes were registered in daf-16 expression, however, our previous study indicating that daf-16 and hlh-30 possibly play a key role in lipid-lowering of BMSE leads us to speculate that daf-16 is involved at the translation level rather than transcriptional level in the regulation of lipophagy by BMSE, though this requires further confirmation[2]. Whether Momordicine I and Momordicine II also act on daf-16 and hlh-30 in the same manner as BMSE still needs to be further verified with C. elegans.
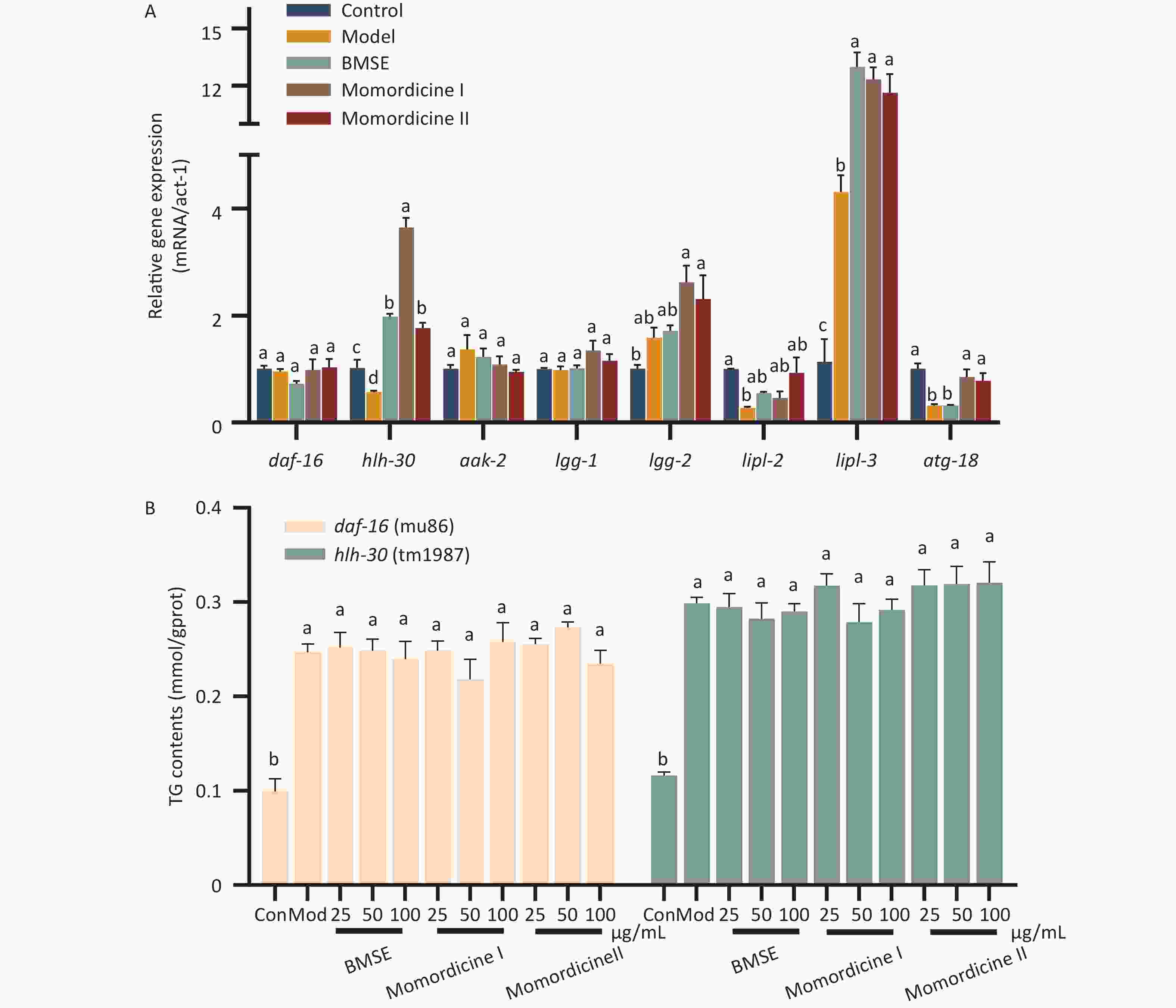
Figure 3. The molecular mechanisms of bitter melon saponin extract (BMSE) in alleviating fat accumulation. (A) N2 Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) were pretreated with 100 μg/mL BMSE, Momordicine I and Momordicine II for 48 hours, and total RNA was extracted. The mRNA level was determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to the expression of act-1. (B) Triglyceride (TG) content in daf-16 and hlh-30 C. elegans was measured. Results are showed as mean ± SEM. Values with different superscripts are significantly different (P < 0.05).
The inhibition of fat accumulation in daf-16 and hlh-30 C. elegans was diminished with the administration of BMSE, Momordicine I and Momordicine II, which combined with the previous study certifies that the saponins in bitter melon largely depended on daf-16 and hlh-30 to reduce fat storage[2] (Figure 3B). FoxO1 and TFEB could induce the expression of LAL, either alone or in combination, to promote autophagolysosome-mediated fat degradation and fatty acid β-oxidation[7]. Studies have revealed that FoxO1, as a significant regulator of the energy stress response, was directly regulated by the upstream target AMPK. TFEB was the major inducer of lysosomal biogenesis and autophagosome-lysosomal fusion, negatively regulated by the upstream target mTOR[8]. This re-confirmed that the AMPK/mTOR pathway speculated upon in network pharmacology played a key role in lipid reduction of BMSE, largely related to lipophagy. The diagram of the lipid-lowering mechanism of BMSE and its potential active compounds is shown in Supplementary Figure S4 (available in www.besjournal.com). In all, Momordicine I and Momordicine II alleviate fat deposition in obese C. elegans via daf-16/FoxO1 and hlh-30/TFEB mediated lipophagy.
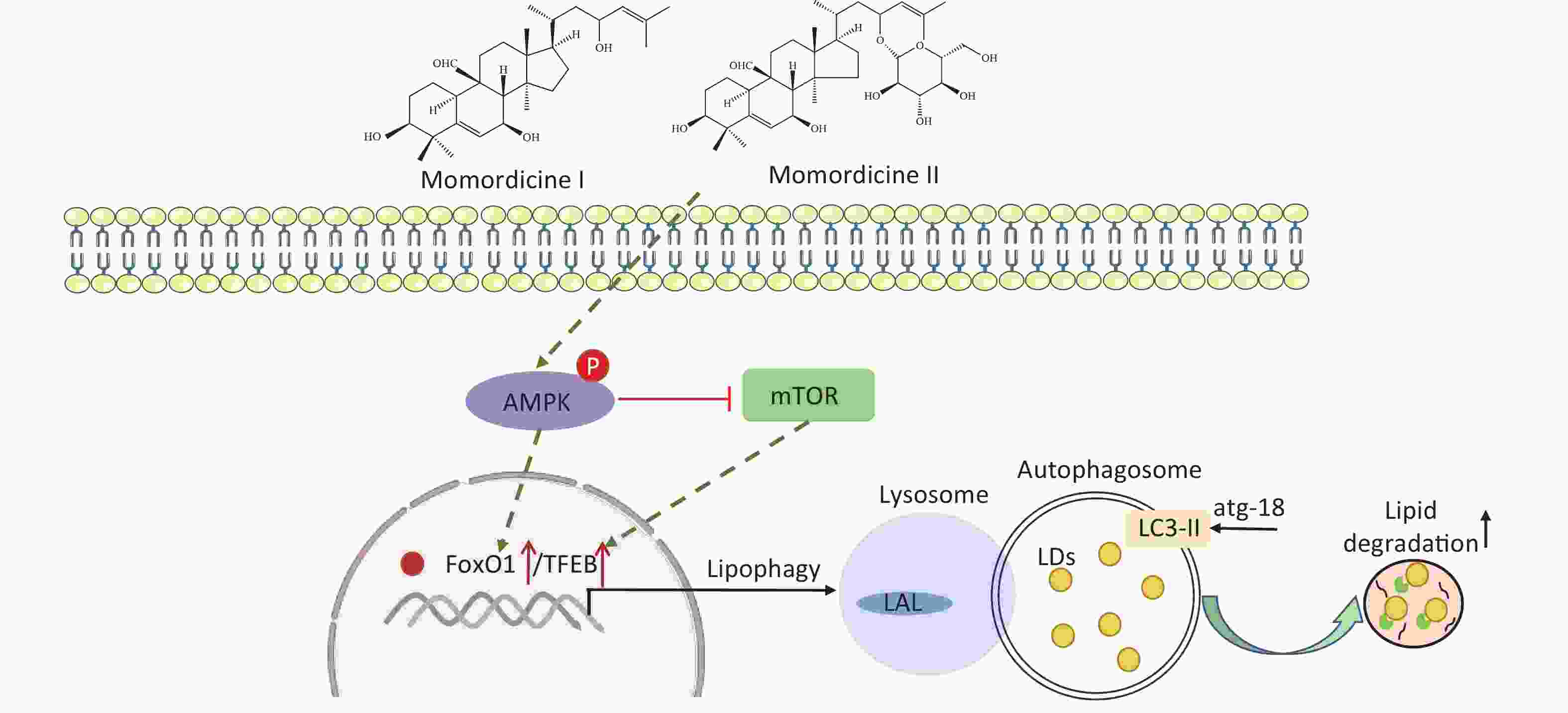
Figure S4. The diagram of the lipid-lowering mechanism of bitter melon saponin extract (BMSE) and its potential active compounds.
In summary, based on LC/Q-TOF-MS/MS combined with network pharmacology, Momordicine I and Momordicine II were identified as the main compounds responsible for lowing lipid levels by BMSE. Experimental studies have verified that BMSE exerted remarkable lipid-lowering activity in obese C. elegans, along with Momordicine I, with 100 μg/mL providing the strongest effect. Most of all, Momordicine I and Momordicine II exerted their lipid-reduction capacity via daf-16/FoxO1 and hlh-30/TFEB mediated lipophagy, consistent with the KEGG predicted AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Overall, our findings not only identified pure compounds responsible for lipid-lowering effects in the ethyl alcohol extract of bitter melon, but also provided new insights into its underlying mechanisms. This study is expected to benefit the development of lipid-lowering products with clear efficacy and mechanisms.
ID Pathway Count Gene hsa04933 AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications 12 ICAM1, JAK2, JUN, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, MAPK1, MAPK8, SELE, STAT3, TNF, VEGFA hsa04931 Insulin resistance 12 MTOR, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PPARA, APK8, PTPN1, PTPRF, RPS6KB1, STAT3, TNF, NR1H3 hsa05417 Lipid and atherosclerosis 13 ICAM1, JAK2, JUN, MMP3, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PPARG, MAPK1, MAPK8, SELE, STAT3, TNF hsa04152 AMPK signaling pathway 10 MTOR, HMGCR, IGF1R, PFKFB3, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PPARG, RPS6KB1, SCD hsa04151 PI3K-Akt signaling pathway 15 CDK2, CHRM1, FGFR1, MTOR, IGF1R, IL2, JAK2, NTRK2, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PIK3CG, MAPK1, RPS6KB1, VEGFA hsa04930 Type II diabetes mellitus 7 MTOR, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, MAPK1, MAPK8, TNF Table S6. KEGG enrichment pathway and corresponding target classification and number
HTML
 23388-S.pdf
23388-S.pdf
|

|







 Quick Links
Quick Links
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: