HTML
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) is the etiological agent of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV-1 is a highly variable virus, and on the basis of genetic similarities, it has been classified into four groups including M (the 'major' group) and O (the 'outlier' group), as well as groups N and P. Group M viruses, including subtypes A, B, C, D, F, G, H, J, and K; several unique recombinant forms (URFs); and circulating recombinant forms (CRFs), are responsible for the majority of the global HIV-1 infections[1-2]. In China, the greatest diversity of HIV-1 subtypes, known as CRFs, emerged via recombination. A recent report of a nationwide molecular epidemiological survey in China indicated that three recombinant subtypes, CRF01_AE, CRF07_BC, and CRF08_BC, are responsible for 35.5%, 27.6%, and 20.1%, respectively, of infections among drug users, whereas subtype B' accounts for 9.6% of infections. CRF01_AE has replaced subtype B' as the major causative agent of infection among men who have sex with men (MSM)[3-4].
It also should be noted that strong multiple-drug resistance may be induced by recombination; this phenomenon should be considered during formulation of strategies for antiretroviral therapy (ART) to combat HIV infection in China[5]. Genetic recombination may also lead to structural changes of critical proteins, such as the envelope and capsid; these alterations may have a considerable influence on any drug design program based on such targets[6].
Sticht et al. in 2005 reported identification of capsid assembly inhibitor (CAI), a 12-mer peptide, by phage display techniques, and demonstrated in vitro that it targets the capsid and inhibits HIV-1 assembly[7] by interfering with the formation of immaturelike and maturelike particles. In contrast, CAI cannot penetrate cells; therefore, it does not have any antiviral activity against HIV-1 in cell-culture-based assays and hence is unsuitable as an antiviral drug. Using an i, i+4-hydrocarbon stapling technique[8-10], our group converted CAI to NYAD-1, and showed its ability to penetrate cells and its anti-HIV-1 activity[11]. Recently, we reported i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides, including NYAD-36, -67, and -66, which show somewhat less penetration of target cells than i, i+4-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides do. Nonetheless, they bind to the capsid strongly in isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) assays, as well as in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis, and they impair processing of a Gag precursor. Furthermore, these i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides were shown to target both viral assembly and entry[12]. Our earlier study on NYAD-36 identified two mutations in the envelope glycoprotein V120Q in conserved region 1 of gp120 and A327P at the base of the V3 loop in gp120, respectively[12], and confirmed that these stapled peptides have dual targets.
The present study shows evaluation of the sensitivity of HIV-1 subtypes CRF01_AE and CRF07_BC, which have been the predominantly circulating subtypes in China, to the dual-acting i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides. Our study is expected to shed light on the antiviral efficacy of the stapled peptides and to provide valuable information on the rational design of stapled peptides for HIV-1 CRFs and URFs in China and other countries.
-
Three i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides (Table 1), NYAD-36, -67, and -66, were synthesized by CPC Scientific Inc. (San Jose, CA) as previously described[12]. TZM-bl cells, which originate from HeLa cells and express CD4, CCR5, CXCR4, β-galactosidase, and luciferase, were obtained through the NIH AIDS Reagent Program. HEK 293T/17 cells and TZM-bl cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (Hyclone, Logan, UT) containing 1% of a penicillin solution (Gibco, Massachusetts, USA), 10% of fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, Massachusetts, USA), and 1% of a streptomycin solution (Gibco, Massachusetts, USA). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from concentrated white blood cells using Ficoll-Paque™ PLUS (GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ), a sterile density gradient centrifugation medium. Concentrated white blood cells were separated from healthy donors' whole blood collected at the Beijing Red Cross Blood Center (http://www.brcbc.org/) with the informed consent signed, in accordance with the national standard (GB 18467-2011). The researchers who used the PBMCs for culturing HIV-1 isolates did not have information about the relation of samples to the blood donors. PBMCs were grown in the RPMI 1640 medium (Hyclone) supplemented with recombinant interleukin 2 (IL-2; Sigma; 20 U/mL), penicillin and streptomycin solution (1%), and FBS (10%). The HIV-1 clinical isolates, CRF_01AE and CRF07_BC, were isolated from the blood of preselected patients infected with HIV-1, who participated in a multicenter AIDS Cohort Study in China during 2005-2008, with the informed consent signed[13].
Peptide Sequence Net Charge MW CAI ITFEDLLDYYGP NYAD-36 ISF-R8-ELLDYY-S5-ESGS -4 1857 NYAD-66 ISF-R8-ELLDYY-S5-ED -4 1740 NYAD-67 ISF-R8-EWLQAY-S5-EDE -4 1863 Note.S5 [(S)-2-(4'-pentenyl) alanine] and R8 [(R)-2-(7'-octenyl) alanine] indicate stapling sites in the peptide sequence. MW, molecular weight. Table 1. The Sequences of Three i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled Peptides
-
Inhibitory activity of the i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides on infection by primary HIV-1 isolates was determined as described elsewhere[14]. Briefly, PBMCs were resuspended at 3 × 106/mL in RPMI-1640 containing 10% of FBS, 5 μg/mL phytohemagglutinin, and 20 U/mL IL-2 (Sigma), followed by incubation at 37 ℃ for 3 days. The phytohemagglutinin-stimulated cells (105) were infected with the corresponding primary HIV-1 isolates and Laboratory-adapted HIV-1 strain SF33 at 50% tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) of 200 in the absence or presence of i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides at graded concentrations. HIV-1 fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide (T-20) and protease inhibitor ritonavir served as controls. Culture media were changed every 3 days. The supernatants were collected 7 days postinfection and tested for the p24 antigen by a sandwich ELISA. The percentage of relative inhibition of p24 production and half-inhibitory concentration (IC50) values were calculated as previously described[14].
-
Viral RNA was extracted from a virus isolated from HIV-1 patients using an RNA extraction kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The viral RNA was used to generate reverse-strand cDNA by means of an RT-PCR kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). The sequences of gag, pol, and env regions were then amplified by nested PCR[3, 15-16]. The amplified fragments were identified by agarose gel electrophoresis, purified with the QIAquick Gel Extraction kit (QIAGEN), directly sequenced on an ABI 377 Sequencer (Applied Biosciences), and then analyzed by Sequencher 4.10.1 and MEGA5.
-
The panel of chronic CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE gp160 clones was derived from intravenous drug users and MSM and was obtained from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Stocks of single-round-infection HIV-1 Env pseudovirus were produced by cotransfecting 293T/17 cells (3 × 106-5 × 106 cells per T-75 flask) with 4 µg of an HIV-1 env expression plasmid and 8 µg of an env-deficient HIV-1 backbone plasmid (pSG3△Env) using the FuGENE reagent. The pseudovirus-containing supernatant was harvested 24-48 h after transfection and clarified by centrifugation and 0.45-μm filtration. Single-use aliquots (1.0 mL) were stored at -80 ℃. TCID50 for each pseudovirus preparation was determined by infection of TZM-bl cells as previously described[17].
-
The inhibitory activity of the i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides on infection by Env-pseudotyped HIV-1 viruses was tested in TZM-bl cells[12]. Briefly, 100 µL of TZM-bl cells at 105/mL was added into the wells of a 96-well tissue culture plate and incubated at 37 ℃ overnight. Next, 50 µL of a serially diluted i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptide or a complete culture medium was mixed with 50 µL of the Env-pseudotyped virus at TCID50 of 100. Following incubation at 37 ℃ for 30 min, the mixture was added to the cells and cocultured for 48 h. T-20 served as a control. Luciferase activity was measured using a luciferase assay kit (Promega Corp.). The percent inhibition and the IC50s were calculated using three replicates for each virus and expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
-
Toxicity of the i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides for PBMCs and TZM-bl cells was analyzed by means of the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8; Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan)[14]. Briefly, 100 µL of a peptide at graded concentrations was added to an equal volume of cells (PBMCs 106/mL and TZM-bl cells 105/mL) in 96-well plates followed by incubation at 37 ℃; the procedure was similar to the antiviral activity assay (except the medium was added instead of the virus). After addition of the CCK-8 reagent, the culture supernatant was analyzed colorimetrically at 450 nm 2 h later with a reference at 630 nm. The percentage cytotoxicity and the half maximal growth inhibitory concentration (CC50) values were calculated in the GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad Software Inc.).
-
Correlations between antiviral activity and variables were analyzed by Spearman's rank test (SPSS software package, version 17.0). The P value of ≤ 0.05 served as the criterion for statistical significance.
Stapled Peptides, Cells, and Viruses
Antiviral Activity of the i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled Peptides against Primary HIV-1 Isolates CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE in PBMCs
Analysis of Isolated HIV-1 gag, pol, and env Regions
HIV-1 Env Pseudovirus Production and Titration
Antiviral Activity of the i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled Peptides against CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE Env-pseudotyped Virus in TZM-bl Cells
Cytotoxicity Assay
Statistical Analysis
-
Five HIV-1 CRF07_BC isolates using CCR5 as a coreceptor were isolated from HIV-1-positive patients who had the average viral load of 5.56 log10 copies/mL, ranging from 4.0 to 6.2 log copies/mL, and the average CD4 count of 303 cells/µL, ranging from 75 to 590 cells/µL. Three HIV-1 CRF01_AE isolates using CCR5 as a coreceptor came from HIV-1-positive patients who had the average viral load of 5.63 log10 copies/mL, ranging from 5.2 to 5.9 log copies/mL, and the average CD4 count of 613 cells/µL, ranging from 598 to 628 cells/µL[13].
The phylogenetic tree was constructed to compare the sequences of gag, pol, and env genes of these isolated viruses with the reference sequences (e.g., HIV-1 subtype B, CRF07_BC, and CRF01_AE) available from the HIV database (http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/components/sequence/HIV/search/search.html) (Figure 1). CBJB257, CBJB256, XJDC6291, XJDC6371, and XJDC6331 were identified as subtype CRF07_BC. CYM015, BJMSM543, and BJMSM376 were identified as subtype CRF01_AE.
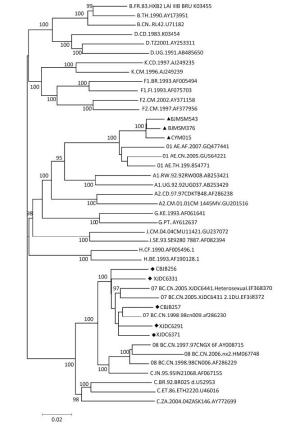
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of HIV-1 isolates predominantly circulating in China. The viral gag, pol, and env sequences were obtained by PCR analysis of a virus isolated from HIV-1 patients in China. '◆' and '▲' represent CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE strains under study, respectively. Bootstrap values ( > 70) are shown at the corresponding nodes. The reference sequences were downloaded from the HIV database (http://ww.hiv.lanl.gov.contont/sequence/HIV/mainpage.html).
-
The inhibitory activity of the three i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides against eight HIV-1 clinical isolates from China was first evaluated by a multicycle infectivity assay. To this end, we infected PBMCs with these isolates in the presence of various concentrations of a stapled peptide. We quantified the p24 antigen by the sandwich ELISA for evaluation of viral infectivity and to calculate the IC50 value for each inhibitor. The i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides effectively inhibited infection of PBMCs by the primary HIV-1 isolates from China at concentrations in the low micromolar range (Table 2). All the isolates were sensitive to the three stapled peptides with average IC50 values of 8.75 ± 3.57, 15.43 ± 6.08, and 8.68 ± 3.81 μmol/L for NYAD-36, NYAD-66, and NYAD-67, respectively. NYAD-66 showed significantly less antiviral activity than did NYAD-36 (P = 0.018) and NYAD-67 (P = 0.019). Although CRF07_BC isolates were less sensitive than CRF01_AE to the three i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides, there was no significant difference among the subtypes of HIV-1 isolates. It is notable that the relative inhibition rates of the three peptides were different within the same subtype. For example, BJMSM376 was more sensitive to the stapled peptides than CYM015 within subtype CRF01_AE, which may have resulted from gene diversity and polymorphism in the same subtype.
Virus Co-receptor NYAD-36 NYAD-66 NYAD-67 T20 RTV Subtype B SF33 R5/X4 13.886 ± 1.443 15.921 ± 2.102 6.603 ± 0.543 0.008 ± 0.001 0.091 ± 0.011 CRF 07_BC CBJB257 R5 7.031 ± 0.208 8.619 ± 1.018 6.942 ± 1.240 0.038 ± 0.006 0.272 ± 0.027 CBJB256 R5 6.280 ± 1.646 10.947 ± 0.351 7.487 ± 1.130 0.063 ± 0.002 0.261 ± 0.007 XJDC6291 R5 12.495 ± 0.377 17.074 ± 0.822 7.210 ± 0.616 0.028 ± 0.005 0.229 ± 0.016 XJDC6371 R5 9.979 ± 0.735 23.512 ± 3.329 13.356 ± 0.643 0.045 ± 0.001 0.062 ± 0.002 XJDC6331 R5 10.483 ± 0.007 21.238 ± 1.312 10.145 ± 0.722 0.096 ± 0.001 0.220 ± 0.018 Mean 9.254 ± 2.565 16.278 ± 6.416 9.028 ± 2.739 0.054 ± 0.026 0.209 ± 0.085 CRF 01_AE CYM015 R5 14.132 ± 0.316 21.510 ± 2.031 14.923 ± 0.057 0.070 ± 0.009 0.280 ± 0.025 BJMSM543 R5 5.612 ± 1.301 10.176 ± 0.850 4.472 ± 0.108 0.063 ± 0.004 0.156 ± 0.012 BJMSM376 R5 3.957 ± 0.071 10.345 ± 0.553 4.896 ± 0.178 0.081 ± 0.005 0.464 ± 0.120 Mean 7.900 ± 5.460 14.010 ± 6.495 8.097 ± 5.915 0.071 ± 0.009 0.300 ± 0.155 Note.Each sample was tested in triplicate, and each experiment was repeated twice. IC50s (μmol/L) data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. The CC50 values of the three peptides in PBMCs were > 100 μmol/L, which was the maximal available concentration. Table 2. Sensitivity of HIV-1 Isolates from China to the Dual-acting i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled Peptides
-
The inhibitory activity of the three i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides (NYAD-36, NYAD-66, and NYAD-67) was analyzed against 14 HIV-1 Env-pseudotyped viruses (10 CRF 07_BC and 4 CRF 01_AE strains) and two subtype B pseudoviruses (serving as a control) in a single-cycle assay. All the Env-pseudotyped reference viruses were sensitive to the three stapled peptides with average IC50 values of 7.07 ± 2.76, 11.31 ± 3.94, and 6.51 ± 3.85 μmol/L for NYAD-36, NYAD-66, and NYAD-67, respectively (Table 3). NYAD-67 showed antiviral activity similar to that of NYAD-36, but was 2-fold more potent than NYAD-66 (P = 0.0007). CRF01_AE Env-pseudotyped viruses appeared to be more sensitive than CRF07_BC Env-pseudotyped viruses, but there was no significant difference (P > 0.05). CH64, CH91, CH117, and CH120 of CRF07_BC showed the lowest sensitivity to each of the three stapled peptides as compared to the other viruses tested, while CH070, CH114, and CH115 of CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE Env-pseudotyped reference viruses showed similar sensitivity to the three stapled peptides.
Virus NYAD-36 NYAD-66 NYAD-67 T-20 Subtype B SF162.LS 5.984 ± 0.560 8.597 ± 0.484 4.480 ± 0.003 0.237 ± 0.008 REJO4541.67 11.832 ± 0.174 12.734 ± 0.241 5.408 ± 0.090 0.099 ± 0.001 Mean 8.908 ± 4.135 10.666 ± 2.925 4.944 ± 0.656 0.168 ± 0.098 CRF07_BC CH064 8.530 ± 0.279 18.939 ± 0.546 15.912 ± 0.605 0.059 ± 0.001 CH070 5.542 ± 0.897 10.037 ± 0.157 2.192 ± 0.588 0.165 ± 0.063 CH091 10.476 ± 0.852 12.907 ± 0.804 10.915 ± 0.937 0.069 ± 0.003 CH110 6.095 ± 0.727 10.929 ± 0.850 8.000 ± 0.707 0.025 ± 0.002 CH114 5.313 ± 0.347 7.117 ± 0.112 4.184 ± 0.232 0.096 ± 0.007 CH115 4.884 ± 0.833 6.932 ± 0.693 3.745 ± 0.359 0.065 ± 0.006 CH117 14.543 ± 0.089 18.711 ± 0.027 6.519 ± 0.581 0.037 ± 0.002 CH119 6.207 ± 0.869 10.258 ± 0.947 7.420 ± 0.622 0.031 ± 0.008 CH120 9.386 ± 0.478 15.390 ± 0.411 10.696 ± 0.860 0.118 ± 0.006 CH181 5.852 ± 0.041 10.635 ± 0.393 5.632 ± 0.297 0.138 ± 0.020 Mean 7.683 ± 3.065 12.186 ± 4.276 7.522 ± 4.091 0.080 ± 0.048 CRF01_AE 2149_39_2_2 6.230 ± 0.749 9.814 ± 0.134 6.099 ± 0.333 0.022 ± 0.000 2249_13_2_1 5.971 ± 0.311 8.362 ± 0.939 3.835 ± 0.886 0.045 ± 0.003 2316_14_22_3 4.728 ± 0.117 11.403 ± 0.106 2.689 ± 0.007 0.032 ± 0.003 2498_40_32_4 5.202 ± 0.131 6.967 ± 0.488 3.338 ± 0.221 0.052 ± 0.007 Mean 5.533 ± 0.692 9.137 ± 1.906 3.990 ± 1.482 0.038 ± 0.013 Note.Each sample was tested in triplicate, and each experiment was repeated twice. IC50s (μmol/L) data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. The CC50 values of the three peptides in TZM-bl cells were > 100 μmol/L, which was the maximal available concentration. Table 3. Antiviral Activity (IC50s) of the Stapled Peptides against HIV-1 Env-pseudotyped Reference Viruses
-
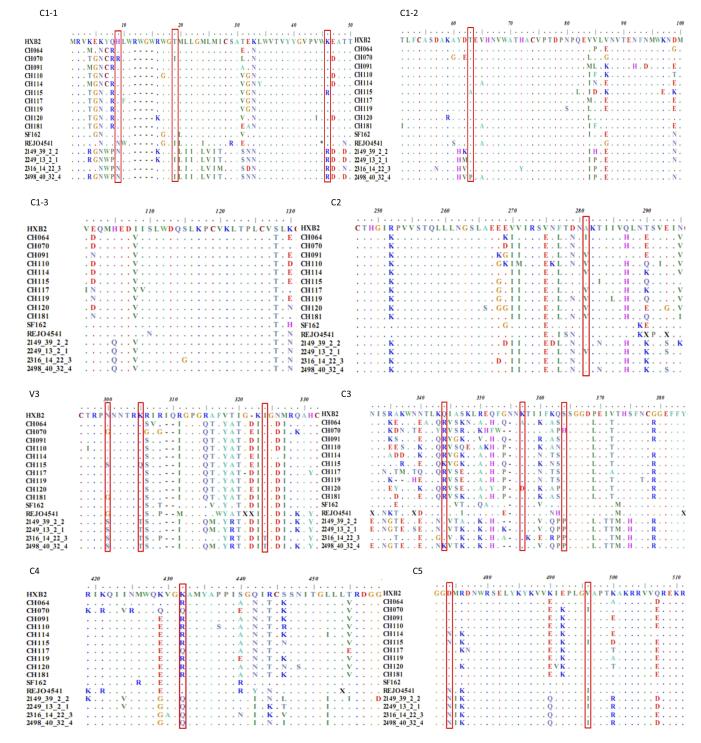
The amino acid sequences of gp120 were analyzed to identify the possible natural polymor-phism of gp120 related to the resistance to three peptides in all HIV-1 Env-pseudotyped reference viruses. The amino acid sequence of HXB2 was employed as the corresponding reference sequence. According to Spearman's test, the polymorphisms of H9R/N (C1), T19I (C1), K46R (C1), T63A/P (C1), A281V/I (C2), N300G/S (V3), K305Q/T (V3), I323T (V3), Q344K/R (C3), K357A/D (C3), S364H/P (C3), R432K/Q (C4), D474N (C5), and V496I (C5) were associated with the sensitivity of HIV-1 Env-pseudotyped reference viruses (including CRF01_AE, CRF07_BC, and subtype B) to the three stapled peptides (Figure 2). Viruses with the polymorphisms at positions 46 (K46R), 300 (N300S), 305 (K305T), and 474 (D474N) in all CRF01_AE and CH115 strains

Figure 2. Alignment of gp120 sequences from HIV-1 Env-pseudotyped viruses. The conserved sequences and V3 of gp120 were found to be highly polymorphic as compared to HXB2, which served as a reference sequence. These polymorphic sites, shown in the boxes, may be associated with the sensitivity of the HIV-1 Env-pseudotyped reference virus to the three stapled peptides.(Figure 2; C1-1, V3, and C5) showed higher sensitivity to each of the three stapled peptides. The polymorphism at position 364 (S364P) may be related to the higher sensitivity of subtype CRF01_AE to NYAD-67.
Characteristics of HIV-1 Predominantly Circulating in China
Phenotypic Sensitivity of HIV-1 Clinical Isolates from China to the i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled Peptides
The i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled Peptides Potently Inhibited a Panel of HIV-1 Subtype CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE Env-pseudotyped Reference Viruses
Sequence Analysis of gp120 in HIV-1 Env-pseudotyped Reference Viruses
-
Antiretroviral drugs (ARVs), namely, four nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, one non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), and one protease inhibitor, have been provided by the Chinese government free of charge to HIV-infected patients in China[18-19]. Application of ARVs in combination, i.e., antiretroviral therapy (ART), does indeed result in a significant reduction of morbidity and mortality among HIV/AIDS patients in China[20-21]. Nevertheless, almost 8.5% of HIV/AIDS patients have failed to respond to these ARVs because of the emergence of drug-resistant HIV-1 variants[22-23]. In China, the commonly observed drug-resistant viruses contain single amino acid mutations in reverse transcriptase (RT), Y181C and K103Q, and are resistant to nevirapine, delavirdine, efavirenz, and other NNRTIs[24]. The potential contribution of recombination to the development of HIV-1 resistance to multiple drugs has been investigated[5]. CRF07_BC strains, whose sequences harbor a few highly prevalent polymorphisms in both protease and RT regions, have a decreased genetic barrier for the V106M mutation with strong resistance to all current NNRTIs[15]. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new ARVs, especially those against diverse targets, for ART in China.
The i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides, NYAD-36, -66, and -67, derived from CAI show dual-targeted anti-HIV activities by binding to capsid (CA) to impair Gag precursor processing and by interacting with the gp120 V3 loop to block virus entry[12]. They are effective in inhibiting infection by HIV-1 subtypes A, A/D, A2/D, AG, B, C, and D Env-pseudotyped viruses[12]. In this study, the activity of three stapled peptides was evaluated in PBMCs against infection by HIV-1 subtypes predominantly circulating in China, including CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE. These peptides significantly inhibited infection by all these primary isolates tested, confirming their broad anti-HIV-1 activity. The inhibitory activity of these three stapled peptides on HIV-1 entry into the target cells was compared using CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE Env-pseudoviruses, which represent genetically and geographically diverse subsets of viruses that are generally representative of primary isolate strains in China in a single-cycle assay. NYAD-67 was found to be the most active, corroborating the findings of Zhang[12], while NYAD-66 is the least effective against the pseudoviruses tested, confirming that these i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides may also interact with the HIV-1 Env to block viral entry into the target cells[25]. Meanwhile, high variation in the antiviral data was observed among the pseudoviruses, as in the primary clinical isolates described above. This finding might result from the high variability among HIV-1 Env glycoproteins from different HIV-1 viruses[26]. As reported elsewhere, natural polymorphism among HIV-1 variants may be associated with the drug resistance and drug sensitivity of viruses[26-28].
To provide a sound scientific foundation for the rational design of i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides, the antiviral activity and the polymorphic sites of gp120 and CA in the isolated viruses and Env-pseudotyped viruses were compared here to find novel target amino acid residues. In clinical isolates, no related polymorphic site was found in CA and gp120, possibly because of the small number of strains in the analysis and dual-targeted activities of the i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides, which both impair Gag precursor processing and inhibit virus entry for the same virus. In our previous studies on HIV-1 pNL4-3, some polymorphic sites of gp120 in Env-pseudotyped viruses, such as V120Q and A327P located in conserved region 1 (C1) and at the base of the V3 loop in gp120, respectively, revealed a significant correlation with the antiviral activity[12]. In these HIV-1 Env-pseudotyped reference viruses, K46R in C1, N300G/S and K305Q/T in V3, and D474N in C5 showed a significant correlation with the antiviral activity of NYAD-36, NYAD-66, and NYAD-67. Thus, R46K, S300N/G, T305K, and D474N may be the possible NYAD-36 and NYAD-67 resistance-related substitutions and needed to be further characterized.
In summary, the three i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides tested against three subtypes of HIV-1 predominantly circulating in China showed broad-spectrum anti-HIV-1 activity. CRF07_BC Env-pseudotyped viruses were slightly less sensitive to the three i, i+7-hydrocarbon-stapled peptides than CRF01_AE Env-pseudotyped viruses were. Sensitivity to these stapled peptides may be associated with the naturally occurring polymorphisms in the CRF07_BC subtype. Therefore, this study provides useful information for the rational design of stapled peptides to inhibit the infection with different HIV-1 subtypes.
the New York Blood Center AKD
the Key Project of the State Key Laboratory for Infectious Diseases Prevention and Control (SKLID) 2011SKLID102
the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) 81261120384
the Ministry of Science and Technology of China 2012ZX10001-002
the European Research Infrastructures for Poverty Related Diseases 312661
NIH Grant RO1 AI104416 AKD







 Quick Links
Quick Links
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: