HTML
-
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication or detectable serum HBV DNA has been shown to be closely associated with the progression of liver disease, liver function decompensation, and the occurrence of cirrhosis and liver cancer in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) infection[1]. HBV replication or serum HBV DNA load has also been shown to be closely associated with other organic diseases associated with HBV, such as glomerulonephritis[2]. Antiviral therapy is the most important strategy to slow the disease progression and prevent the occurrence of hepatic cancer and cirrhosis, thus reducing the mortality related with liver disease[3]. Maintaining low HBV replication and HBsAg, especially HBsAg seroconversion by antiviral therapy, can improve the long-term outcomes in patients.
In antiviral therapy, interferon (IFN) exhibits direct antiviral[4-5] and immune regulation actions by which it inhibits HBV replication and induces or strengthens the HBV-specific or -nonspecial immunity, thereby leading to elimination of the virus-infected cells[5-6] and clearing the cccDNA content or reducing HBsAg levels[7-8]. Several studies have demonstrated that serum HBsAg levels correlated with the cccDNA content in the liver[9-10] and can reflect the extent of infected cell clearance and the immune control against HBV infection. This is because serum HBsAg levels were significantly lower in inactive HBsAg carriers than those in patients with active liver inflammation[11]. Serum HBsAg concentration is also an important indicator that reflects whether the patients exhibit active liver inflammation[12-13]. HBsAg loss is the only factor indicating good long-term outcome, which is defined as no occurrence of hepatic cell carcinoma (HCC) and decompensation of liver function, for the individual patient[14-15]. Moreover, HBsAg loss is a unique parameter determining drug withdrawal in HBeAg-negative patients after antiviral treatment and also the ideal endpoint or the ultimate aim of antiviral therapy[14]. HBsAg loss/seroconversion is associated with improved long-term outcomes in patients with HB infection[16]. Therefore, t he mechanism of predicting and increasing the rate of HBsAg loss is very important in clinical practice for patients during antiviral treatment. Reducing the incidence of HCC by antiviral therapy in patients with chronic HBV infection has been considered as an important goal in guidelines[14, 17-19]. China is a country with a high incidence of CHB virus infection, with > 80% of HCC occurring in patients with chronic HBV infection[20]. Therefore, HBsAg loss is of most importance in Chinese patients with chronic HBV infection. Previous studies have demonstrated that patients with HBeAg-positive CHB infection who can mount a response, defined as HBeAg seroconversion after treatment, to interferon therapy should exhibit early and sharp decline of HBsAg levels and that HBsAg loss during antiviral treatment was rare. To our knowledge, there has been no study investigating the change in HBsAg levels in patients with CHB infection who achieved HBsAg loss during Pegylated interferonalpha-2 (PEG-IFNα-2a) treatment. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to determine the baseline characteristics and the pattern of changes in HBsAg levels during PEG-IFNα-2a treatment in patients with HBeAg-positive CHB infection who achieved HBsAg loss during the treatment.
-
This retrospective study comprised the population of consecutive patients with HBeAg-positive CHB infection who achieved HBsAg loss/seroconversion during PEG-IFNα-2a therapy at the liver disease center of Beijing Ditan Hospital from December 2008 to September 2016. The study participants included treatment-naive patients, patients who maintained undetectable serum levels of HBV DNA with nucleotide analog (NA) treatment, and those who remained HBV DNA positive with NA treatment, including patients with relapse, resistance, or poor response. The naive patients who were HBsAg positive and HBeAg-positive for more than 6 months and had detectable HBV DNA levels and abnormal glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (ALT) for more than 3 months were enrolled. Patients who remained HBsAg positive and HBeAg-positive, with detectable or undetectable HBV DNA levels and abnormal or normal ALT, even after treatment with an NA, were also included. The exclusion criteria were active consumption of alcohol and/or drugs, coinfection with human immunodeficiency virus or hepatitis C virus, cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis, evidence of neoplastic liver disease, and contraindications to IFN. All patients were positive for HBsAg and negative for anti-HBs prior to treatment with PEG-IFNα-2a.
After enrollment, patients received weekly subcutaneous injections of PEG-IFNα-2a 180 mg, but the use of other immunosuppressive, regulatory, and antiviral drugs was prohibited during the PEG-IFNα-2a treatment. In clinical practice, patients received tailored treatment time for HBsAg loss, and if there was a sustained HBsAg decline based on undetectable HBV DNA during the PEG-IFNα-2a treatment, the therapy will be continued until the patients achieved HBsAg loss.
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the ethics committees of Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University. All patients gave their written consent.
-
Liver function parameters, including serum ALT, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), albumin (ALB), and total bilirubin (Tbil) concentrations, were measured using an automated biochemical analyzer (Hitachi 7600-11; Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) approximately every 1-3 months.
HBV DNA was quantitated using a commercially available real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR kit with a limit of detection of 100 IU/mL (Piji Company, Shenzhen City, China). HBsAg, anti-HBs, HBeAg, and anti-HBe were detected using Abbott Architect i2000 kits (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL, USA), which was based on an automated chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay. Serum quantitative HBsAg levels were determined using Abbott Architect HBsAg QT assay (range: 0.05-250 IU/mL). Samples were finally diluted 1:1, 000 with the Architect HBsAg diluent to expand the upper limit of the dynamic range from 250 to 250, 000 IU/mL. HBsAg loss was defined as HBsAg concentration < 0.05 IU/mL. Anti-HBs were measured using the Architect i2000 kit (Abbott Laboratories), with a range of 0.00-1, 000 mIU/mL. Anti-HB concentration ≥ 10 mIU/L was considered positive. All parameters were monitored at baseline and every 3 months during treatment.
-
The primary endpoint was HBsAg loss/seroconversion with the treatment, and the secondary endpoint was the decline in HBsAg levels, compared to those at baseline, and the rate of undetectable HBV DNA after the treatment.
-
Kidney function and peripheral blood neutrophil and platelet counts were determined before treatment and every 1-3 months, and thyroid function, antithyroglobulin antibody (TgAb), and thyroidperoxidase antibodies (TPOA b) were monitored every 3 months during the treatment.
-
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS (version 19, Chicago, IL, USA). Serum HBV DNA levels and HBsAg concentrations were logarithmically transformed for analysis. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation or median (interquartile range, IQR) and median (range), and categorical variables were expressed as absolute and relative frequencies. Characteristics were compared between groups using χ2 or Fisher's exact tests for analysis of categorical variables and Mann-Whitney and two-sample Student's t-tests for analysis of continuous variables, as appropriate. A two-sided P value of < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
-
Of 1, 024 patients with HBeAg-positive CHB infection who received PEG-IFNα-2a treatment, there were 121 patients who achieved HBsAg loss/seroconversion and were enrolled in the analysis. Of the 121 patients, there were 81 males and 40 females, with a median age of 28.00 (range: 4-63) years, viral genotype C 72, and viral genotype B 49, as shown in Table 1. Patients with viral genotype C accounted for the majority, a finding consistent to that reported by Jiang et al.[21]. Besides 84 treatment-naive patients, there were 37 patients who had been treated with NAs (of which 14 were treated with ADV, 5 with ETV, and 18 with LAM, with 12 showing drug resistance or poor response). The individual-based treatment time was 107 (range: 16-304) weeks.
Clinical Characteristics Total (N = 121) Naive (N = 84) NA Treatment (N = 37) Male/female 81/40 54/30 27/10 Age (y) (median, range) 28.00 (4-63) 29.00 (4-63) 27.00 (17-55) Years of HBV infection (y) (median, range) 12.23 (2-30) 9.36 (2-30) 13.28 (6-24) ALT leve l (median, IQR) 86.0 (40.0, 209.5) 116.0 (61.0, 242.0) 31.5 (19.0, 86.3) No. of HBV DNA (+) 96 84 12 HBV DNA load (log IU/mL) (mean ± SD) 6.15 ± 1.45 6.23 ± 1.33 5.91 ± 1.74 No. of HBV DNA (-) 25 0 25 HBeAg content (PEIU/mL) (median, IQR) 534.54 (16.87, 1295.63) 683.79 (56.00, 1330.00) 39.34 (4.56, 857.51) HBsAg level (log IU/mL) (mean ± SD) 3.08 ± 0.97 3.23 ± 0.89 2.75 ± 1.08 Viral genotype C 72 50 22 B 49 34 5 NA treatment course (m) (median, range) 24.0 (4-84) - 24.0 (4-84) Table 1. Baseline Characteristic of the Patients
-
The median ALT level in all patients was 86.0 (range: 40.0-209.5) U/L. Median ALT level in treatment-naive patients was 116.0 (range: 61.0-242.0) U/L, which was much higher than the level recommended by guidelines for patients who need to be treated (2ULN, 80 U/L). There were 96 patients who were HBV DNA positive before treatment (84 treatment-naive patients and 12 re-treatment patients). The mean serum HBV DNA load was 6.15 ± 1.45 log IU/mL. In all patients, the mean baseline serum HBsAg level was 3.08 ± 0.97 log IU/mL and the median serum HBeAg content was 534.54 (range: 16.87-1295.63) PEIU/mL. The baseline characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1.
-
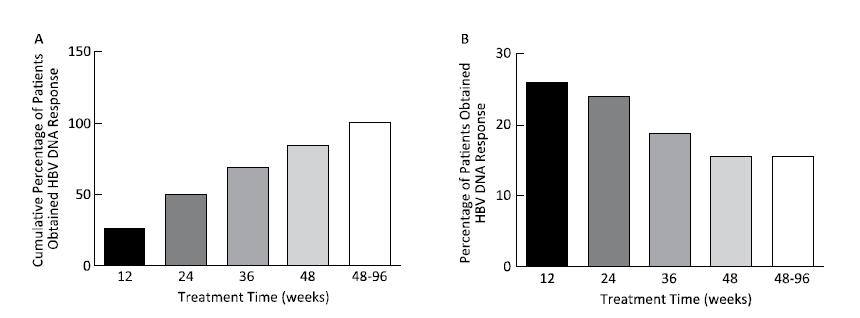
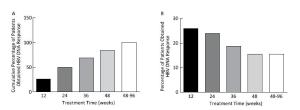
All patients obtained virological response (less than the lower limit of detection); the time to achieve undetectable HBV DNA was 24.50 (range: 2-93) weeks, 50% (48 cases) of patients achieved in 24 weeks, 84.37% (81 cases) in 48 weeks, and all patients in 96 weeks, as shown in Figure 1.
-
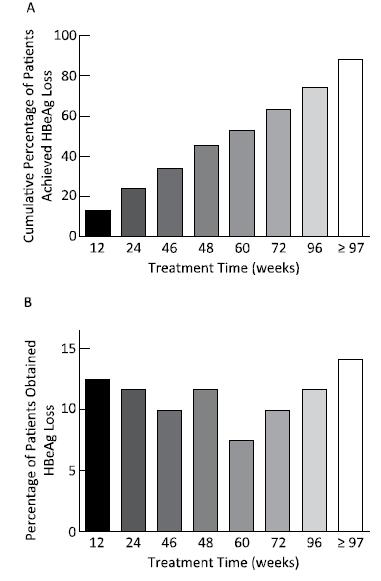
A total of 88.4% (107 cases) of patients achieved serum HBeAg loss. The serum HBeAg loss occurred was at 48.0 (range: 2.0-257.0) weeks of treatment, and the time of HBeAg seroconversion occurred at 53.0 (range: 2.0-257.0) weeks. The rate of HBeAg loss occurred at every point time was similar, as shown in Figure 2. Serum HBeAg in 14 (11.6%) patients who had achieved HBsAg loss was still positive, with the HBeAg content of 7.04 ± 8.65 PEIU/mL.
-
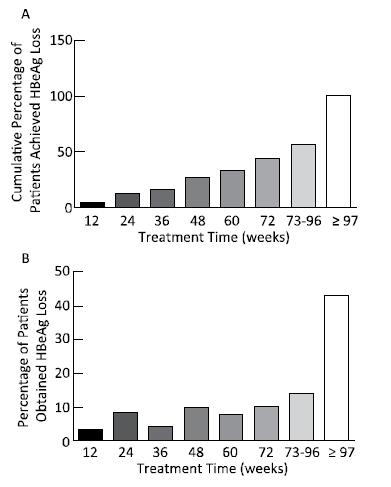
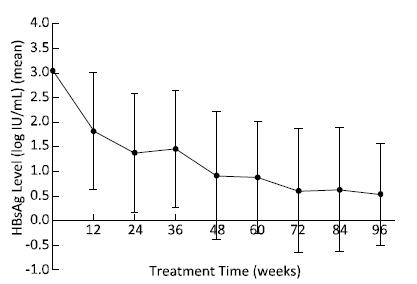
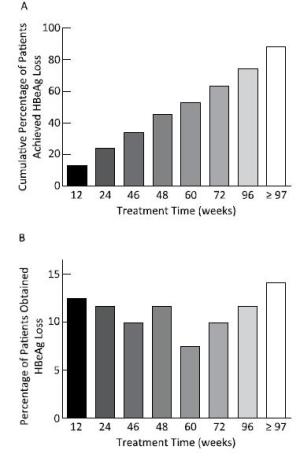
The median time for HBsAg loss was 84 (range: 7-273) weeks, and 74.38% (90 cases) of the patients achieved after extended treatment (> 48 weeks), as shown in Figure 3. However, HBsAg levels in patients who achieved HBsAg loss after 48 weeks reached extremely low values [10.95 (range: 1.73-81.42) IU/mL]. All patients had a sustained decrease in HBsAg levels during treatment and had a sharp and significant decline at 12 (t = 6.532, P < 0.001) and 24 weeks (t = 8.878, P < 0.001), with degrees of 1.27 ± 1.06 log IU/mL and 1.80 ± 1.10 log IU/mL, respectively, compared to those at baseline, as shown in the Figure 4. 88.1% of patients at 12 weeks and 92.6% of patients at 24 weeks achieved HBsAg < 1, 500 IU/mL.
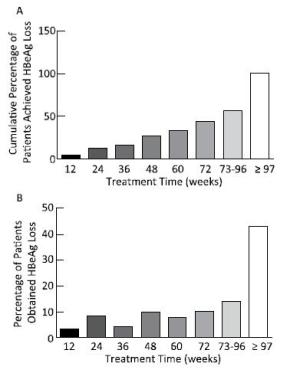
Figure 3. Percentage of HBsAg loss occurring in patients during different treatment time points. Although the cumulative percentage of HBsAg loss increased with extended treatment (A), more than half of the HBsAg loss (57.02%) occurred after 73 weeks of treatment (B).
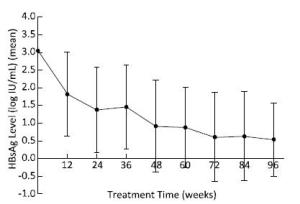
Figure 4. The change in HBsAg levels during treatment in all patients. HBsAg levels decreased continuously, and there was a sharp decrease at 12 and 24 weeks.
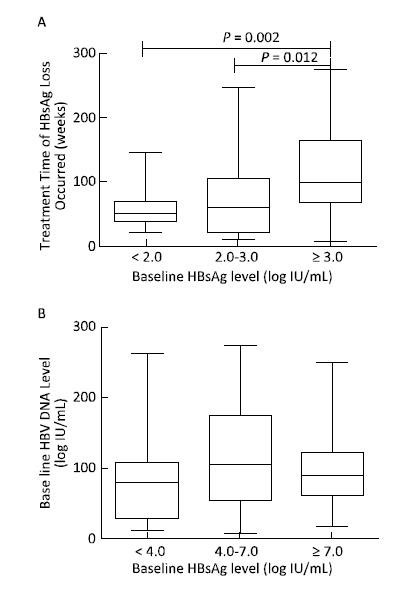
Using baseline HBsAg and HBV DNA levels as independent variables for correlation analysis, we observed that the treatment time needed for HBsAg loss correlated with baseline HBsAg levels (B = 14.465, t = 2.342, P = 0.021); the higher the HBsAg level, the longer the treatment time needed for achieving HBsAg loss. However, baseline HBV DNA did not correlate with the treatment time needed for HBsAg loss (B = 5.016, t = 1.402, P = 0.164), as shown in Figure 5.
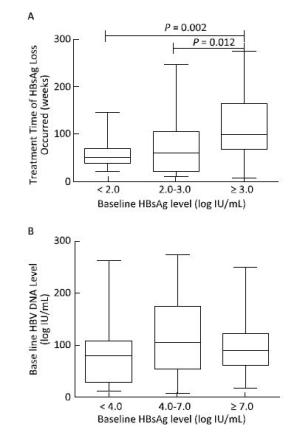
Figure 5. The relationship between baseline HBV DNA, HBsAg level, and the treatment time needed for HBsAg loss. The treatment time needed for HBsAg loss increased with high baseline HBsAg levels (A). However, baseline HBV DNA load was not related to the treatment time needed for HBsAg loss (B).
Results of the regression analysis showed that the degree of HBsAg decline at 12 and 24 weeks compared to those at baseline did not significantly correlate with the treatment time needed for HBsAg loss (B = -9.038, t = -9.038, P = 0.414 and B = -12.204, t = -12.204, P = 0.247). Nevertheless, when baseline HBsAg level and the degree of HBsAg decline at 12 and 24 weeks on treatment were combined into the analysis, the results revealed that baseline HBsAg level and the degree of HBsAg decline at 24 weeks significantly correlated with the treatment time needed for HBsAg loss (B = 29.862, t = −4.890, P < 0.001 and B = -27.993, t = -27.993, P = 0.005). This result indicated that the treatment time needed for HBsAg loss was determined by baseline HBsAg level combined with the decline degree at 24 weeks; the lower the baseline level of HBsAg and the more greatly HBsAg decreased at 24 weeks of treatment, the shorter the treatment time needed for HBsAg loss.
-
The natural history of chronic HBV infection can be divided into phases as follows: immunetolerant, HBeAg-positive immune active or known as immune clearance, and inactive and HBeAg-negative immune reactive phases[14, 18-19]. In HBeAg-positive immune active and HBeAg-negative immune reactive phases, patients have moderate-to-severe inflammation or fibrosis, and antiviral therapy is the important method for preventing and delaying the progression of liver disease. Although using NAs can effectively inhibit HBV replication and remit liver inflammation, viral relapse and inflammatory reactions often occur after cessation of therapy even after achieving HBeAg seroconversion during treatment[14]. In contrast to patients who often show relapse with HBeAg seroconversion achieved by NA therapy, response can be sustained in patients who achieve HBeAg seroconversion by interferon treatment[22-23]. Therefore, PEG-IFN is recommended as the first-line drug for treating patients with HBeAg-positive CHB infection[24]. Viral response can be sustained in most patients who achieve HBeAg seroconversion by PEG-IFN treatment, but a rate of 1.5%-3.3% of relapse annually has been reported in these inactive carriers[25-27], and 1%-17% of cases had sustained reversion back to HBeAg-positive hepatitis in a long-term longitudinal study[28]. Patients who are HBeAg-negative still develop HCC[29]. The only predictive factor for a good long-term clinical outcome was HBsAg loss[14-15]. Thus, HBsAg loss has become the ideal endpoint and the ultimate goal of antiviral therapy in patients with CHB infection[14, 18-19].
HBsAg loss was rare in standard treatment (PEG-IFN for 48 weeks) of patients with CHB infection[30-31]. For enhancing the efficacy of PEG-IFN treatment, patients needed extended treatment and received tailored treatment time[31-32]. Thus, early prediction of the response is important in patients with CHB infection treated with PEG-IFN. Baseline HBsAg level and the decline with treatment can predict HBeAg seroconversion after treatment in HBeAg-positive patients[31, 33] and the sustained viral response in HBeAg-negative patients[34-36]. HBeAg-positive patients with HBsAg < 1, 500 IU/mL had high rates of HBeAg seroconversion and sustained viral response[31, 37-38], and in patients with HBsAg > 20, 000 IU/mL at week 24, the treatment should be stopped[33].
Only few studies have been conducted to predict HBsAg loss during treatment with PEG-IFN in HBeAg-positive patients. In this study, we investigated the HBsAg level and its declining pattern with PEG-IFN treatment in patients with HBeAg-positive CHB infection who achieved HBsAg loss during treatment. We observed that serum HBV DNA in all patients reached undetectable levels at a median of 24.50 weeks, although the median time needed for HBsAg loss was 84 weeks. This finding agrees with another study that reported that HBV DNA response at 24 weeks was the basic factor for predicting the efficacy of PEG-IFN in HBeAg-positive patients[31]. The results indicate that HBV DNA reaching undetectable levels early was necessary for HBsAg loss in patients with HBeAg-positive CHB infection during pegylated interferon alpha-2a treatment.
In the present study, patients had a baseline HBsAg level of 3.08 ± 0.97 log IU/mL, which was lower than that reported in another study on HBsAg levels of HBeAg-positive patients on the natural history of the infection[39], and baseline HBsAg level correlated with the time needed for HBsAg loss. All patients had a sharp and great degree of HBsAg decrease at 12 and 24 weeks, with decreases of 1.27 ± 1.06 log IU/mL and 1.80 ± 1.10 log IU/mL, respectively, compared to those at baseline. Moreover, 88.1% of patients at 12 weeks and 92.6% of patients at 24 weeks achieved HBsAg < 1, 500 IU/mL. However, the degree of HBsAg decrease at 12 and 24 weeks showed no correlation with the time needed for HBsAg loss. Nevertheless, combining baseline HBsAg level and its decrease at 12 and 24 weeks for regression analysis revealed that baseline HBsAg level and its decrease at 24 weeks correlated with the time needed for HBsAg loss.
It was observed that extended treatment can improve the efficacy, including enhancing the rate of HBsAg loss and seroconversion, of PEG-IFN treatment in patients with CHB infection[40]. In this study, all patients received a tailored treatment course for HBsAg loss based on sustained HBsAg decrease. Although patients in our study had an early viral response, low baseline HBsAg levels, and a great degree of HBsAg decline early, HBsAg loss occurred at 84 weeks and 74.4% of patients needed extended treatment for HBsAg loss; the higher the baseline HBsAg level, the longer the time required to treat.
There were few limitationsin the present study. A liver biopsy was not taken in patients; thus, the effects of the degree of liver inflammation and the stage of fibrosis on the efficacy of PEG-IFN treatment were not analyzed.
Results of this study suggested that based on early viral response, low baseline HBsAg levels with a great degree of decrease and extended treatment were an indicator for patients who could achieve HBsAg loss on PEG-IFN treatment. Based on these results, it is suggested that baseline HBsAg levels[41-42] and extended therapy are critical steps toward HBsAg loss. In clinical practice, for patients with low baseline HBsAg levels with a significant decrease during early therapy, their treatment course should be extended to improve the rate of HBsAg loss. It is worth nothing that although patients achieved HBsAg loss, 11.6% of them had no HBeAg loss. The long-term outcome in these patients needs further observation.







 Quick Links
Quick Links
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: