-
Early pregnancy loss, defined as a nonviable intrauterine pregnancy occurring before 12 weeks of gestation, is estimated to affect 25% of clinically diagnosed pregnancies[1]. Several demographic, lifestyle, and environmental risk factors have been reported to associate with the risk of early pregnancy loss, yet the causes of most early pregnancy losses remain elusive; thus, further studies are needed. Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) are a class of widespread environmental pollutants that can adversely affect human reproductive health. Humans are inevitably exposed to PFCs through diet, water, air and dust. A wealth of epidemiological and toxicological research using a variety of animal models has warned of the persistence, bioaccumulation, and toxicity of PFCs[2]. For instance, researchers have reported that PFCs can cause fetal growth retardation and abnormal placentation, indicating it is important to study the associations between PFC exposure and early pregnancy loss[3]. However, few studies have examined the effects of PFC exposure, and analyses have been based on only Danish and Swedish populations [4]. Thus, the aim of the present study was to evaluate the potential associations between the exposure to major PFCs during early pregnancy and the risk of early pregnancy loss among a Chinese population.
A nested case-control study was conducted in a prospective cohort of patients from Shunyi Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Beijing, China from March 2018 to June 2020. Pregnant women aged ≥ 18 years coming for an antepartum examination at ≤ 8 gestational weeks and living in Shunyi District for ≥ 1 year were enrolled. Upon enrollment, women were asked to complete a structural questionnaire about their basic social-demographic characteristics, and their blood was collected at the same time. Follow-ups continued until delivery or pregnancy termination to collect information on the pregnancy outcomes, which were subsequently confirmed by clinical records. Early pregnancy loss was defined as the spontaneous demise of a pregnancy between 9–12 weeks of gestation. Forty-one early pregnancy losses occurring between September 2018 and May 2019 were selected as cases. Forty-seven controls were randomly selected from pregnancies ending in healthy singleton live births with a gestation period of ≥ 37 weeks to represent the cohort from which the cases came from. The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of Beijing Shunyi Women’s and Children’s Hospital (2018-27), and written informed consents were obtained from all subjects before completing the questionnaire and collecting the blood.
PFCs in maternal serum specimens were quantified by an ultraperformance liquid chromatography system coupled to a 5500 Q-Trap triple quadrupole mass spectrometry system (AB Sciex, Canada). We measured 32 PFC compounds (Supplementary Table S1, available in www.besjournal.com). However, only those above the limit of detection in N > 80% of the samples were used for subsequent analysis. Values below the limit of detection were replaced with half of the limit of quantification.
Table S1. Maternal serum concentrations of perfluorinated compounds during early pregnancy (ng/mL)
PFCs LOD N > LOD (%) 25% 50% 75% PFCA PFBA 0.083 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD PFHpA 0.051 11 (12.50) < LOD < LOD < LOD PFHxA 0.200 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD PFNA 0.337 86 (97.27) 0.718 0.996 1.323 PFDA 0.042 88 (100.00) 0.499 0.810 1.155 PFUdA 0.040 88 (100.00) 0.378 0.539 0.727 PFDoA 0.022 88 (100.00) 0.050 0.070 0.098 PFTrDA 0.017 88 (100.00) 0.091 0.120 0.180 PFTeDA 0.004 88 (100.00) 0.010 0.015 0.025 P5MHpA 0.070 3 (3.41) < LOD < LOD < LOD P6MHpA 0.040 27 (30.68) < LOD < LOD 0.043 P4MHpA 0.100 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD PFOA 0.500 88 (100.00) 4.287 5.640 10.194 PFSA L-PFBS 0.018 64 (72.73) < LOD 0.029 0.058 L-PFHxS 0.036 88 (100.00) 0.474 0.714 0.986 L-PFDS 0.005 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD L-PFHpS 0.034 80 (90.91) 0.076 0.117 0.175 P44DMHxS 0.005 44 (50.00) < LOD < LOD 0.007 P5MHpS 0.020 85 (96.59) 0.160 0.228 0.357 P4MHpS 0.010 85 (96.59) 0.118 0.174 0.240 P3MHpS 0.010 84 (95.45) 0.099 0.141 0.191 P6MHpS 0.050 76 (86.36) 0.179 0.301 0.594 P1MHpS 0.050 83 (94.32) 0.109 0.160 0.235 PFOS 1.500 88 (100.00) 3.423 5.244 9.027 4:2FTS 0.103 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD 6:2FTS 0.200 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD 8:2FTS 0.300 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD 6:2diPAP 0.030 87 (98.86) 0.164 0.312 0.594 PFOS substitute 11CL-PF3OUdS 0.007 88 (100.00) 0.025 0.038 0.063 9CL-PF3ONS 0.025 88 (100.00) 1.064 1.871 2.682 TA 0.019 14 (15.91) < LOD < LOD < LOD TeA 0.048 8 (9.09) < LOD < LOD < LOD Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated Compounds; LOD: lower limit of detection; PFCA: perfluorocarboxylic acid; PFBA: Perfluoro-n-butanoic acid; PFHpA: Perfluoro-n-heptanoic acid; PFHxA: Perfluoro-n-hexanoic acid; PFNA: Perfluoro-n-nonanoic acid; PFDA: Perfluoro-n-decanoic acid; PFUdA: Perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid; PFDoA: Perfluoro-n-dodecanoic acid; PFTrDA: Perfluoro-n-tridecanoic acid; PFTeDA: Perfluoro-n-tetradecanoic acid; P5MHpA: Perfluoro-5-methylheptane acid; P6MHpA: Perfluoro-6-methylheptane acid; P4MHpA: Perfluoro-4-methylheptane acid; PFOA: Perfluoro-n-octanoic acid; PFSA: perfluorosulfonic acid; L-PFBS: Potassium perfluoro-1-butanesulfonate; L-PFHxS: Sodium perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonate; L-PFDS: Sodium perfluoro-1-decanesulfonate; L-PFHpS: Sodium perfluoro-1-heptanesulfonate; P44DMHxS: Perfluoro-4,4-dimethylhexane sulfonate; P5MHpS: Perfluoro-5-methylheptane sulfonate; P4MHpS: Perfluoro-4-methylheptane sulfonate; P3MHpS: Perfluoro-3-methylheptane sulfonate; P6MHpS: Perfluoro-6-methylheptane sulfonate; P1MHpS: Perfluoro-1-methylheptane sulfonate; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate; 4:2FTS: Sodium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorohexane sulfonate (4:2); 6:2FTS: Sodium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctane sulfonate (6:2); 8:2FTS: Sodium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecane sulfonate (8:2); 6:2diPAP: Sodium bis (1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctyl)phosphate; 11CL-PF3OUdS: Potassium 11-chloroeicosafluoro-3-oxaundecane-1-sulfonate; 9CL-PF3ONS: Potassium 9-chlorohexadeca-fluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate; TA: perfluoro-2,5-dimethyl-3,6-dioxanonanoic acid; TeA: perfluoro- (2,5,8-trimethyl-3,6,9-trioxadodecanoic) acid. PFC levels were first analyzed as categorical data with the median level as the cut-off point. Differences in maternal serum concentrations of PFCs between early-pregnancy-loss cases and controls were examined with the Mann–Whitney U test, considering that most PFCs were not normally distributed, while differences in basic socio-demographic, passive smoking, drinking, and disease history characteristics were examined with the chi-square test. Associations between maternal serum PFC concentrations and early pregnancy loss were examined using multivariate unconditional logistic regression models. Considering that many chemicals belong to the same class and may be highly correlated due to shared exposure sources or common metabolic pathways, we further used principal component analysis to identify the potential underlying compounds of PFCs, explore the synthesized effects of different PFC compounds, and detect new metrics of chemical exposures while avoiding possible multi-collinearity biases caused by close correlation of these compounds. The number of principal components was extracted based on the eigenvalues N > 1 and Varimax rotation. The result of the Kaiser–Mayer–Olkin test was 0.763, and the P value of the Bartlett Test of Sphericity was < 0.001, indicating strong correlations among PFC compounds and the suitability of principal component analysis. Factor loadings >|0.3| were then used to identify the variables mainly comprising a principal component. Categorical forms of principal components using the median levels as cut-off points were analyzed in unconditional multiple logistic regression models. To better understand how risk of early pregnancy loss changed with rising levels of principal components, restricted cubic spline models with four knots selected at the 5th, 35th, 65th, and 95th percentiles of the distribution were also built. The statistical analyses of data were performed by the R 4.0.4 package (R Development Core Team, Vienna, Austria).
The baseline characteristics of early pregnancy loss cases and controls are presented in Supplementary Table S2, available in www.besjournal.com. The majority of women in the analysis were older than 32 years of age (56.82%) and nulliparous (59.09%). Significant statistical differences existed between cases and controls in terms of parity, maternal passive smoking during the first trimester, and the mother experiencing vaginal bleeding during pregnancy.
Table S2. Maternal socio-demographic, passive smoking, drinking, and disease history characteristics of early pregnancy loss cases and controls
Characteristics Case (n = 41) Control (n = 47) P n (%) n (%) Maternal age at conception < 32 17 (41.46) 21 (44.68) ≥ 32 24 (58.54) 26 (55.32) 0.761 Parity Nulliparous 33 (82.50) 19 (59.38) Parous 7 (17.50) 13 (40.63) 0.029 Maternal history of pregnancy loss No 32 (78.05) 39 (82.98) Yes 9 (21.95) 8 (17.02) 0.559 Maternal education High school or lower 13 (31.71) 12 (25.53) College school or higher 28 (68.29) 35 (74.47) 0.522 Paternal education High school or lower 16 (39.02) 18 (38.30) College school or higher 25 (60.98) 29 (61.70) 0.944 Maternal alcohol drinking during first trimester No 36 (87.80) 46 (97.87) Yes 5 (12.20) 1 (2.13) 0.093* Maternal passive smoking during first trimester No 21 (51.22) 36 (76.60) Yes 20 (48.78) 11 (23.40) 0.013 Mother having fever during pregnancy No 38 (92.68) 46 (97.87) Yes 3 (7.32) 1 (2.13) 0.335* Mother having infections during pregnancy No 40 (97.56) 46 (97.87) Yes 1 (2.44) 1 (2.13) 1.000* Mother having serious nausea and vomiting during pregnancy No 39 (95.12) 44 (93.62) Yes 2 (4.88) 3 (6.38) 1.000* Mother having vaginal bleeding during pregnancy No 25 (60.98) 43 (91.49) Yes 16 (39.02) 4 (8.51) 0.001* Note. *Fisher’s exact test. Supplementary Table S1 shows the maternal serum concentrations of PFCs during early pregnancy. Eighteen PFC compounds were detected in more than 80% of samples, among which perfluoro-n-octanoic acid (PFOA), perfluoro-n-decanoic acid (PFDA), perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid (PFUdA), perfluoro-n-tridecanoic acid (PFTrDA), perfluoro-n-dodecanoic acid (PFDoA), perfluoro-n-tetradecanoic acid (PFTeDA), sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate (PFOS), perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonate (L-PFHxS), potassium 9-chlorohexadeca-fluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate (9CL-PF3ONS), and potassium 11-chloroeicosafluoro-3-oxaundecane-1-sulfonate (11CL-PF3OUdS) were detected in all samples.
Supplementary Table S3 (available in www.besjournal.com) presents the differences in the maternal serum concentrations of major PFCs (with median concentration levels ≥ 0.500 μg/mL) between early pregnancy loss cases and controls. The median levels of the maternal serum concentrations of PFDA and PFUdA were significantly higher in cases than those in controls.
Table S3. Differences of maternal serum concentrations of major perfluorinated compounds between early pregnancy loss cases and controls (ng/mL)
PFCs Median and Interquartile Ranges Pa Cases (n = 41) Controls (n = 47) ∑PFCA 8.856 (6.886−13.711) 8.090 (6.149−14.877) 0.532 PFOA 5.444 (4.836−9.257) 5.723 (4.090−10.371) 0.940 PFNA 0.943 (0.722−1.562) 1.019 (0.700−1.240) 0.837 PFDA 0.961 (0.586−1.454) 0.668 (0.423−0.985) 0.012 PFUdA 0.633 (0.429−0.780) 0.481 (0.335−0.672) 0.016 ∑PFSA 8.087 (5.376−12.632) 7.032 (4.945−11.346) 0.469 PFOS 5.996 (3.848−9.222) 4.976 (2.885−8.685) 0.187 L-PFHxS 0.678 (0.63−0.882) 0.733 (0.493−1.120) 0.260 ∑PFOS substitute 1.917 (1.477−3.044) 1.947 (0.961−2.360) 0.226 9CL-PF3ONS 1.819 (1.437−3.002) 1.910 (0.943−2.295) 0.240 ∑PFCs 19.680 (13.779−29.266) 19.780 (13.864−24.971) 0.746 Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated Compounds; PFCA: perfluorocarboxylic acid; PFOA: Perfluoro-n-octanoic acid; PFNA: Perfluoro-n-nonanoic acid; PFDA: Perfluoro-n-decanoic acid; PFUdA: Perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid; PFSA: perfluorosulfonic acid; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate;L-PFHxS: Sodium perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonate; 9CL-PF3ONS: Potassium 9-chlorohexadeca-fluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate. ∑PFCA were the sum of PFNA, PFDA, PFUdA, PFDoA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA, and PFOA; ∑PFSA were the sum of L-PFHxS, L-PFHpS, P5MHpS, P4MHpS, P3MHpS, P6MHpS, P1MHpS, and PFOS; ∑PFOS substitute was the sum of 11CL-PF3OUdS and 9CL-PF3ONS; ∑PFCs were the sum of ∑PFCA, ∑PFSA, ∑PFOS substitute, and 6:2diPAP. aMann – Whitney U test. Table 1 displays the associations between maternal serum concentrations of major PFCs and risk of early pregnancy loss. After adjusting for parity, maternal passive smoking during the first trimester, and the mother experiencing vaginal bleeding during pregnancy, women with PFDA or PFUdA levels above or equal to the median had higher odds of early pregnancy loss (aOR = 5.00, 95% CI: 1.53–16.33; aOR = 3.87, 95% CI: 1.26–11.89).
Table 1. Association between maternal serum concentrations of major perfluorinated compounds and risk of early pregnancy loss
PFCs (ng/mL) Cases (n = 41) Controls (n = 47) cOR (95% CI) aOR (95% CI)a ∑PFCA < 8.297 19 25 1.00 1.00 ≥ 8.297 22 22 1.32 (0.57–3.05) 1.37 (0.48–3.98) PFOA < 5.640 25 22 1.00 1.00 ≥ 5.640 19 22 0.76 (0.33–1.76) 0.83 (0.29–2.39) PFDA < 0.810 17 30 1.00 1.00 ≥ 0.810 27 14 3.40 (1.42–8.19) 5.00 (1.53–16.33) PFUdA < 0.539 17 30 1.00 1.00 ≥ 0.539 27 14 3.40 (1.42–8.19) 3.87 (1.26–11.89) ∑PFSA < 7.514 20 24 1.00 1.00 ≥ 7.514 21 23 1.10 (0.47–2.53) 1.51 (0.52–4.43) PFOS < 5.244 22 25 1.00 1.00 ≥ 5.244 22 19 1.32 (0.57–3.05) 1.34 (0.46–3.86) L-PFHxS < 0.715 25 22 1.00 1.00 ≥ 0.715 19 22 0.76 (0.33–1.76) 0.84 (0.28–2.52) 9CL-PF3ONS < 1.871 24 23 1.00 1.00 ≥ 1.871 20 21 0.91 (0.40–2.11) 1.53 (0.52–4.47) ∑PFCs < 19.809 21 23 1.00 1.00 ≥ 19.809 20 24 0.913 (0.40–2.11) 1.06 (0.36–3.10) Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated compounds; PFCA: perfluorocarboxylic acid; cOR: crude odds ratio; aOR: adjusted odds ratio; PFOA: Perfluoro-n-octanoic acid; PFNA: Perfluoro-n-nonanoic acid; PFDA: Perfluoro-n-decanoic acid; PFUdA: Perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid; PFSA: perfluorosulfonic acid; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate;L-PFHxS: Sodium perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonate; 9CL-PF3ONS: Potassium 9-chlorohexadeca-fluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate. ∑PFCA were the sum of PFNA, PFDA, PFUdA, PFDoA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA, and PFOA; ∑PFSA were the sum of L-PFHxS, L-PFHpS, P5MHpS, P4MHpS, P3MHpS, P6MHpS, P1MHpS, and PFOS; ∑PFOS substitute was the sum of 11CL-PF3OUdS and 9CL-PF3ONS; ∑PFCs were the sum of ∑PFCA, ∑PFSA, ∑PFOS substitute, and 6:2diPAP. aAdjusted for parity, maternal passive smoking during first trimester and mother having vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. When the 18 PFC compounds were applied in principal component analysis models, three principal components were identified (Supplementary Table S4, available in www.besjournal.com). The first principal component had high factor loadings for most PFSA compounds and explained 32.78% of the total variations in the original PFC concentrations. The second principal component had high factor loadings for most perfluorocarboxylic acid (PFCA) compounds and explained 23.52% of the total variations. The third principal component had high factor loadings for two perfluorosulfonic acid (PFOS) substitutes and PFOA and explained 14.94% of the total variations. Altogether, the three components explained 71.24% of the total variations of PFCs.
Table S4. Rotated factor loading of three principal components identified by principal component analysis
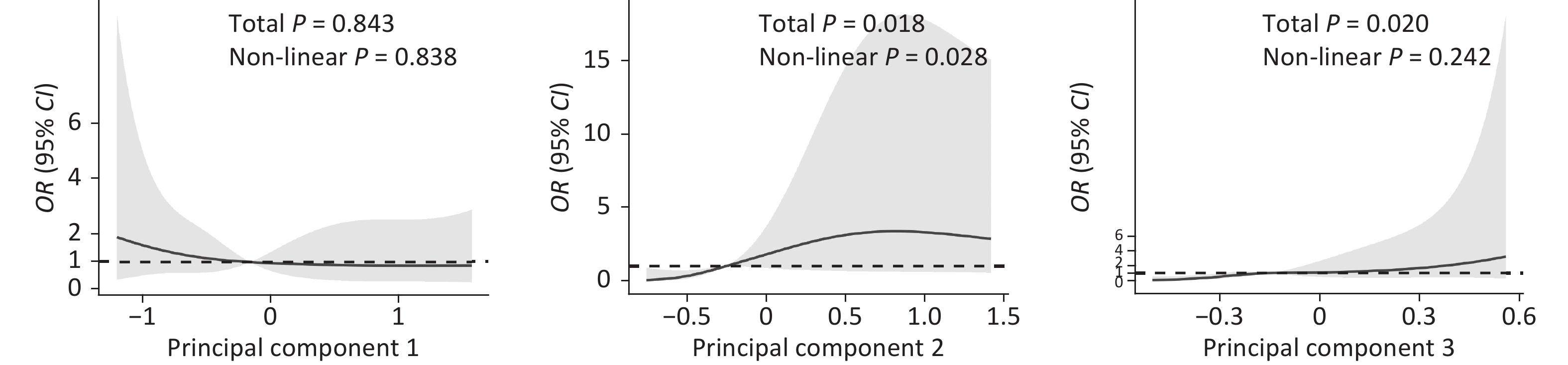
PFCs Factor loading* Explained variance (%) Explained variance cumulative(%) PC-1 (PFSAs) P5MHpS 0.91 32.78 32.78 P4MHpS 0.89 P1MHpS 0.86 P3MHpS 0.74 L-PFHpS 0.67 PFOS 0.62 P6MHpS 0.58 PC-2 (PFCAs) PFDA 0.92 23.52 56.30 PFDoA 0.82 PFUdA 0.79 PFNA 0.45 PFTrDA 0.42 PC-3 (PFOS substitutes) 11CL-PF3OUdS 0.88 14.94 71.24 9CL-PF3ONS 0.83 PFOA 0.40 Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated Compounds; PFNA: Perfluoro-n-nonanoic acid; PFDA: Perfluoro-n-decanoic acid; PFUdA: Perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid; PFDoA: Perfluoro-n-dodecanoic acid; PFTrDA: Perfluoro-n-tridecanoic acid; PFTeDA: Perfluoro-n-tetradecanoic acid; L-PFHpS: Sodium perfluoro-1-heptanesulfonate; P5MHpS: Perfluoro-5-methylheptane sulfonate; P4MHpS: Perfluoro-4-methylheptane sulfonate; P3MHpS: Perfluoro-3-methylheptane sulfonate; P6MHpS: Perfluoro-6-methylheptane sulfonate; P1MHpS: Perfluoro-1-methylheptane sulfonate; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate; 11CL-PF3OUdS: Potassium 11-chloroeicosafluoro-3-oxaundecane-1-sulfonate; 9CL-PF3ONS: Potassium 9-chlorohexadeca-fluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate; PFOA: Perfluoro-n-octanoic acid. PC: principal component. *Factor loadings are the correlation coefficients between the original variables (levels of PFCs) and the extracted components. Principal components with eigenvalue >1 are retained. Variable levels are sorted by the size of the loading coefficients. Variable level with factor loading below |0.30| are not listed. Table 2 presents the associations between the principal component scores of maternal serum concentrations of PFCs in early pregnancy and the risk of early pregnancy loss. The median level of the principal component was taken as the cut-off point to distinguish the higher exposure group and the lower exposure group. After adjustment, women with higher levels of components mainly representing PFCAs or PFOS substitutes had a higher risk of early pregnancy loss (OR = 7.87, 95% CI: 2.19–28.28; OR = 6.91, 95% CI: 2.03–23.56). Figure 1 presents the results of restricted cubic spline analysis that flexibly modeled and visualized the relationships of the three principal components of maternal serum concentrations of PFCs with early pregnancy loss. The patterns of association between PFCs and early pregnancy loss were quite different across the different principal components. Continuously decreasing odds of early pregnancy loss were observed with rising levels of component 1 (mainly representing PFSAs), although the results were not significant. On the contrary, the risk of early pregnancy loss increased significantly (total P < 0.05) until the level of principal component 2 (mainly representing PFCAs) reached approximately −0.25, and became flatter thereafter (P for non-linearity < 0.05). With rising levels of principal component 3 (mainly representing PFOS substitutes), the risk of early pregnancy loss also increased significantly (total P < 0.05).
Table 2. Association between principal component scores of perfluorinated compounds and risk of early pregnancy loss
PFCs (ng/mL) Cases (n = 41) Controls (n = 47) cOR (95% CI) aOR (95% CI) a Principal component 1 (main components: PFSAs) < Median 23 21 1.00 1.00 ≥ Median 18 26 0.63 (0.27–1.47) 0.61 (0.21–1.80) Principal component 2 (main components: PFCAs) < Median 13 31 1.00 1.00 ≥ Median 28 16 4.17 (1.71–10.19) 7.87 (2.19–28.28) Principal component 3 (main components: PFOS substitutes) < Median 14 30 1.00 1.00 ≥ Median 27 17 3.40 (1.41–8.19) 6.91 (2.03–23.56) Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated compounds; cOR: crude odds ratio; aOR: adjusted odds ratio; PFSA: perfluorosulfonic acid; PFCA: perfluorocarboxylic acid; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate. aAdjusted for parity, maternal passive smoking during first trimester and mother having vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. 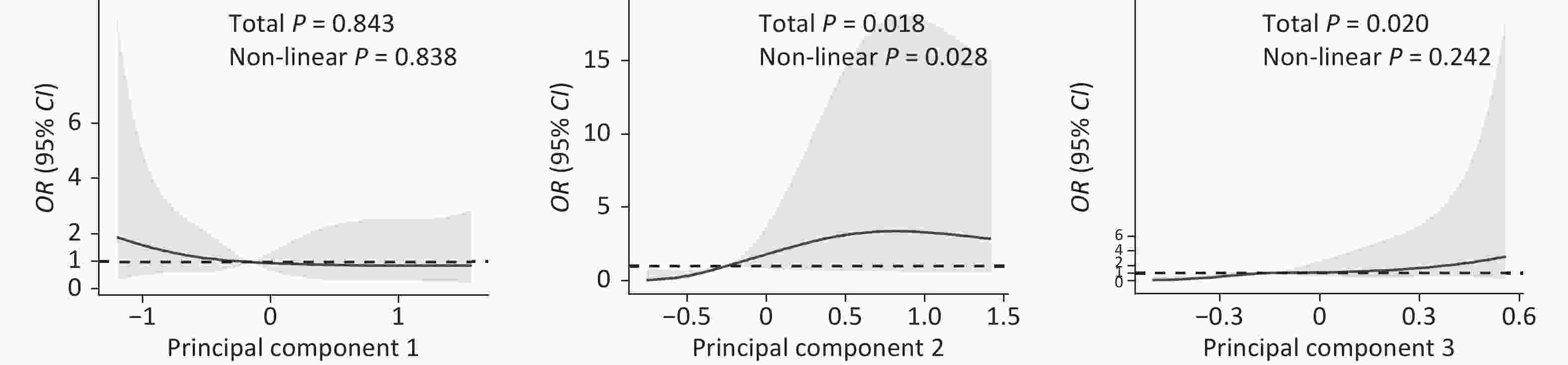
Figure 1. Odds ratio (OR) for early preganncy loss according to continuous value of principal components using restricted cubic spline models. The three principal components were generated through principal component analysis, with Principal Component 1 mainly representing perfluorosulfonic acid, Principal Component 2 representing perfluorocarboxylic acid and Principal Component 3 representing sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate substitutes.
This is the first nested case-control study in a Chinese population to observe that higher levels of maternal serum concentrations of PFDA and PFUdA were associated with an elevated risk of early pregnancy loss. Higher levels of principal components, either representing PFCA or PFOS substitutes, were also associated with an increased risk of early pregnancy loss. These results were consistent with findings from toxicological studies using a variety of animal models, which showed that maternal exposure to PFCs during pregnancy can lead to fetal DNA methylation[5], placental dysfunction[6], and increased reactive oxygen species generation [7]. The findings that all pregnant women were exposed to several kinds of PFCs and the potential association of the exposure with early pregnancy loss calls for added attention on adverse effects of widespread PFC exposure on adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Until now, few studies have reported an association between maternal PFC exposure and pregnancy loss. Of these studies, only Danish and Swedish populations have been analyzed, and the results were inconsistent[3-4,8-9]. The associations between early pregnancy loss and exposure to the most common PFC compounds is still controversial, which might be due to population disparities. Our study did not observe a relationship between early pregnancy loss and PFOA, PFOS, and PFNA, the most widely investigated PFC compounds in previous studies. However, we did identify its relationship with PFDA and PFUdA. In addition, principal component analysis further indicated the synthesized effects of PFCAs and PFOS substitutes. PFDA and PFUdA had relatively low levels compared to PFOA, yet they are all classified as PFCA compounds that have a similar molecular structure, and thus, should have a similar biological toxicity. Therefore, our findings indicated that PFDA and PFUdA were associated with an increased risk of early pregnancy loss, while further studies involving larger cohorts are needed to better understand the mechanisms of actions of PFOA compounds.
To our knowledge, this study is the first to explore the relationship of maternal exposure to PFCs during early pregnancy and risk of early pregnancy loss in a Chinese population. As a nested case-control study in a prospective cohort, the exposure factors of PFCs were collected prior to the occurrence of the adverse pregnancy outcome, thus assisting with the establishment of temporality. Our ability to assess maternal serum concentrations of PFCs during pregnancy adds another strength, considering most previous studies only used serum concentrations of PFCs before or after pregnancy[8] or used historical data to estimate serum concentrations of PFCs during pregnancy[9]. Given the fact that using numerous individual parameters would create false positive results when performing multiple comparisons, and close correlations would likely exist among certain PFC compounds, our study used principal component analysis to help resolve possible multi-collinearity, thereby avoiding misleading interpretations of the effects of individual predictor variables[10]. Furthermore, analyzing the association between principal components and early pregnancy loss was consistent with the fact that humans are exposed to a mixture of PFC compounds simultaneously rather than individual ones.
The primary limitation of our study was the limited sample size, which could have reduced the statistical power and possibly led to insignificant results of the most-often-detected associations of PFOA and PFOS with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Furthermore, many pregnancy losses occur before 8 weeks of gestation. Therefore, the fact that our study did not start follow-up until 8 weeks of gestation might have created a "depletion of susceptibles" bias, wherein the women who were most susceptible to having an early pregnancy loss due to PFC exposure were already lost before their first prenatal visit. Subsequent studies should consider starting follow-up and collecting blood specimens around the time of conception and/or implantation.
In summary, our study found that higher maternal serum concentrations of certain PFCs were associated with an elevated risk of early pregnancy loss within 12 weeks of gestation. Larger cohort and mechanistic studies are needed to further verify our findings and identify the mechanisms behind the associations between maternal exposure to PFCs during pregnancy and adverse pregnancy outcomes, including early pregnancy loss.
Declaration of competing interest None declared.
Acknowledgements We thank the support of Shunyi Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Beijing, China.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.026
Maternal Perfluorinated Compound Exposure and Risk of Early Pregnancy Loss: A Nested Case-control Study
-
&These authors contributed equally to this work.
注释: -
Figure 1. Odds ratio (OR) for early preganncy loss according to continuous value of principal components using restricted cubic spline models. The three principal components were generated through principal component analysis, with Principal Component 1 mainly representing perfluorosulfonic acid, Principal Component 2 representing perfluorocarboxylic acid and Principal Component 3 representing sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate substitutes.
S1. Maternal serum concentrations of perfluorinated compounds during early pregnancy (ng/mL)
PFCs LOD N > LOD (%) 25% 50% 75% PFCA PFBA 0.083 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD PFHpA 0.051 11 (12.50) < LOD < LOD < LOD PFHxA 0.200 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD PFNA 0.337 86 (97.27) 0.718 0.996 1.323 PFDA 0.042 88 (100.00) 0.499 0.810 1.155 PFUdA 0.040 88 (100.00) 0.378 0.539 0.727 PFDoA 0.022 88 (100.00) 0.050 0.070 0.098 PFTrDA 0.017 88 (100.00) 0.091 0.120 0.180 PFTeDA 0.004 88 (100.00) 0.010 0.015 0.025 P5MHpA 0.070 3 (3.41) < LOD < LOD < LOD P6MHpA 0.040 27 (30.68) < LOD < LOD 0.043 P4MHpA 0.100 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD PFOA 0.500 88 (100.00) 4.287 5.640 10.194 PFSA L-PFBS 0.018 64 (72.73) < LOD 0.029 0.058 L-PFHxS 0.036 88 (100.00) 0.474 0.714 0.986 L-PFDS 0.005 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD L-PFHpS 0.034 80 (90.91) 0.076 0.117 0.175 P44DMHxS 0.005 44 (50.00) < LOD < LOD 0.007 P5MHpS 0.020 85 (96.59) 0.160 0.228 0.357 P4MHpS 0.010 85 (96.59) 0.118 0.174 0.240 P3MHpS 0.010 84 (95.45) 0.099 0.141 0.191 P6MHpS 0.050 76 (86.36) 0.179 0.301 0.594 P1MHpS 0.050 83 (94.32) 0.109 0.160 0.235 PFOS 1.500 88 (100.00) 3.423 5.244 9.027 4:2FTS 0.103 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD 6:2FTS 0.200 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD 8:2FTS 0.300 0 (0.00) < LOD < LOD < LOD 6:2diPAP 0.030 87 (98.86) 0.164 0.312 0.594 PFOS substitute 11CL-PF3OUdS 0.007 88 (100.00) 0.025 0.038 0.063 9CL-PF3ONS 0.025 88 (100.00) 1.064 1.871 2.682 TA 0.019 14 (15.91) < LOD < LOD < LOD TeA 0.048 8 (9.09) < LOD < LOD < LOD Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated Compounds; LOD: lower limit of detection; PFCA: perfluorocarboxylic acid; PFBA: Perfluoro-n-butanoic acid; PFHpA: Perfluoro-n-heptanoic acid; PFHxA: Perfluoro-n-hexanoic acid; PFNA: Perfluoro-n-nonanoic acid; PFDA: Perfluoro-n-decanoic acid; PFUdA: Perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid; PFDoA: Perfluoro-n-dodecanoic acid; PFTrDA: Perfluoro-n-tridecanoic acid; PFTeDA: Perfluoro-n-tetradecanoic acid; P5MHpA: Perfluoro-5-methylheptane acid; P6MHpA: Perfluoro-6-methylheptane acid; P4MHpA: Perfluoro-4-methylheptane acid; PFOA: Perfluoro-n-octanoic acid; PFSA: perfluorosulfonic acid; L-PFBS: Potassium perfluoro-1-butanesulfonate; L-PFHxS: Sodium perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonate; L-PFDS: Sodium perfluoro-1-decanesulfonate; L-PFHpS: Sodium perfluoro-1-heptanesulfonate; P44DMHxS: Perfluoro-4,4-dimethylhexane sulfonate; P5MHpS: Perfluoro-5-methylheptane sulfonate; P4MHpS: Perfluoro-4-methylheptane sulfonate; P3MHpS: Perfluoro-3-methylheptane sulfonate; P6MHpS: Perfluoro-6-methylheptane sulfonate; P1MHpS: Perfluoro-1-methylheptane sulfonate; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate; 4:2FTS: Sodium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorohexane sulfonate (4:2); 6:2FTS: Sodium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctane sulfonate (6:2); 8:2FTS: Sodium 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecane sulfonate (8:2); 6:2diPAP: Sodium bis (1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctyl)phosphate; 11CL-PF3OUdS: Potassium 11-chloroeicosafluoro-3-oxaundecane-1-sulfonate; 9CL-PF3ONS: Potassium 9-chlorohexadeca-fluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate; TA: perfluoro-2,5-dimethyl-3,6-dioxanonanoic acid; TeA: perfluoro- (2,5,8-trimethyl-3,6,9-trioxadodecanoic) acid. S2. Maternal socio-demographic, passive smoking, drinking, and disease history characteristics of early pregnancy loss cases and controls
Characteristics Case (n = 41) Control (n = 47) P n (%) n (%) Maternal age at conception < 32 17 (41.46) 21 (44.68) ≥ 32 24 (58.54) 26 (55.32) 0.761 Parity Nulliparous 33 (82.50) 19 (59.38) Parous 7 (17.50) 13 (40.63) 0.029 Maternal history of pregnancy loss No 32 (78.05) 39 (82.98) Yes 9 (21.95) 8 (17.02) 0.559 Maternal education High school or lower 13 (31.71) 12 (25.53) College school or higher 28 (68.29) 35 (74.47) 0.522 Paternal education High school or lower 16 (39.02) 18 (38.30) College school or higher 25 (60.98) 29 (61.70) 0.944 Maternal alcohol drinking during first trimester No 36 (87.80) 46 (97.87) Yes 5 (12.20) 1 (2.13) 0.093* Maternal passive smoking during first trimester No 21 (51.22) 36 (76.60) Yes 20 (48.78) 11 (23.40) 0.013 Mother having fever during pregnancy No 38 (92.68) 46 (97.87) Yes 3 (7.32) 1 (2.13) 0.335* Mother having infections during pregnancy No 40 (97.56) 46 (97.87) Yes 1 (2.44) 1 (2.13) 1.000* Mother having serious nausea and vomiting during pregnancy No 39 (95.12) 44 (93.62) Yes 2 (4.88) 3 (6.38) 1.000* Mother having vaginal bleeding during pregnancy No 25 (60.98) 43 (91.49) Yes 16 (39.02) 4 (8.51) 0.001* Note. *Fisher’s exact test. S3. Differences of maternal serum concentrations of major perfluorinated compounds between early pregnancy loss cases and controls (ng/mL)
PFCs Median and Interquartile Ranges Pa Cases (n = 41) Controls (n = 47) ∑PFCA 8.856 (6.886−13.711) 8.090 (6.149−14.877) 0.532 PFOA 5.444 (4.836−9.257) 5.723 (4.090−10.371) 0.940 PFNA 0.943 (0.722−1.562) 1.019 (0.700−1.240) 0.837 PFDA 0.961 (0.586−1.454) 0.668 (0.423−0.985) 0.012 PFUdA 0.633 (0.429−0.780) 0.481 (0.335−0.672) 0.016 ∑PFSA 8.087 (5.376−12.632) 7.032 (4.945−11.346) 0.469 PFOS 5.996 (3.848−9.222) 4.976 (2.885−8.685) 0.187 L-PFHxS 0.678 (0.63−0.882) 0.733 (0.493−1.120) 0.260 ∑PFOS substitute 1.917 (1.477−3.044) 1.947 (0.961−2.360) 0.226 9CL-PF3ONS 1.819 (1.437−3.002) 1.910 (0.943−2.295) 0.240 ∑PFCs 19.680 (13.779−29.266) 19.780 (13.864−24.971) 0.746 Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated Compounds; PFCA: perfluorocarboxylic acid; PFOA: Perfluoro-n-octanoic acid; PFNA: Perfluoro-n-nonanoic acid; PFDA: Perfluoro-n-decanoic acid; PFUdA: Perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid; PFSA: perfluorosulfonic acid; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate;L-PFHxS: Sodium perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonate; 9CL-PF3ONS: Potassium 9-chlorohexadeca-fluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate. ∑PFCA were the sum of PFNA, PFDA, PFUdA, PFDoA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA, and PFOA; ∑PFSA were the sum of L-PFHxS, L-PFHpS, P5MHpS, P4MHpS, P3MHpS, P6MHpS, P1MHpS, and PFOS; ∑PFOS substitute was the sum of 11CL-PF3OUdS and 9CL-PF3ONS; ∑PFCs were the sum of ∑PFCA, ∑PFSA, ∑PFOS substitute, and 6:2diPAP. aMann – Whitney U test. Table 1. Association between maternal serum concentrations of major perfluorinated compounds and risk of early pregnancy loss
PFCs (ng/mL) Cases (n = 41) Controls (n = 47) cOR (95% CI) aOR (95% CI)a ∑PFCA < 8.297 19 25 1.00 1.00 ≥ 8.297 22 22 1.32 (0.57–3.05) 1.37 (0.48–3.98) PFOA < 5.640 25 22 1.00 1.00 ≥ 5.640 19 22 0.76 (0.33–1.76) 0.83 (0.29–2.39) PFDA < 0.810 17 30 1.00 1.00 ≥ 0.810 27 14 3.40 (1.42–8.19) 5.00 (1.53–16.33) PFUdA < 0.539 17 30 1.00 1.00 ≥ 0.539 27 14 3.40 (1.42–8.19) 3.87 (1.26–11.89) ∑PFSA < 7.514 20 24 1.00 1.00 ≥ 7.514 21 23 1.10 (0.47–2.53) 1.51 (0.52–4.43) PFOS < 5.244 22 25 1.00 1.00 ≥ 5.244 22 19 1.32 (0.57–3.05) 1.34 (0.46–3.86) L-PFHxS < 0.715 25 22 1.00 1.00 ≥ 0.715 19 22 0.76 (0.33–1.76) 0.84 (0.28–2.52) 9CL-PF3ONS < 1.871 24 23 1.00 1.00 ≥ 1.871 20 21 0.91 (0.40–2.11) 1.53 (0.52–4.47) ∑PFCs < 19.809 21 23 1.00 1.00 ≥ 19.809 20 24 0.913 (0.40–2.11) 1.06 (0.36–3.10) Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated compounds; PFCA: perfluorocarboxylic acid; cOR: crude odds ratio; aOR: adjusted odds ratio; PFOA: Perfluoro-n-octanoic acid; PFNA: Perfluoro-n-nonanoic acid; PFDA: Perfluoro-n-decanoic acid; PFUdA: Perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid; PFSA: perfluorosulfonic acid; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate;L-PFHxS: Sodium perfluoro-1-hexanesulfonate; 9CL-PF3ONS: Potassium 9-chlorohexadeca-fluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate. ∑PFCA were the sum of PFNA, PFDA, PFUdA, PFDoA, PFTrDA, PFTeDA, and PFOA; ∑PFSA were the sum of L-PFHxS, L-PFHpS, P5MHpS, P4MHpS, P3MHpS, P6MHpS, P1MHpS, and PFOS; ∑PFOS substitute was the sum of 11CL-PF3OUdS and 9CL-PF3ONS; ∑PFCs were the sum of ∑PFCA, ∑PFSA, ∑PFOS substitute, and 6:2diPAP. aAdjusted for parity, maternal passive smoking during first trimester and mother having vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. S4. Rotated factor loading of three principal components identified by principal component analysis
PFCs Factor loading* Explained variance (%) Explained variance cumulative(%) PC-1 (PFSAs) P5MHpS 0.91 32.78 32.78 P4MHpS 0.89 P1MHpS 0.86 P3MHpS 0.74 L-PFHpS 0.67 PFOS 0.62 P6MHpS 0.58 PC-2 (PFCAs) PFDA 0.92 23.52 56.30 PFDoA 0.82 PFUdA 0.79 PFNA 0.45 PFTrDA 0.42 PC-3 (PFOS substitutes) 11CL-PF3OUdS 0.88 14.94 71.24 9CL-PF3ONS 0.83 PFOA 0.40 Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated Compounds; PFNA: Perfluoro-n-nonanoic acid; PFDA: Perfluoro-n-decanoic acid; PFUdA: Perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid; PFDoA: Perfluoro-n-dodecanoic acid; PFTrDA: Perfluoro-n-tridecanoic acid; PFTeDA: Perfluoro-n-tetradecanoic acid; L-PFHpS: Sodium perfluoro-1-heptanesulfonate; P5MHpS: Perfluoro-5-methylheptane sulfonate; P4MHpS: Perfluoro-4-methylheptane sulfonate; P3MHpS: Perfluoro-3-methylheptane sulfonate; P6MHpS: Perfluoro-6-methylheptane sulfonate; P1MHpS: Perfluoro-1-methylheptane sulfonate; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate; 11CL-PF3OUdS: Potassium 11-chloroeicosafluoro-3-oxaundecane-1-sulfonate; 9CL-PF3ONS: Potassium 9-chlorohexadeca-fluoro-3-oxanonane-1-sulfonate; PFOA: Perfluoro-n-octanoic acid. PC: principal component. *Factor loadings are the correlation coefficients between the original variables (levels of PFCs) and the extracted components. Principal components with eigenvalue >1 are retained. Variable levels are sorted by the size of the loading coefficients. Variable level with factor loading below |0.30| are not listed. Table 2. Association between principal component scores of perfluorinated compounds and risk of early pregnancy loss
PFCs (ng/mL) Cases (n = 41) Controls (n = 47) cOR (95% CI) aOR (95% CI) a Principal component 1 (main components: PFSAs) < Median 23 21 1.00 1.00 ≥ Median 18 26 0.63 (0.27–1.47) 0.61 (0.21–1.80) Principal component 2 (main components: PFCAs) < Median 13 31 1.00 1.00 ≥ Median 28 16 4.17 (1.71–10.19) 7.87 (2.19–28.28) Principal component 3 (main components: PFOS substitutes) < Median 14 30 1.00 1.00 ≥ Median 27 17 3.40 (1.41–8.19) 6.91 (2.03–23.56) Note. PFCs: Perfluorinated compounds; cOR: crude odds ratio; aOR: adjusted odds ratio; PFSA: perfluorosulfonic acid; PFCA: perfluorocarboxylic acid; PFOS: Sodium perfluoro-octanesulfonate. aAdjusted for parity, maternal passive smoking during first trimester and mother having vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. -
[1] Wang XB, Chen CZ, Wang LH, et al. Conception, early pregnancy loss, and time to clinical pregnancy: a population-based prospective study. Fertil Steril, 2003; 79, 577−84. doi: 10.1016/S0015-0282(02)04694-0 [2] Buck RC, Franklin J, Berger U, et al. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: terminology, classification, and origins. Integr Environ Assess Manag, 2011; 7, 513−41. doi: 10.1002/ieam.258 [3] Liew Z, Luo JJ, Nohr EA, et al. Maternal plasma perfluoroalkyl substances and miscarriage: a nested case-control study in the Danish national birth cohort. Environ Health Perspect, 2020; 128, 047007. doi: 10.1289/EHP6202 [4] Liu XT, Chen D, Wang B, et al. Does low maternal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances elevate the risk of spontaneous preterm birth? A nested case- control study in China. Environ Sci Technol, 2020; 54, 8259−68. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c01930 [5] Starling AP, Liu CN, Shen GN, et al. Prenatal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, umbilical cord blood DNA methylation, and cardio-metabolic indicators in newborns: the healthy start study. Environ Health Perspect, 2020; 128, 127014. doi: 10.1289/EHP6888 [6] Wan HT, Wong AYM, Feng S, et al. Effects of In utero exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate on placental functions. Environ Sci Technol, 2020; 54, 16050−61. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c06569 [7] Sonkar R, Kay MK, Choudhury M. PFOS modulates interactive epigenetic regulation in first-trimester human trophoblast cell line HTR-8/SVneo. Chem Res Toxicol, 2019; 32, 2016−27. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.9b00198 [8] Stein CR, Savitz DA, Dougan M. Serum levels of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate and pregnancy outcome. Am J Epidemiol, 2009; 170, 837−46. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwp212 [9] Savitz DA, Stein CR, Bartell SM, et al. Perfluorooctanoic acid exposure and pregnancy outcome in a highly exposed community. Epidemiology, 2012; 23, 386−92. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e31824cb93b [10] Jolliffe IT, Cadima J. Principal component analysis: a review and recent developments. Philos Trans Roy Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci, 2016; 374, 20150202. -
 21353Supplementary Materials.pdf
21353Supplementary Materials.pdf

-




 下载:
下载:





 Quick Links
Quick Links