-
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a common allergic condition affecting approximately 10%−40% of the world’s population and may be accompanied by eye symptoms [1]. In many AR children, paroxysmal sneezing and runny nose symptoms can be traced to early childhood [2]. The pathogenesis of AR is complex. Environmental factors in addition to genetic factors, such as atopic predisposition, are possible reasons for the increasing trend of AR in recent years. There is evidence that exposure to particulate matter (PM2.5) in the environment may increase the degree of DNA methylation in the body. Furthermore, environmental factors can also lead to phenotypic genetic changes that promote an increase in allergic diseases [3].
Phthalates are widely used synthetic chemicals, and studies have found that they are common contaminants in surrounding environments; thus, human exposure to these chemicals is ubiquitous [4, 5]. Phthalates form weak chemical bonds and are easily leached into the surrounding environment [6]. Particularly concerning are exposures that occur during pregnancy, as phthalates can cross the placenta, impair normal placental function, and lead to abnormal fetal development and future disease [7]. He et al. reported that phthalate metabolites facilitated the symptoms of AR in mice [8]. Recently, several studies have reported an association of phthalate exposure with breathing, allergies, and wheezing in offspring [9]. Our previous study identified associations between prenatal phthalate exposure and inflammatory mRNA expression in large samples of human placentae [10]. However, to the best of our knowledge, few human studies have investigated the associations between maternal phthalate exposure and AR in fetuses.
Inflammatory biomarkers mostly exist in the placenta, and changes in these markers may not be monitored in maternal circulation because pro-inflammatory cytokines cannot cross a fully developed placental barrier [11]. Based on previous studies, we selected placental cytokines to quantify gene expression. Experimental studies have shown that di-2-(ethylhexyl) phthalate (DnBP) increases interleukin-1β (IL-1β) secretion in murine testicular macrophages [12]. A birth cohort study in Puerto Rico showed that DEHP metabolites, mono (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP), mono (2-ethyl-5-hydroxyl) phthalate (MEHHP), and mono (2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate (MEOHP) had significant positive associations with IL-6 concentrations [13]. Changes in placental inflammatory mRNAs may also lead to abnormal fetal development and future diseases. Prenatal phthalate exposure has been associated with asthma and wheezing in fetuses. AR is the most common immunological disease and has been associated with inflammatory responses [14]. Therefore, we investigated whether inflammatory factors played a role in the association between phthalate exposure and AR.
The aim of the present study was first to quantify urine phthalate exposure levels and placental inflammatory mRNAs, including pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, INF-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8), anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4 and IL-10), and chemokines (MCP-1 and GRP78), as well as activated macrophage biomarkers (CD68 and CD206). The second aim was to determine whether inflammatory mRNA expression acted as a mediator in phthalate exposure and AR.
-
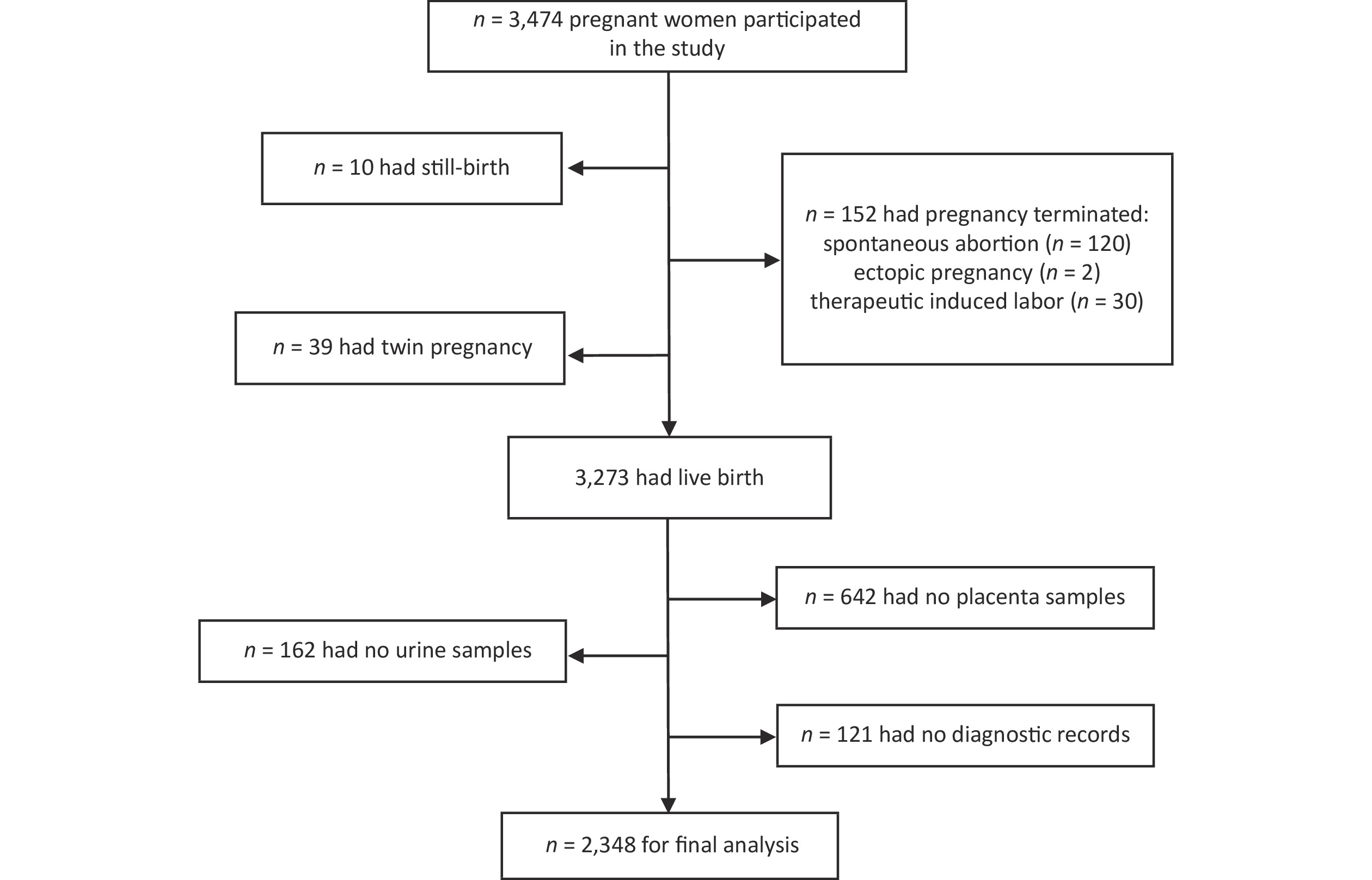
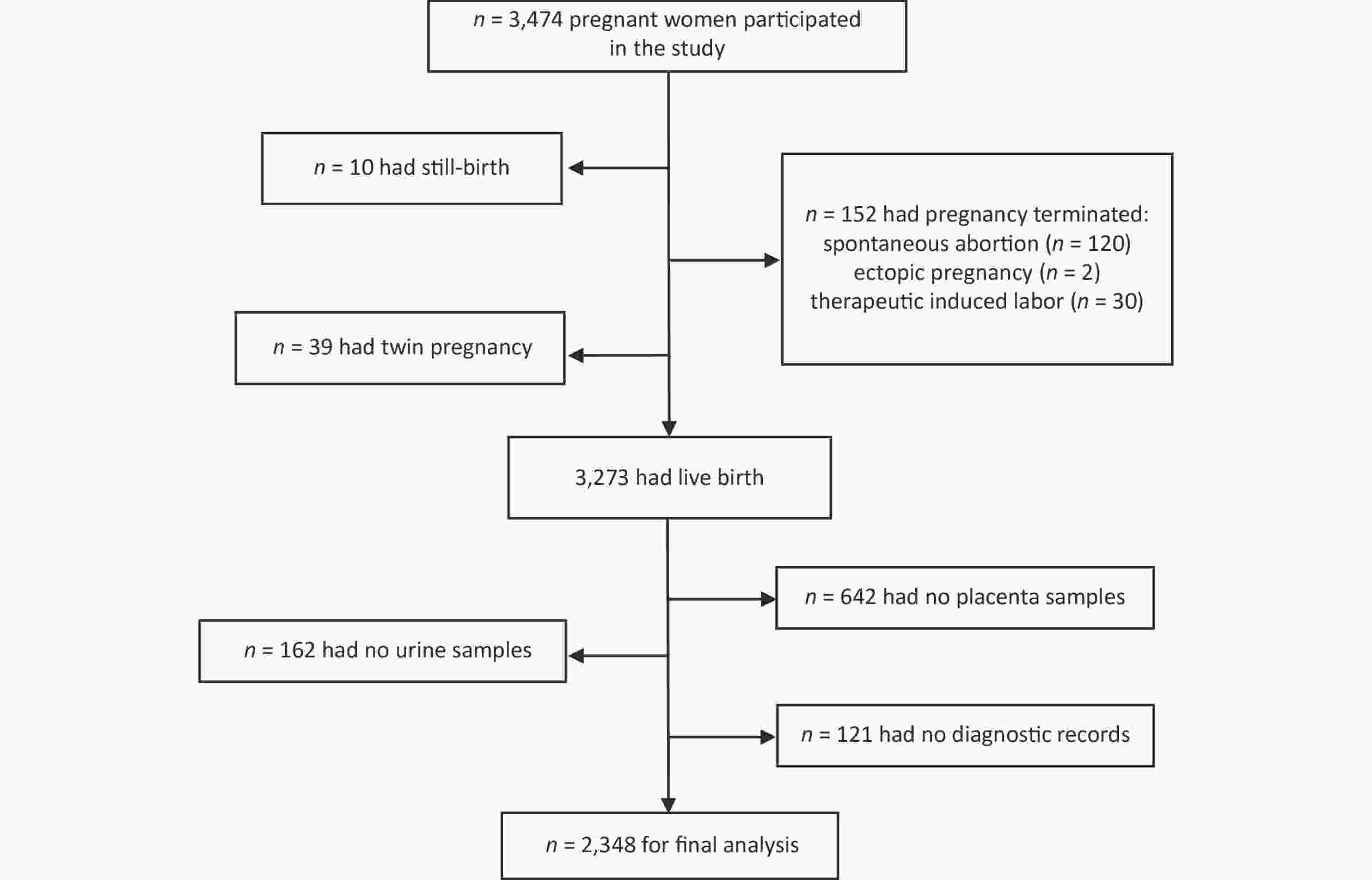
The study participants included 2,348 pregnant women who were screened before antenatal visits and met the inclusion criteria for the Ma’anshan Birth Cohort (MABC) at the Maternal and Child Health Hospital in Ma’anshan, Anhui Province, China, from May 2013 to September 2014. During the follow-up of participants, some were excluded due to pregnancy termination (n = 152), still birth (n = 10), twin pregnancy (n = 39), unavailable urine samples (n = 162), no placental samples (n = 642), or no diagnostic records (n = 121). Ultimately, 2,348 pregnant women were enrolled in the present study (Figure 1). Information on maternal pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), maternal educational level, and residence in the previous 6 months during pregnancy was obtained. Information on breastfeeding, pets, and family history of AR was obtained from questionnaires during the first 36 months of life. We obtained informed consent from all the participants (World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki, revised in 2013, Fortaleza). This study was approved by the Biomedical Ethics Committee of Anhui Medical University (Number: 20131195).
-
Urine samples were collected in the first trimester and stored at −20 °C until the day of analysis. The following seven phthalate metabolites were measured according to previous methods [15]: monomethy phthalate (MMP), monoethyl phthalate (MEP), mono-n-butyl phthalate (MBP), mono benzyl phthalate (MBzP), MEHP, MEHHP, and MEOHP. Phthalate measurements have been previously reported [16, 17]. The limits of detection (LODs) (S/N = 3) of the phthalate metabolites ranged from 13.43 to 80.21 ng/L. Concentrations of phthalate metabolites below the LOD were replaced by LOD/
$ \sqrt{2} $ for statistical analyses. Urinary creatinine was determined using a creatinine assay kit (picric acid method; Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China) to analyze the Jaffe reaction. -
A total of 2,348 placental tissue samples were from Ma’anshan Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Anhui Province, China. Within 5 min after the mother’s delivery of the placenta, complete placental lobules were taken throughout the maternal and fetal surfaces. After being washed with normal saline, a section ≤ 0.5 cm was cut in the sagittal direction using scissors. The extracted sample was then later placed into a cryopreservation tube for RNA analyses. The fresh specimens were stored at −80 °C in liquid nitrogen until further use. Using the TRI reagent (MRC, Cincinnati, OH, USA), total RNA was isolated according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
-
The amplification reactions were run on a Light Cycler® 480II instrument (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). The real-time PCR protocol consisted of an initial hold step (95 °C for 10 min), followed by 45 cycles of a three-step PCR (95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 15 s, and 72 °C for 20 s). All RT-qPCR data were normalized to the 18S endogenous reference. Delta Ct (ΔCt) was defined as the expression difference between the target mRNA and the normalizing RNA as follows: ΔCt = Ct mRNA − Ct normalizing RNA.
-
Descriptive statistics for maternal demographic and clinical characteristics were calculated according to the study outcomes using the mean ± standard deviation (SD). In the present study, the relationships between various placental inflammatory mRNAs and phthalate metabolite concentrations were analyzed using Spearman’s correlation analysis. We analyzed potential associations between the concentrations of phthalate metabolites and AR stratified by sex of the fetus using the independent samples t-test. Logistic regression analysis was used to detect the associations of phthalates, placental mRNA expression, and AR in infants of different sexes. The population characteristics included race (Han or other), residence in the last 6 months (rural or urban), household income (China Yuan/CNY < 2,500, 2,500−4,000, or > 4,000), maternal age, method of delivery, maternal complication, gestational age, and parity (nulliparous or parous). Statistical analyses were two-sided, and the significance level was P < 0.05. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS statistical software for Windows, version 16.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
-
Subjects with urinary exposure and placental inflammatory biomarkers were enrolled in the present study (final n = 2,348); the participants’ characteristics are described in Table 1. Regarding the women who had infants with AR, the average maternal age was 26.8 years, and the average pre-pregnancy BMI was 21.2 kg/m2. Some of the women were of Han ethnicity (10.35%), and 6.69% of the women were well-educated (above high school). Moreover, 9.84% of the women were urban residents, and 8.43% of the women had household incomes above 2,500 CNY per month. The prevalence of tobacco and alcohol consumption was high (6.56% and 6.39%, respectively). Of the 2,348 placental samples, 244 (10.4%) were from women with AR, and 2,104 (89.6%) were from non-AR women.
Characteristics Allergic rhinitis
(n = 244)Non-allergic rhinitis
(n = 2,104)P-value Age (Mean ± SD) 26.8 ± 3.5 26.6 ± 3.6 0.338 BMI (Mean ± SD) 21.2 ± 3.0 21.4 ± 3.2 0.313 Race, n (%) 0.175 Han ethnicity 243 (10.35) 2,073 (88.29) Other 1 (0.04) 31 (1.32) Education, n (%) 0.079 ≤ High school 87 (3.70) 873 (37.18) > High school 157 (6.69) 1,231 (52.43) Residence in the previous 6 months, n (%) 0.108 Village 13 (0.55) 174 (7.41) City 231 (9.84) 1,930 (82.20) Family monthly income, yuan/CNY, n (%) 0.010 < 2,500 46 (1.96) 552 (23.51) 2,500−4,000 108 (4.60) 898 (38.25) > 4,000 90 (3.83) 654 (27.85) Cigarette smoking, n (%) 0.594 Yes 154 (6.56) 1,291 (54.98) No 90 (3.83) 813 (34.63) Alcohol consumption, n (%) 0.974 Yes 150 (6.39) 1,279 (54.47) No 94 (4.00) 825 (35.14) Note. Continuous variables were shown as mean ± SD. Categorical variables were shown as percentage. P-value estimates are based on Student’s t-test for variables expressed as mean ± SD. χ2 test for variables expressed as percentages. BMI, Body Mass Index. Table 1. Study population characteristics (n = 2,348)
-
Spearman’s correlation analysis of phthalate metabolite concentrations was performed (Table 2). MEHHP was positively correlated with the other six phthalate metabolites, ranging from 0.114 to 0.602. Independent samples t-tests were used to analyze maternal urinary phthalate metabolite levels in the first trimester of pregnancy stratified by fetal AR status (Table 3). We found that AR in male fetuses was correlated with levels of MEOHP and MEHHP in maternal urine (P = 0.017 and P = 0.047, respectively), but the association of AR in female infants and maternal phthalates was not significant. For infant AR risk, urinary MEOHP and MEHHP levels were positively associated with AR in male infants, but not in female infants [in male infants; P = 0.022 and P = 0.042; odds ratio (OR): 1.285; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.037−1.591 and OR: 1.232; 95% CI: 1.008−1.507, respectively] (Table 4). Altogether, these data suggested that the levels of maternal urinary phthalate metabolites, MEOHP and MEHHP, may be correlated with AR in male fetuses.
Phthalate metabolites MEP MBP MBzP MEHP MEOHP MEHHP MMP 0.352** 0.451** 0.131** 0.233** 0.458** 0.372** MEP 0.314** 0.099** 0.150** 0.241** 0.235** MBP 0.170** 0.217** 0.322** 0.393** MBzP 0.026 0.059** 0.114** MEHP 0.521** 0.602** MEOHP 0.602** Note. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. MMP, monomethyl phthalate; MEP, monoethyl phthalate; MBP, mono-n-butylphthalate; MBzP, mono-benzyl phthalate; MEHP, monoethylhexyl phthalate; MEOHP, mono-(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate; MEHHP, mono-(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate. Table 2. Spearman correlation coefficients of phthalate metabolites
Variables Male Female Allergic rhinitis
(n = 152)Non-allergic rhinitis
(n = 1,047)P-value Allergic rhinitis
(n = 92)Non-allergic rhinitis
(n = 1,057)P-value MMP 2.68 ± 1.21 2.60 ± 1.10 0.397 2.58 ± 1.27 2.64 ± 1.14 0.594 MEP 2.36 ± 1.22 2.26 ± 1.19 0.330 2.32 ± 1.28 2.25 ± 1.21 0.610 MBP 4.00 ± 1.11 3.92 ± 1.11 0.431 3.82 ± 1.22 3.95 ± 1.13 0.310 MBzP −2.34 ± 1.70 −2.54 ± 1.57 0.148 −2.37 ± 1.71 −2.50 ± 1.67 0.472 MEHP 1.05 ± 1.24 0.95 ± 1.03 0.303 1.04 ± 1.15 0.95 ± 1.03 0.433 MEOHP 2.12 ± 0.77 1.96 ± 0.81 0.017 1.92 ± 1.19 2.01 ± 0.88 0.410 MEHHP 1.84 ± 0.82 1.69 ± 0.86 0.047 1.57 ± 1.22 1.66 ± 0.87 0.358 Note. MMP, monomethyl phthalate; MEP, monoethyl phthalate; MBP, mono-n-butylphthalate; MBzP, mono-benzyl phthalate; MEHP, monoethylhexyl phthalate; MEOHP, mono-(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate; MEHHP, mono-(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate. All values are showed as average ± standard deviation. Table 3. Maternal urinary phthalate metabolites levels stratified by allergic rhinitis status
Variablesa Male Female OR (95% CI) P-value OR (95% CI) P-value MMP 1.067 (0.912, 1.250) 0.417 0.963 (0.799, 1.161) 0.701 MEP 1.052 (0.912, 1.214) 0.483 1.048 (0.878, 1.250) 0.605 MBP 1.059 (0.906, 1.238) 0.473 0.905 (0.750, 1.092) 0.296 MBzP 1.083 (0.973, 1.205) 0.146 1.050 (0.925, 1.192) 0.449 MEHP 1.094 (0.929, 1.288) 0.281 1.087 (0.882, 1.340) 0.433 MEOHP 1.285 (1.037, 1.591) 0.022 0.902 (0.719, 1.133) 0.376 MEHHP 1.232 (1.008, 1.507) 0.042 0.903 (0.727, 1.121) 0.353 Note. aAdjusted for maternal age, race, residence in the previous 6 months, smoking status, alcohol consumption. Table 4. Logistic regression analysis of PAEs and allergic rhinitis in infants of different gender
-
Spearman’s correlation analyses revealed a high association between placental inflammatory-related HIF1α and GRP78 mRNA (correlation coefficient: 0.853) and four inflammatory factors among each other (MCP-1, HO-1, IL-6, and CD68; correlation coefficient: > 0.7). Detailed information on the analyses is shown in Table 5. Independent samples t-tests (Table 6) showed that the placental levels of inflammatory factors, including HO-1 and IL-4, were statistically higher in male children with AR. Moreover, the levels of IL-10, IL-4, CD206, and CRP (a marker of inflammation) had a statistically significant relationship with AR in female fetuses.
Variables IL-10 MCP-1 CRP HO-1 HIF1α GRP78 TNF-α IL-4 IL-6 IL-8 CD206 CD68 INF-γ IL-1 0.482** 0.447** 0.380** 0.410** 0.461** 0.344** 0.307** 0.135** 0.259** 0.363** 0.164** 0.297** 0.209** IL-10 0.445** 0.423** 0.444** 0.473** 0.400** 0.216** 0.154** 0.217** 0.261** 0.159** 0.286** 0.146** MCP-1 0.329** 0.617** 0.721** 0.654** 0.355** -0.003 0.365** 0.176** 0.030 0.429** 0.075** CRP 0.434** 0.403** 0.355** 0.150** 0.152** 0.143** 0.168** 0.157** 0.182** 0.083** HO-1 0.687** 0.701** 0.295** 0.044* 0.283** 0.209** 0.046* 0.411** 0.048* HIF1α 0.853** 0.291** −0.045* 0.378** 0.194** −0.029 0.446** −0.008 GRP78 0.295** −0.077** 0.333** 0.156** −0.089** 0.472** −0.042* TNF-α 0.295** 0.644** 0.541** 0.307** 0.671** 0.382** IL-4 0.290** 0.497** 0.690** 0.121** 0.463** IL-6 0.513** 0.290** 0.710** 0.260** IL-8 0.465** 0.489** 0.446** CD206 0.167** 0.425** CD68 0.253** Note. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. Table 5. Spearman correlation coefficients of placenta mRNA
Variables Male Female Allergic rhinitis
(n = 152)Non-allergic rhinitis
(n = 1,047)P-value Allergic rhinitis
(n = 92)Non-allergic rhinitis
(n = 1,057)P-value IL-1 0.97 ± 1.43 0.88 ± 1.42 0.445 1.06 ± 1.55 0.88 ±1.39 0.238 IL-10 1.11 ± 1.39 1.04 ± 1.60 0.433 1.38 ± 1.58 1.01 ± 1.57 0.034 MCP-1 0.67 ± 1.46 0.47 ± 1.39 0.105 0.80 ± 1.25 0.51 ± 1.36 0.055 CRP 1.27 ± 2.16 1.11 ± 2.30 0.423 1.93 ± 2.12 1.39 ± 2.24 0.027 HO-1 1.27 ± 1.50 0.97 ± 1.40 0.012 1.28 ± 1.54 1.00 ± 1.41 0.070 HIF-1α 0.73 ± 1.52 0.50 ± 1.41 0.063 0.63 ± 1.66 0.50 ± 1.43 0.419 GRP78 1.43 ± 1.91 1.25 ± 1.94 0.285 1.61 ± 1.97 1.23 ± 2.01 0.085 TNF-α 1.57 ± 1.50 1.43 ± 1.50 0.273 1.70 ± 1.52 1.43 ± 1.50 0.086 IL-4 1.21 ± 1.42 0.83 ± 1.52 0.004 1.29 ± 1.53 0.87 ± 1.51 0.012 IL-6 0.91 ± 1.23 0.80 ± 1.36 0.340 1.08 ± 1.44 0.80 ± 1.34 0.049 IL-8 0.80 ± 1.42 0.70 ± 1.36 0.380 1.00 ± 1.32 0.75 ± 1.42 0.103 CD206 1.56 ± 1.55 1.37 ± 1.64 0.179 1.82 ± 1.65 1.35 ± 1.65 0.008 CD68 2.10 ± 1.89 1.90 ± 1.92 0.241 2.25 ± 1.99 1.95 ± 1.90 0.140 IFN-γ 1.36 ± 1.66 1.21 ± 1.77 0.317 1.39 ± 1.56 1.11 ± 1.76 0.141 Note. All values are showed as average ± standard deviation. Table 6. Placenta mRNA expression levels stratified by allergic rhinitis status
Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to determine the associations of placental mRNA expressions and AR in infants of different sexes. Adjustments were made for the following co-variates in the analysis: maternal age, race, residence in the previous 6 months, smoking status, and alcohol consumption. As shown in Table 7, the placental levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokines, HO-1 and IL-4, were positively correlated with AR in male fetuses (OR: 1.175; P = 0.011 and OR: 1.181, P = 0.004, respectively). AR in female infants was positively correlated with anti-inflammatory factors, including IL-4 (OR: 1.190; P = 0.015), IL-10 (OR: 1.148; P = 0.042), and CD206 (OR: 1.189; P = 0.011). Together, these results showed significant relationships between irritably-elevated, anti-inflammatory cytokines in the placenta, especially HO-1, IL-4, CD206, and IL-10, and in fetuses with AR.
Variablesa Male Female OR (95% CI) P-value OR (95% CI) P-value IL-1 1.041 (0.923, 1.174) 0.517 1.091 (0.938, 1.270) 0.260 IL-10 1.036 (0.930, 1.154) 0.524 1.148 (1.005, 1.311) 0.042 MCP-1 1.108 (0.978, 1.255) 0.107 1.159 (0.986, 1.361) 0.073 CRP 1.083 (0.973, 1.205) 0.146 1.050 (0.925, 1.192) 0.449 HO-1 1.175 (1.038, 1.329) 0.011 1.154 (0.994, 1.339) 0.059 HIF-1α 1.123 (0.995, 1.267) 0.060 1.060 (0.912, 1.231) 0.450 GRP78 1.054 (0.964, 1.153) 0.249 1.106 (0.989, 1.237) 0.079 TNFα 1.074 (0.957, 1.206) 0.225 1.127 (0.977, 1.300) 0.102 IL-4 1.181 (1.056, 1.322) 0.004 1.190 (1.035, 1.369) 0.015 IL-6 1.075 (0.945, 1.223) 0.272 1.161 (0.988, 1.363) 0.069 IL-8 1.064 (0.938, 1.206) 0.335 1.114 (0.960, 1.292) 0.157 CD206 1.081 (0.971, 1.204) 0.154 1.189 (1.041, 1.358) 0.011 CD68 1.064 (0.971, 1.165) 0.184 1.086 (0.968, 1.218) 0.161 IFN-γ 1.059 (0.959, 1.170) 0.256 1.093 (0.965, 1.238) 0.161 Note. aAdjusted for maternal age, race, residence in the previous 6 months, smoking status, alcohol consumption. Table 7. Logistic regression analysis of placenta mRNA expression and allergic rhinitis in infants of different gender
-
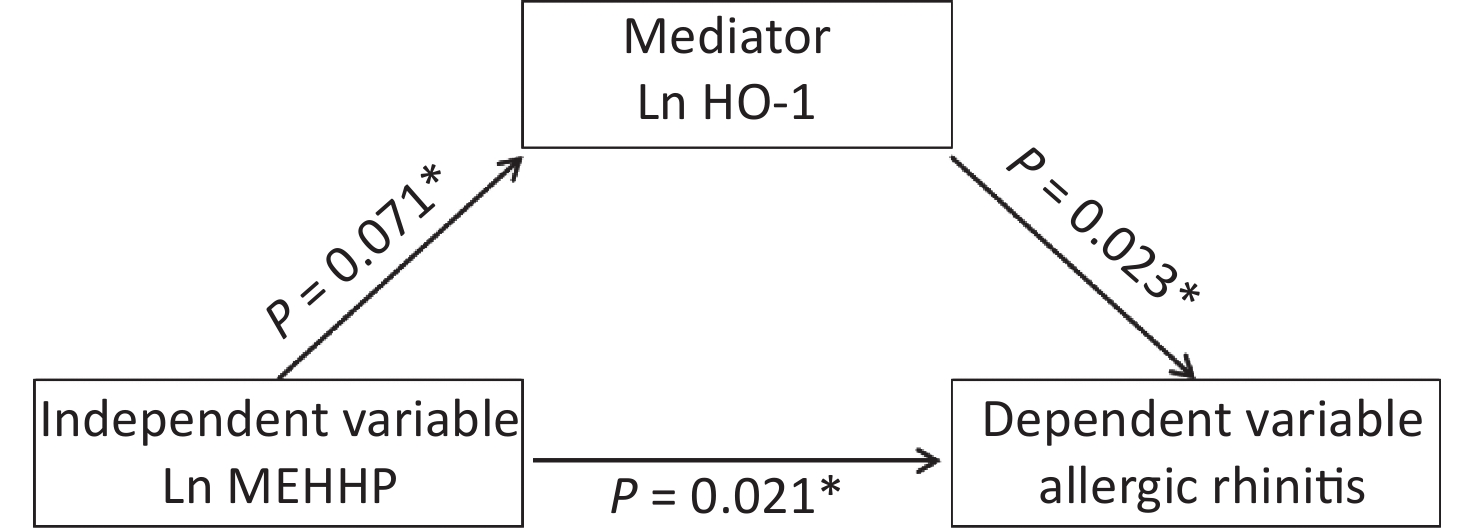
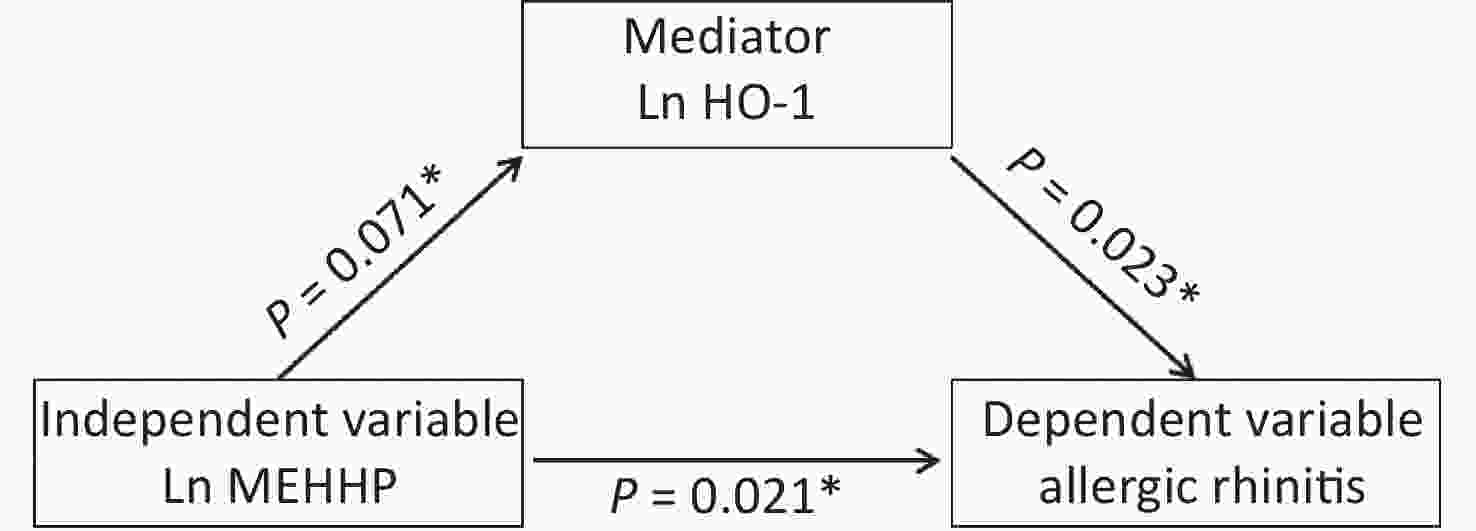
To verify whether associations between urinary phthalates and the risk of being diagnosed with AR were associated with maternal placental inflammatory cytokines, we determined whether requirements to indicate mediation were present (Table 8, Figure 2). The MEHHP phthalate metabolite was positively associated with AR in fetuses (P = 0.021), and the association between MEHHP and the placental inflammatory factor HO-1 was marginally significant (P = 0.071). There was a statistically significant association between placental HO-1 mRNA and AR in fetuses (P = 0.023). Thus, these results suggested that HO-1 may be a partial mediator in the associations between MEHHP and AR.
Type Value Bootstrap
SEBootstrap 90% CI Relative
effect ratio (%)Upper limit Lower limit Total
effect0.021 100 Direct
effect0.019 90.5 Indirect
effect0.002 0.001 0.001 0.005 9.5 Table 8. Bootstrap results of mediation effects (standardization)
-
AR is the most common allergic disease. Diagnosis of AR in the Chinese population has exceeded 17% with a significant increasing trend in recent years [18, 19]. Numerous risk factors have been found to predispose patients to AR. These risk factors include a family history of allergic diseases, male sex, and birth during the pollen season, first born status, early life antibiotic use, maternal smoking, and indoor allergen exposure [20]. AR may start early in life and can particularly impair the function of children in school and other aspects of life [21].
Phthalates have been suspected as risk factors for allergies in children, and inconsistent associations between environmental exposure to phthalates and allergic disorders have been found in different populations. Lee et al. proposed that environmental exposure to phthalates may affect the immune system and increase the occurrence of allergic symptoms in children [22]. The total amount of phthalate metabolites may have adverse health effects on asthma and allergic symptoms in Chinese children [23]. In an AR mouse model, DEHP promotes an increase in the Th2 response and oxidative stress, and causes mucosal damage in nasal mucosal cells [24]. We previously investigated whether maternal exposure to phthalate was associated with placental inflammatory-related cytokines. We found that mRNA expressions of IL-6, CRP, MCP-1, HO-1, HIF1α, and GRP78 in placentas were positively associated with MBP, and that these associations were stronger than those of the other metabolites. The expressions of HO-1, HIF1α, and GRP78 in male and female placentas are positively correlated with MEHHP exposure [10]. In addition, studies have reported that the concentrations of increased IL-1β, fluctuant monocytes, macrophages, and T cells may be related to DnBP exposure in murine testicular macrophages [12, 25]. MEHP, MEHHP, and MEOHP are metabolites of DEHP, a high molecular weight phthalate. Our previous study reported conflicting results between DEHP metabolites and placental inflammatory transcriptional biomarkers [10]. In the present study, there was a negative correlation between MEHP and MCP-1 levels in the placentas of male fetuses. Although MEHHP induced the expression of IL-6 and CD68 mRNA, the mRNA expression of CD206 was increased, suggesting that MEHHP also induced anti-inflammatory activity in the placentas of male fetuses. In the placentas of female fetuses, we did not observe a relationship between DEHP metabolites and placental inflammatory markers, except for MEOHP, which was negatively associated with expressions of CRP, MCP-1, and CD68 mRNA. Because maternal phthalate exposure was closely associated with placental inflammatory markers, we speculated that maternal phthalate exposure changed the levels of placental inflammatory factors, thus, inducing AR in offspring.
AR, a chronic reactive disease, is the most common allergic immunological disease that has been associated with inflammatory responses [26, 27]. AR increases the levels of Th2 cytokines, IgE, histamine, chemokine, and periostin, which are secreted and recruited by immune and epithelial cells in the nasal mucosa [28, 29]. The prevalence of allergic diseases has dramatically increased worldwide in recent decades [30, 31]. Previous research has linked adverse pregnancy outcomes and birth characteristics to several chronic disorders, including AR. Evidence has shown that the risk of allergic disease was influenced by the early development of the immune system [32, 33]. Multiple potential effects, including fetal allergic disease, were included in the panel of inflammation-related factors in the placental samples, such as inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses (HO-1, Th1, and Th2 cytokines) as well as macrophage biomarkers (CD68 and CD206). However, the associations between early-life factors and the risk of AR are not completely understood, and little is known about the influence of perinatal conditions on the development of AR. In this prospective cohort, we observed significant associations between placental inflammatory-related cytokines and AR in children, and suggested that these associations may be influenced by sex. Male children with AR had higher levels of placental inflammatory factors, including HO-1 and IL-4, and female fetuses had a statistically significant association with IL-10, IL-4, CD206, and CRP mRNA, but not HO-1. Nikolic et al. reported that airways started developing 4 weeks after conception [34], and prenatal maternal phthalate exposure was associated with asthma and wheezing in children [35, 36]. After adjustments for confounding variables, we found that MEHHP had positive correlations with other phthalate metabolites, and of all metabolites; MEOHP and MEHHP had the strongest associations with infant AR, which was more obvious in the placentas of male fetuses. However, no relationship was observed between phthalate metabolites and AR in female fetuses. Furthermore, the present study suggested that placental HO-1 may be a partial mediator in the association between maternal MEHHP and infant AR. Therefore, our findings demonstrated that maternal phthalate exposure and placental inflammatory factors were associated with AR in fetuses.
Considering the conflicting results, we believed that a study that determined the relationships between prenatal exposure and birth outcomes in different sexes was necessary. Our previous studies indicated that exposure to phthalates may cause morphological changes in placentas, such as more circular and thicker placentas of male fetuses than female fetuses [37], suggesting that phthalate exposure may be correlated with levels of reproductive hormones. Studies have reported that maternal urinary phthalates were associated with higher mRNA levels of chorionic gonadotropin α/β and human chorionic gonadotropin in the placentas of female fetuses, as well as with lower mRNA levels of these hormones in the placentas of male fetuses [38]. The regulation of genes in networks, pathways, and functional groups in placentas of female fetuses exhibit a highly coordinated response. For adverse intrauterine conditions, the placentae initiate complex adaptive responses that may contribute to better pregnancy outcomes for female infants [39]. In the present study, the association with maternal phthalate exposure was higher in male fetuses with AR than in female fetuses with AR, suggesting that male fetuses had a higher sensitivity to phthalates. Consequently, these controversial results need to be validated by additional research, especially in vivo studies and studies of human pregnancies.
The present study was large, population-based, and prospective, and it established a temporal relationship between maternal phthalate exposure and AR in offspring and placental inflammatory factors. However, phthalates have also been shown to be correlated with personal food consumption habits and product uses, and exposure to phthalates often occurs together with other environmental pollutants; therefore, the observed associations with phthalates and AR may have also resulted from combined exposures. Another limitation of the present study was the collection of spot urine samples, which are relatively easy to collect, but significant variability may exist in the data with respect to exposure prediction. In addition, qPCR, which is a relative quantification tool, was used to assess RNA expression. Other quantitative tools for analyzing transcriptional-level RNA are RNA-seq and microarrays. However, due to their high costs, RNA-seq and microarrays are more often used for screening small samples for genes of interest [40, 41]. A limitation of qPCR was that the results reflected only the gene mRNA transcript level. Information regarding the protein levels of these genes was not obtained because there was no suitable tool available for assessing these levels in the large population included in our study. However, the expression levels of placental inflammatory biomarkers can to a certain extent indirectly reflect the expression of proteins.
-
The present study was the first to identify the associations between prenatal phthalate exposures in large samplings of human placentas and fetal AR. We found that maternal phthalate metabolite levels were related to infant AR, and the associations were stronger in males with AR than in females with AR. Due to the ability of mRNAs to regulate cellular pathways, the state of fetal growth is dependent on the expression of placental mRNAs. Once biological processes are disrupted by phthalate exposure, the expression of mRNAs may be altered. Additionally, we found that placental inflammatory factors were associated with AR in both male and female fetuses, and placental HO-1 was a partial mediator in the associations between maternal MEHHP and AR in fetuses. Overall, we propose that placental mRNA regulation is a potentially significant mechanism in associations between maternal phthalate exposure and fetal AR, which warrants future investigation.
-
We are most grateful to the participants of the MABC cohort study and the study team, research nurses, interviewers, research assistants, and other staff who were involved in gathering the data for this study
-
None declared.
Mediation Effects of Placental Inflammatory Transcriptional Biomarkers on the Sex-Dependent Associations between Maternal Phthalate Exposure and Infant Allergic Rhinitis: A Population-Based Cohort Study
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.093
- Received Date: 2021-12-22
- Accepted Date: 2022-03-10
-
Key words:
- Phthalate /
- Infants /
- Allergic rhinitis /
- Inflammation /
- Sex difference
Abstract:
| Citation: | WANG Jian Qing, LI Zhi Juan, GAO Hui, SHENG Jie, LIANG Chun Mei, HU Ya Bin, XIA Xun, HUANG Kun, WANG Su Fang, ZHU Peng, HAO Jia Hu, TAO Fang Biao. Mediation Effects of Placental Inflammatory Transcriptional Biomarkers on the Sex-Dependent Associations between Maternal Phthalate Exposure and Infant Allergic Rhinitis: A Population-Based Cohort Study[J]. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(8): 711-721. doi: 10.3967/bes2022.093 |








 Quick Links
Quick Links
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: