HTML
-
Candida albicans (C. albicans), an opportunistic fungal pathogen, can cause clinical symptoms that range from mucocutaneous infections to life-threatening systemic infections with high morbidity and mortality[1, 2]. The pathogenesis of C. albicans is associated with several virulence factors, such as adhesion, morphological transition, hydrolase or other metabolite secretion, and biofilm formation[3-6]. The adhesion of C. albicans cells to the host surface is a prerequisite for colonization and infection and may establish a reservoir for candidiasis[7]. The adhesion protects C. albicans cells from elimination by the scavenging action of bathing mucosal secretions, which is mediated by cell wall adhesins[8].
Several lipids, secreted proteins, carbohydrates, and cell wall proteins are utilized in the adhesion of C. albicans to biotic and abiotic surfaces[8-10]. For example, C. albicans cells that are deficient in the O-glycosylation gene (MNT2) exhibit certain defects in adhesion ability[9]. Agglutinin-like sequence (ALS) proteins, as the well-characterized adhesins comprise signal peptides and glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors[11]. ALS3 and ALS9 are ALS proteins that are required for the adhesion of fungal cells to host cell surfaces[12]. ALS3 is particularly important for cell adhesion and is expressed predominately in C. albicans cells in hyphal form[12].
Under certain circumstances, C. albicans cells can form microcolonies, wherein yeast transition into hyphal form and secrete hydrolases, including proteases, phospholipases, and lipases. These hydrolases promote host tissue penetration and extracellular nutrient acquisition by C. albicans cells[8]. For example, ECE1, a hypha-specific gene, encodes candidalysin, a secreted cytolytic toxin that can cause cell lysis by attacking cell membranes and forming pores on epithelial cell membranes[13]. PLB4 encodes GPI-anchored phospholipase B, which hydrolyzes acyl ester bonds in phospholipids and lysophospholipids[14]. LIP1, another hydrolase gene, encodes a secreted lipase that hydrolyzes ester bonds in lipid substrates[15]. These genes are involved in extracellular nutrient acquisition and tissue damage[16]. Hyphal formation plays a key role in tissue damage and host cell invasion[17]. C. albicans invade endothelial cells through two separate pathways: induced endocytosis and active penetration. Induced endocytosis relies on host cadherin interaction with C. albicans invasin (ALS3), whereas active penetration requires live fungal cells and is driven by hyphal extension and hydrolytic enzyme release[18, 19].
The development of novel antifungal agents and improvements in candidiasis treatment have attracted increasing attention given the emergence of antifungal drug resistance and the limited number of antifungal agents[20-22]. Attractive alternative approaches, such as screening for alternative agents against the virulence related factors of C. albicans, have become necessary to develop and improve antifungal agents. The intravaginal administration of human domain antibodies against mannoprotein or secretory aspartyl proteinase can efficiently reduce tissue fungal burden and prevent vaginal candidiasis by inhibiting cell adherence[23]. The aspartic proteinase inhibitors APG12 and APG19 can mitigate vaginal C. albicans infections[24]. Moreover, the quorum-sensing molecule farnesol can be used to treat and prevent oral candidiasis by inhibiting the morphological transition of C. albicans cells[25]. These novel antifungals have greater potential for reducing the development of drug-resistant C. albicans than traditional antifungal drugs that suppress pathogen growth or cause fungal cell death[26].
cis-2-Dodecenoic acid (BDSF), a compound that is structurally related to farnesol and produced by Burkholderia cenocepacia, can suppress germ tube formation in C. albicans[27]. In vitro biofilm assays have demonstrated that BDSF can repress C. albicans biofilm formation by inhibiting hyphal growth and fungal cell adherence[11, 28]. In the present study, we found that BDSF can inhibit the adhesion of fungal cells to epithelial cells, reduce the invasive ability of C. albicans by inhibiting morphological transition, and decrease the secretion of hydrolases. Given these effects, BDSF can attenuate the epithelial cell damage caused by C. albicans. The results of our in vivo experiment further confirmed that BDSF can prevent and treat vaginal candidiasis by inhibiting the expression of the virulence factors of C. albicans.
-
The standard strain C. albicans SC5314 was cultured in YPD (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, and 2% glucose) liquid medium and incubated overnight in an orbital shaker at 200 rpm and 35 ℃. Fungal cells were harvested through centrifugation and washed twice prior to use in experiments. The egg yolk agar plate used in the phospholipase activity assay consisted of 1% glucose, 1% peptone, 2% agar, 10% sterile yolk, 1 mol/L NaCl, and 0.005 mol/L CaCl2[29]. Itraconazole was purchased from Sigma, and BDSF was synthesized in accordance with a previous report[30]. BDSF stock solution (0.3 mol/L) was prepared in an ethanol/water mixture (1:1), and itraconazole was suspended in DMSO. BDSF and itraconazole stock solutions were diluted to the concentration of 250 μmol/L using the corresponding medium and suspended in 0.3% Noble agar. The vehicle was added as the control. Each dilution was administered separately through intravaginal instillation.
-
TR146 oral epithelial cells and VK2/E6E7 vaginal epithelial cells were cultured in six-well plates until reaching 95% confluence and used to evaluate the adhesive ability of C. albicans cells. The cells were infected with C. albicans at the rate of 2 × 102 yeast cells per well in DMEM and treated with 0, 3, 30, or 300 μmol/L BDSF. The number of adherent cells was verified through colony counting. After 0.5 and 1 h of incubation, dissociative yeast cells were removed by thrice rinsing the wells gently with 3 mL of PBS. The wells were then covered with YPD agar, and the number of adherent cells was quantified through colony counting. Adhesion efficiency was expressed as the ratio of the number of adherent cells treated with BDSF to that of the cells cultured in DMEM only[31].
-
Candida cells were suspended and diluted in fresh YPD after overnight culture to obtain a 103 CFU/mL suspension for use in the agar invasion assay. Aliquots (20 µL) of yeast suspension was spread on YPD plates supplemented with 0, 3, 30, 100, 200, or 300 μmol/L BDSF. After 72 h of incubation at 37 ℃, the plates were then rinsed under running water to discard noninvasive cells. The washed plates were then incubated for an additional 8 h at 37 ℃ for the observation of the invasive ability of Candida cells.
The epithelial cell invasion assay was performed as previously described[32]. Briefly, TR146 and VK2/E6E7 cells were cultured on circular coverslips with diameters of 12 mm. After 2 days of culture, the cell monolayer was infected with 1 × 105 CFU yeast cells suspended in DMEM medium containing 0, 3, 30, 100, 200, or 300 μmol/L BDSF and placed for 3 h in a humidified incubator. The supernatant was discarded, and cells were rinsed three times with PBS to remove dissociative fungal cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. Any fungal cells that remained attached to epithelial cells were incubated for 1 h with rabbit anti-C. albicans antibodies (ab53891), rinsed thrice with PBS, and stained again with Cy3-tagged anti-rabbit IgG antibodies (ab97075). Fungal cells that did not invade epithelial tissue were labeled with red (Cy3) fluorescence. Next, epithelial cells were washed with PBS, and 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS was added to the wells to permeabilize epithelial cells. Fungal cells were then incubated with FITC-tagged anti-C. albicans antibodies (ab21164) and labeled with green (FITC) fluorescence. Finally, the prepared coverslips were rinsed with PBS and visualized under fluorescence microscopy (Olympus X71).
-
The phospholipase activity of C. albicans was evaluated on egg yolk agar plates[29]. In brief, freshly cultured cells were diluted with PBS to an optical density of 0.6 at 600 nm. Next, 4 µL aliquots of fungal solution were spotted onto egg yolk plates supplemented with 0, 3, 30, 100, 200, or 300 μmol/L BDSF. After 5 days of incubation at 37 ℃, the diameters of colonies and the dense white precipitation zone on each plate were measured. Phospholipase activity (Pz value) was calculated as the colony diameter divided by the total diameter of the colony and precipitation zone.
-
The ability of C. albicans to cause cell damage was determined on the basis of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. LDH release was quantified by using a commercial LDH cytotoxicity detection kit (Roche Applied Science). TR146 cells were seeded in 96-well tissue plates and cultured to 95% confluence. Each well was then infected with 2 × 104 fungal cells suspended in DMEM medium containing 0, 3, 30, 100, 200, or 300 μmol/L BDSF and cultured overnight in a humidified incubator. TR146 cells incubated with DMEM medium were considered as the low control and DMEM containing 0.5% Trion X-100 were considered as the high control. C. albicans cells were also seeded in the absence of epithelial cells. The damage incurred by epithelial cells infected with C. albicans cells was calculated in accordance with the following formula: (test sample release − low control release of TR146 and Candida cells)/(maximum cell release − low control release). The final result was expressed as (damage observed in the BDSF treatment sample)/(cells infected only with C. albicans) × 100[33].
-
A total of 110 female ICR mice (SLAR laboratory animal, Shanghai) aged 8-10 weeks were randomly assigned to four groups. The mouse model was constructed in accordance with a previous report[34, 35]. Mice were subcutaneously injected with 0.5 mg of estradiol valerate at 3 days before infection to induce transient pseudoestrus. On infection day, animals were inoculated intravaginally with 20 μL of yeast cell suspension containing 108 cells/mL. Animals in the negative control group were inoculated with sterile PBS. Mice in the positive control group were infected and received 0.3% Noble agar intravaginally, whereas those in the negative control group were reared without any treatment save for subcutaneous injections of estradiol valerate. The mice then received drug treatment at 24 h after infection. All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health on animal care. The study protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committees of Fudan University.
-
BDSF and itraconazole (250 μmol/L) were dispersed in 0.3% Noble agar and given intravaginally twice a day at the volume of 20 μL on 1-6 days postinfection. On days 1, 2, 4, and 7, the vaginas of the mouse models were swabbed with 200 μL of PBS. Next, 100 μL aliquots of each dilution (10−1 to 10−5) were inoculated on SDA plates for the quantification of fungal load (CFU/mL). Mice were then sacrificed, and blood was taken from the ventral vein and centrifuged to collect serum, which was then stored at −25 ℃. Serum was used to test the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) with a SOD testing kit (Jiancheng bioengineering institute). Vaginal tissue was also used for RNA extraction and histopathological examination (Boyuan biotechnology Co.). Vaginal inflammation was scored as follows: 0- normal; 1- slight inflammatory infiltration and swelling; 2- grade 1 changes involving 50% of the specimen; 3- obvious inflammatory infiltration, swelling, and mild ulceration; 4- grade 3 changes involving 50% of the specimen; and 5- extensive ulceration and necrosis[36].
-
The primers used in this study are shown in Table 1. RNA was obtained from murine vaginal tissue and C. albicans cells by using an RNA fast extracting kit (Tiangen Biotech Co.) and EASY spin yeast kit (Aidlab), respectively. DNA was degraded with DNase (Tiangen Biotech Co.). TevertAid first-strand cDNA synthesis kit (Fermentas) was used to synthesize cDNA, which was then diluted (1:16) with sterile Milli-Q water (Millipore) for real-time RT-PCR. Real-time RT-PCR was performed using SYBR Premix Ex Tag kit (TaKaRa) with a Stratagene Mx3000p System. A series (1:22 to 1:27) of cDNA dilutions were used to construct a standard curve for each primer pair. The reaction procedure consisted of 5 min of incubation at 95 ℃, 40 cycles of amplification (95 ℃ for 15 s, 55 ℃ for 20 s, and 72 ℃ for 30 s), and melting curve construction (95 ℃ for 15 s, 55 ℃ for 30 s, and 95 ℃ for 30 s). Then, the expression of target genes was normalized to that of the housekeeping gene ACT1 and calculated through comparative Ct method (ΔΔCt). Data were expressed as fold changes in the expression of target genes relative to that of the untreated control.
Gene Primer Direction Sequence (5′-3′) C. albicans ALS3 Forward TCCACTTCACAATCCCCATC Reverse CAGTAGTAGTAACAGTAGTAGTTTCATC ALS9 Forward AATGTTCCTGCTGGGTATCG Reverse GATCACATCCCCGCTAGAGT MNT2 Forward CCACCACAATCACCTTCATC Reverse TTGTTTCTCTTGTTGCTGTGG PLB4 Forward AAAGCTCATGAAGATGTGGCT Reverse CCAATCCCGCCATCTATAAC LIP1 Forward ACTGACAATTTGCGTCAAGG Reverse TCCATAACCTCCAGGGAAAG ECE1 Forward AAGAGAGATGTTGCTCCAGCTG Reverse AATGGCATATCAGCAATGATAC ACT1 Forward TTGACCAAACCACTTTCAACTC Reverse AGAAGATGGAGCCAAAGCAG Mouse IGFBP3-1 Forward GGAACTGTGGGAGAGGATATG Reverse ACCATTATTTGCGACATCTCTG MCP-1 Forward ATTCACATGGAAAGCCCCC Reverse TTGAACACAAAGAGTACCAGAG ACT1 Forward TGTTACTGAGCTGCGTTTTAC Reverse CACCGTTCCAGTTTTTAAATCC Table 1. Primers Used in This Study
-
All experiments were performed in triplicate, and results were expressed as means ± SD. One-way ANOVA was applied for the comparison of all groups. Student's t-test was used to compare paired groups. Differences were considered significant when P ≤ 0.05 and nonsignificant when P ≥ 0.05.
C. albicans Culture Conditions and Chemicals
Adherence Assay to Epithelial Cells and Six-well Plates
Invasion Assay
Phospholipase Activity Assay
Damage Assay
Construction of the Estrogen-dependent Vaginal Candidiasis Murine Model
In Vivo Evaluation of BDSF Efficacy against Vaginal Candidiasis
Real-time RT-PCR
Statistical Analysis
-
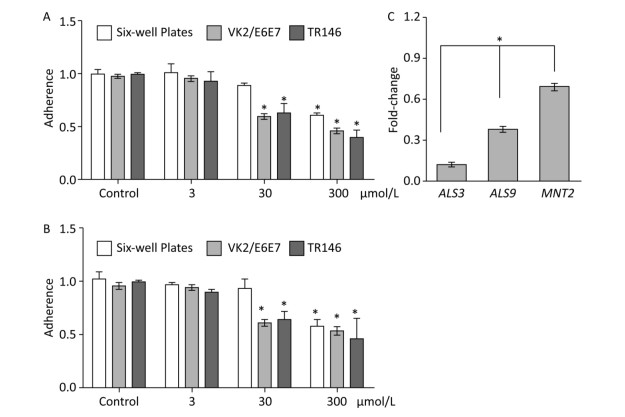
The adherence of C. albicans to tissue and device surfaces is a critical initial step in the development of yeast infections. Some natural or artificial products can reduce the adhesive ability of Candida. Here, we determined the potential inhibitory activity of BDSF against the adhesive ability of C. albicans to six-well plates and host cells. We found that treatment with 3 μmol/L BDSF did not obviously change the adhesive ability of C. albicans to VK2/E6E7 or TR146 cells and plates. Treatment with 30 μmol/L BDSF, however, reduced the adhesive ability of C. albicans cells to VK2/E6E7 cells, TR146 cells, and plates by 39.2%, 36.9%, and 10.3%, respectively. Treatment with 300 μmol/L BDSF reduced the adhesive ability of C. albicans cells to VK2/E6E7 cells, TR146 cells, and plates by 55.9%, 54.3%, 43.3% (Figure 1A), respectively. These results demonstrate that BDSF drastically reduced the adhesive ability of C. albicans cells to epithelial cells and plates. Moreover, the inhibitory effect of BDSF on the adhesive ability of C. albicans cells to host cells is better than that on the adhesive ability of C. albicans cells to abiotic surfaces and remained stable for 1 h (Figure 1B). Given that adhesins mediate the adherence of C. albicans to host cells, we used real-time RT-PCR to investigate the differential expression of the adhesin-related genes ALS3, ALS9, and MNT2. The expression levels of ALS3, ALS9, and MNT2 in cells treated with 100 μmol/L BDSF decreased by 87.4%, 61.9%, and 30.5% respectively, relative to those in untreated yeast cells. These results indicate that BDSF inhibited the adhesive ability of C. albicans by strongly suppressing the expression of ALS3 and ALS9 and slightly decreasing that of MNT2 (Figure 1C).
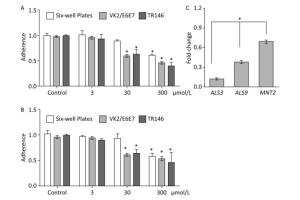
Figure 1. Effect of BDSF on the adherence of C. albicans to mammalian cells and six-well plates after 0.5 (A) and 1 h (B) of incubation in DMEM medium. (C) Comparison of the expression levels of adhesion-related genes after treatment with 100 μmol/L BDSF. The expression levels of target genes were normalized relative to those of the housekeeping gene ACT1. The change in expression level was calculated as the ratio of the expression of a gene in cells treated with 100 μmol/L BDSF to those in untreated cells. Results are expressed as the average and standard errors of three independent replicates. *P < 0.05.
-
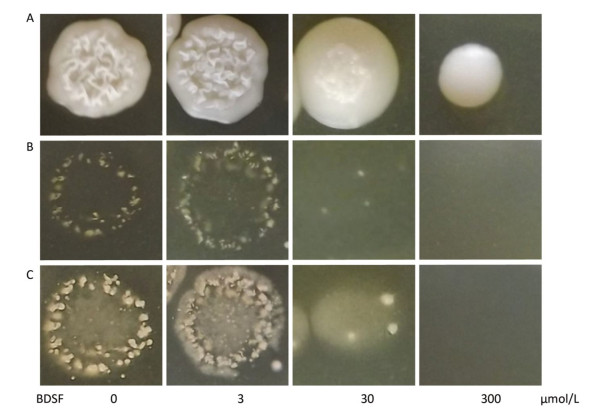
We cultured C. albicans on YPD plates supplemented with different concentrations of BDSF to assess the influence of BDSF on the invasive capability of Candida cells in vitro. As shown in Figure 2A, the growth of C. albicans was unaffected by treatment with BDSF at concentrations of less than 60 μmol/L[26]. Consistent with previously reported results, 300 μmol/L BDSF inhibited the growth of C. albicans cells[28]. After removing noninvasive cells, we found that the invasive capability of C. albicans on YPD agar plates decreased under treatment with 30 μmol/L BDSF (Figure 2B). And this phenomenon was more obvious after the plates were washed and incubated for 8 h at 37 ℃ (Figure 2C).

Figure 2. Invasive growth of C. albicans on YPD agar plates supplemented with different concentrations of BDSF. Plates (A) before and (B) after noninvasive cells were washed away from the agar surface. (C) Plates were cultured for 8 h at 37 ℃ after washing with sterile water.
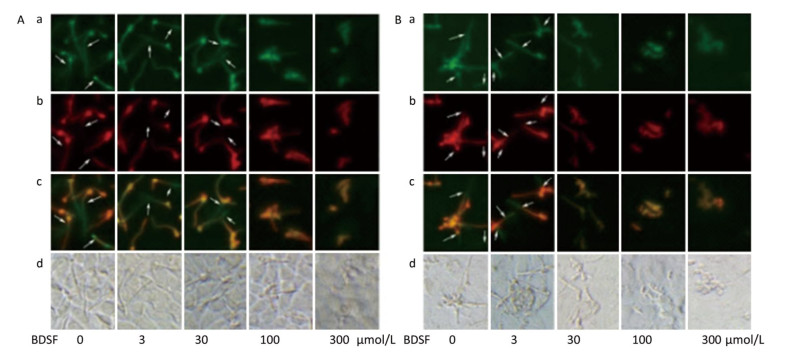
C. albicans invades host tissue mainly through active penetration and endocytosis induction. Active penetration requires hyphal formation and is not influenced by microfilament activity[37]. We evaluated the role of BDSF in the invasion of epithelial cells by C. albicans in vitro. We found that BDSF inhibits the invasion of epithelial cells by C. albicans by suppressing filament formation. As shown in Figure 3, hyphal length is dependent on BDSF concentration. Treatment with BDSF at concentrations of less than 30 μmol/L did not influence the invasion of VK2/E6E7 epithelial cells by C. albicans. By contrast, treatment with 100 μmol/L BDSF inhibited the invasion of VK2/E6E7 epithelial cells by C. albicans and markedly shortened filament length of C. albicans. When BDSF concentration increased to 300 μmol/L, C. albicans was arrested in yeast form (Figure 3A). Similar inhibitory effects were also observed the invasion of TR146 epithelial cells by C. albicans (Figure 3B).
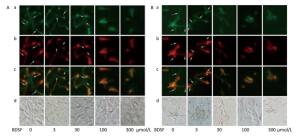
Figure 3. Representative fluorescent images of the invasion of C. albicans into VK2/E6E7 (A) and TR146 (B) epithelial cells under treatment with 0, 3, 30, 100, or 300 μmol/L BDSF. Differential staining of C. albicans hyphae: a (stained red fluorochrome Cy3), extracellular components of C. albicans hyphae and yeast; b (stained green fluorochrome FITC), intact C. albicans hyphae; c (extracellular parts appear pink), merged image of A and B; d, bright-field images. Arrows mark internalized hyphae.
-
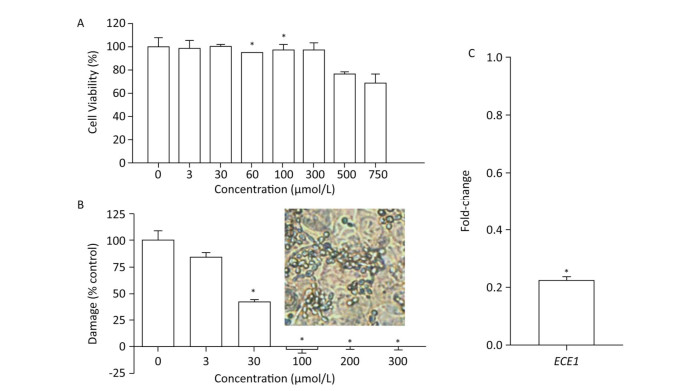
We first evaluated the cytocompatibility of BDSF before assessing its protective effects on tissue. As shown in Figure 4A, the metabolic activity of TR146 cells decreased under treatment with BDSF at concentrations of more than 500 μmol/L. Metabolic activity decreased to 76.6% and 68.7%, respectively, under treatment with 500 and 750 μmol/L BDSF. Treatment with BDSF at concentrations of less than 300 μmol/L did not affect the viability of TR146 cells. Next, we infected oral epithelial cells with C. albicans. We used LDH kit to measure the damage incurred by cells after 12 h of infection. BDSF could prevent C. albicans from damaging oral epithelial cells in a dose-dependent manner. Under treatment with 3 or 30 μmol/L BDSF, the percentage of damaged oral epithelial cells decreased to 84.5% and 57.7%, respectively (Figure 4B). Treatment with 100 μmol/L BDSF completely blocked epithelial cell damage because C. albicans remained in yeast form (Figure 4B inset). RT-PCR results indicated that under treatment with 100 μmol/L BDSF, the expression levels of the hypha-specific genes ECE1 and ALS3 decreased by 79.2% and 87.4% (Figures 1C and 4C), respectively. These results further confirm that BDSF can effectively repress germ tube formation.
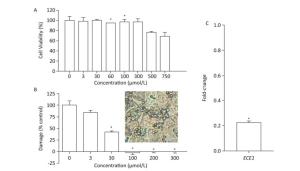
Figure 4. (A) In vitro viability of TR146 cells exposed for 24 h to different concentrations of BDSF; (B) Suppression of TR146 epithelial cell damage by BDSF. Inset shows the morphology of C. albicans coincubated with TR146 after 12 h of treatment with 100 μmol/L BDSF; (C) Expression levels of ECE1 in C. albicans treated with 100 μmol/L BDSF relative to that of housekeeping gene ACT1. Changes in expression levels were calculated as the ratio of the expression of a gene in cells treated with 100 μmol/L BDSF to those in untreated cells. Results are expressed as the average and standard errors of three independent replicates. *P < 0.05.
-
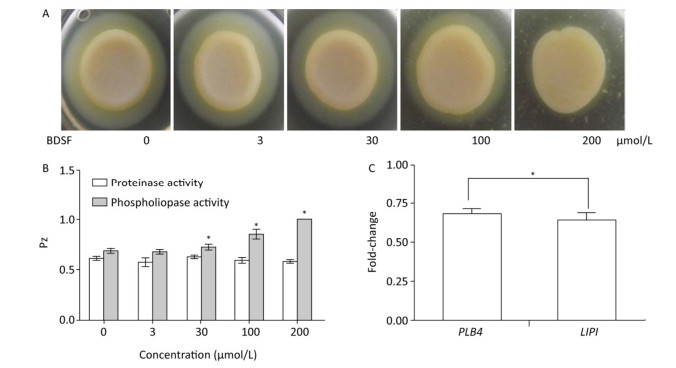
C. albicans colonizes host tissues, secretes a series of degradative enzymes that damage infected tissues, and captures carbon and nitrogen from infected tissues. Degradative enzymes can be classified into two large families: secreted proteinases and phospholipases[16]. Here, we applied the yolk plate method to assess the effect of BDSF on the phospholipase activity of C. albicans. Figure 5A and 5B show that the addition of 3 μmol/L BDSF did not affect phospholipase activity (Pz: 0.683). By contrast, the addition of 30 or 100 μmol/L BDSF slightly and strongly reduced phospholipase activity, respectively. When BDSF concentration increased to 200 μmol/L, secreted lipolytic activity was completely inhibited, and the Pz value increased from 0.855 to 1 (Figure 5B). The change in Pz value indicates that BDSF inhibited phospholipase secretion in a dose-dependent manner. We then performed real-time RT-PCR to determine the differential expression of the genes of phospholipase B4 (PLB4) and secreted lipase (LIP1). The expression levels of PLB4 and LIP1 were inhibited by 31.8% and 36.2%, respectively, under treatment with 100 μmol/L BDSF (Figure 5C). This result is consistent with the results of the yolk plate assay. Furthermore, we determined proteinase activity through the BSA plate method[38]. Different concentrations of BDSF, however, negligibly affected proteinase activity on the BSA plates (Figure 5B).
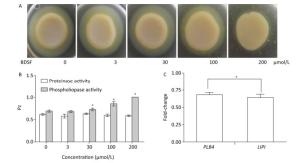
Figure 5. Effect of BDSF on degradative enzyme production. (A) Inhibition of phospholipase production on egg yolk plates supplemented with different concentrations of BDSF; (B) Phospholipase and proteinase activity under different concentrations of BDSF; a high Pz indicates low enzyme production. (C) Expression level ratios of phospholipase-related genes after treatment with 100 μmol/L BDSF. Changes in expression levels were calculated as the ratio of the expression of a gene in cells treated with 100 μmol/L BDSF to that in untreated yeast cells. Results are expressed as the average and standard errors of 3 independent replicates. *P < 0.05.
-
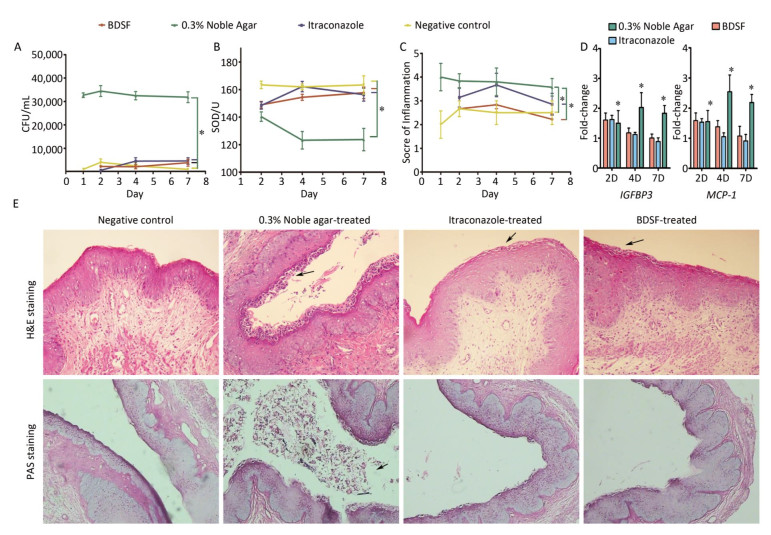
We quantified the CFU counts of vaginal lavage fluid to evaluate the effect of BDSF (250 μmol/L) on vaginal candidiasis. As shown in Figure 6A, the positive control group showed intensive and persistent C. albicans vaginal colonization (> 30, 000 CFU/mL) from days 1 to 7 of infection. By contrast, the negative control group showed low average CFU counts (< 5, 000). These results suggest that the model of fungal vaginitis was constructed successfully (P < 0.0001). As shown by previous studies[39], uncomplicated vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) respond well to short-term topical itraconazole therapy. CFU counts in the itraconazole treatment group were significantly lower (P < 0.0001) than those in the positive control group (Figure 6A). The similar effects of BDSF on VVC (between BDSF treatment group and positive control group, P < 0.0001) provide further evidence that BDSF is a potential therapeutic agent for fungal infections.
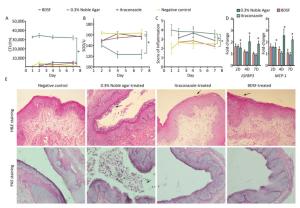
Figure 6. Efficacy of BDSF and itraconazole in the treatment of experimental vaginal candidiasis, (A) fungal burden of lavage fluid from different groups of mice; (B) Superoxide dismutase activity in serum; (C) inflammation score of vaginal tissue; (D) Expression levels of MCP-1 and IGFBP3 in mouse vaginal tissue; (E) H & E staining of vaginal tissues for the examination of the extent of inflammatory infiltration. PAS staining for the examination of C. albicans. All pictures were magnified 200×.
-
We allocated inflammation into six grades on the basis of scores (0-5). The negative control group showed slight inflammation with scores of 2-2.67. The inflammation score of the positive control group consistently remained as high as four throughout the whole experiment and was significantly higher than that of the negative control group (P = 0.0002). This result further confirmed that the model of VVC was successfully established. The inflammatory reactions exhibited by the BDSF (P = 0.001) and itraconazole treatment groups (P < 0.05) were less severe than those exhibited by the positive control group. Meanwhile, the inflammation scores of the BDSF (from 2.67 to 2.83) and itraconazole (from 3.15 to 3.67) treatment groups on day 4 were higher than those on day 1. The individual inflammation scores of the BDSF (2.22) and itraconazole (2.85) treatment groups for day 7 were low. Notably, the inflammation score of the itraconazole treatment group was higher than that of the negative control group, whereas that of the BDSF treatment group did not significantly differ from that of the negative control group (P > 0.05). This result implies that BDSF was as effective as itraconazole (Figure 6C). We subjected infected tissue to histological examination and hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) staining to further assess the protective ability of BDSF. BDSF and itraconazole-treated tissue showed drastic reductions in C. albicans vaginal colonization, whereas the positive control showed severe mucosal damage (Figure 6E, H & E staining) and increased C. albicans cell density in the vaginal lumen (Figure 6E, PAS staining). These results are consistent with those for CFU counts. As indicated by the arrows in Figure 6E, H & E staining, numerous neutrophils and microabscesses in the lamina propria and lumen of untreated mice were observed. By contrast, few Candida or neutrophils were observed in the vaginas of BDSF-treated or itraconazole-treated mice (Figure 6E).
-
Innate immune cells mainly use toxic oxygen metabolites to fight against pathogens. The respiratory burst that occurs when phagocytes are exposed to C. albicans results in superoxide anion production[40]. Superoxide anions may damage normal tissue. SOD removes superoxide anions and is thus indispensable for cell resistance against oxidative stress[41].
Figure 6B shows that SOD activity in the positive control group was significantly lower than that in the other groups (P < 0.05). SOD activity in the positive control decreased from 142 U on day 2 to almost 120 U on days 4 and 7, whereas that in all other groups remained above 150 U throughout days 1 to day 7 (Figure 6B). In contrast to the negative control, neither BDSF nor itraconazole affected SOD activity. This result was consistent with the results of an experiment that subjected mice with systemic candidiasis to glycyrrhizin treatment[42].
-
Previous reports suggested that the production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP3) drastically increase in mice with vaginal candidiasis[43, 44]. Inflammatory chemokines are critical for the recruitment of cells to sites of inflammation and pathogenic insults. We used na ve mice as the control for the investigation of the local expression level of MCP-1 and IGFBP3. The fold change in the gene expression of all four groups versus that of the na ve group is shown in Figure 6D. The expression level of the na ve group was considered as 1. The expression level of MCP-1 in estrogen-treated mice was negligibly lower than that in the na ve mice (data not shown). Additionally, the expression level of IGFBP3 in the negative control group was almost equal to that in the na ve control group. Over time, the expression levels of MCP-1 and IGFBP3 in the positive control group became consistent with those observed in previous studies, whereas those in the BDSF and itraconazole groups decreased. Only the expression levels of MCP-1 and IGFBP3 in the positive control were significantly different from those in the negative control group (P < 0.05). This result indicates that the expression levels of MCP-1 and IGFBP3 in the estrogen-dependent vaginal candidiasis murine model increased over time. Under effective treatment, the expression levels of MCP-1 and IGFBP3 were upregulated, reduced upon symptom mitigation, and recovered. These results show that BDSF can effectively protect against vaginal candidiasis.
Antiadhesive Effect of BDSF
Invasion Assay
Cell Damage
Secretion of Degradative Enzymes
Fungal Burden in Lavage Fluid
Therapeutic Efficacy Measured through Histopathological Examination
SOD Activity
Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and Insulin- like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 Expression
-
The antimicrobial and anticancer properties of unsaturated fatty acids have been widely reported[45, 46]. Unsaturated fatty acids act as effective anticancer agents that can induce apoptotic cell death by impairing mitochondrial membrane permeability or enhancing reactive oxygen species production and apoptotic enzyme expression[46]. For example, analogs of linoleic acid, a polyunsaturated fatty acid, exhibit anticancer activities by enhancing cytochrome-c release and caspase-3 expression[47]. Unsaturated fatty acids exert antibacterial effects by inhibiting enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase and blocking fatty acid synthesis[45]. For instance, clove oil, which consists of unsaturated multiple fatty acids, is an effective antifungal drug against vaginal candidiasis[48].
In this study, we found that in mice, the diffusible fatty acid signal molecule BDSF is effective against the virulence factors of C. albicans and exhibited striking protective activity against vaginal candidiasis. Other fatty acids, including capric acid, lauric acid, myristoleic acid, arachidonic acid, butyric acid, undecylenic acid, and farnesoic acid, have all been proven to be effective against the virulence factors of C. albicans[49-53]. Our present work is the first, however, to demonstrate that BDSF can exert a protective effect against mucosal candidiasis.
The mechanisms underlying the protective effect of BDSF against vaginal candidiasis warrants further investigation. We previously reported that BDSF inhibits the morphogenesis, adhesion, and biofilm formation of C. albicans[11, 27, 28]. Our present in vitro experiment indicated that BDSF also effectively inhibits filament formation on the surfaces of epidermal cells (Figure 3). The host invasion process of C. albicans can be divided into the three successive stages of adhesion, invasion, and host tissue damage[8]. The adhesion of C. albicans to host tissues is an important initial step in infection. In our present study, we found that BDSF inhibits the adherence of C. albicans to epithelial cells and plastic plates. The capacity of C. albicans to adhere to various interfaces, such as host cells and indwelling devices, is a major contributor to its virulence[8]. BDSF can reduce the adhesive ability of C. albicans and promotes the elimination of fungal cells from vaginal tissue. Our real-time PCR results show that BDSF treatment downregulated the expression levels of the adhesion-related genes ALS3, ALS9, and MNT2. Our previous study also indicated that under exposure to BDSF, ALS1, and EAP1, which both promote cell adhesion, were downregulated, whereas YWP1, which inhibits cell adhesion, was overexpressed[11]. Consequently, BDSF may effectively control infection by alleviating vaginal fungal burden through reducing the adherence ability of C. albicans.
The invasion of C. albicans to host tissues after adhesion plays an important role in the physiopathology of mucosal or invasive candidiasis. Consistent with previous studies, in this study, we found that C. albicans cells that have invaded host tissue remained in the hyphal form. This result further confirms that the mycelial form is the invasive form of C. albicans. Therefore, BDSF hindered the invasion of epithelial cells by C. albicans by suppressing germ tube formation in C. albicans (Figure 3). ALS3 is a fungal invasin that induces endocytosis by binding to cadherin on epithelial cells[19, 37]. The expression of ALS3 was downregulated by 87.4% under BDSF treatment. These results indicate that BDSF may attenuate induced endocytosis by decreasing ALS3 expression. Farnesol, a quorum-sensing signal molecule that is structurally related to BDSF, also inhibited filament formation but negligibly influenced the invasive growth of C. albicans even at concentrations of as high as 1 mmol/L[54].
Hyphal formation has long been considered as a vital virulence factor of C. albicans and is a prerequisite for host tissue damage[3, 55]. The tissue injury caused by C. albicans can be blocked by substances that suppress candidal germination[56]. Long germ tubes are associated with severe endothelial cell injury[57]. The discovery of candidalysin, a hypha-associated cytolytic toxin that is responsible for cell lysis, provided further support for the hypothesis that hyphal C. albicans cells exhibit invasive capacity and destructive effects during mucosal infections[3, 13]. In the present study, we found that BDSF can reduce the epithelial cell damage caused by C. albicans. Furthermore, epithelial cells can coexist with C. albicans in culture medium supplemented with 100 μmol/L BDSF because BDSF could effectively suppress germ tube formation and reduce degradative enzyme secretion[10, 57]. The damage caused by the supernatant from the phospholipase-deficient culture was weaker than that caused by the supernatant from the parental culture; this result suggests that phospholipases may augment the virulence of C. albicans by directly disrupting host cell membranes[14, 58]. Blocking phospholipase secretion by C. albicans was more effective than blocking proteinase secretion by BDSF. The inhibitory activity of BDSF is superior to that of lauric acid, capric acid, and caprilic acid[59]. Moreover, BDSF effectively protected the host tissue from Candida infection by inhibiting germ tube formation and reducing cytolytic toxin expression and phospholipase production. These effects, in turn, further relieved inflammatory symptoms.
In conclusion, the preclinical evidence generated by our present study confirmed that BDSF effectively suppresses the virulence factors, such as adhesive ability, morphological transition, and toxic degradative enzyme production, of C. albicans. Given these characteristics, BDSF can be used as a potential agent for the prevention and treatment of candidiasis. Additional experiments are still needed to explore the mechanisms underlying the protective effect of BDSF against candidiasis. The results of such experiments will contribute to the design and data evaluation of prospective clinical trials on the use of BDSF as an antifungal agent.
-
The authors declare no conflict of interest.







 Quick Links
Quick Links
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: