HTML
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. Pneumoniae) is a bacterial pathogen that causes atypical pneumonia and community-acquired respiratory tract infections, particularly in school-age children and young adults[1]. M. pneumoniae infections can be persistent and difficult to eradicate[1-2]. The antibiotics widely used to treat M. pneumoniae infections include macrolides, tetracycline and fluoroquinolone, however, the latter two antibiotics were not recommended for use in children because of their toxicity[1].
The prevalence of macrolide resistant M. pneumoniae strains has increased rapidly worldwide since 2000[3-11]. This increase is especially evident in Asia, with recent studies showing that more than 90% of M. pneumoniae clinical isolates in China and Japan are macrolide resistant[7, 9]. Many studies have suggested that point mutations in the 23S rRNA gene are predominantly responsible for macrolide resistance in M. pneumoniae[2, 12-13], other mutations, such as mutations in the ribosomal proteins L4 and L22, were very rare in previous studies[14]. However, the high resistance rates of M. pneumoniae in China and Japan may be also because of the other possibility resistance mechanisms in this organism. To address this, we performed whole-genome sequencing to identify new mutations and mechanisms associated with drug resistance in recently isolated macrolide resistant clinical strains of M. pneumoniae.
-
The present project was performed in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration (Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects) and was approved by the research board of the Ethics Committee of our institute. All patient data were anonymously reported. Based on the guidelines of the Ethics Committee of our institute this study did not need to be examined by the ethical committee, and therefore informed consent was not sought from patients.
-
Ten clinical strains of M. pneumoniae were isolated in 2010 (CIP10349 and CIP10361) and 2012 (CIP12206, CIP12235, CIP12261, CIP12265, CIP12267, CIP12311, CIP12355, and CIP12357) from pediatric patients' bronchoalveolar lavage fluids in the affiliated children's hospital of the Capital Institute of Pediatrics, and all patients were treated with azithromycin with 4-5 courses and didn't use other antibiotics. These clinical isolates were cultured in PPLO broth (Becton, Dickinson and company, USA), yeast extract (10%, Oxoio LTD, England), unheated horse serum (20%, Lanzhou national Hyclone Bio-Engineering Co.LTD, China), glucose (50%, CR Double-Crane Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd, China), phenol red (0.4%, Amresco, OH, USA), and penicillin (1, 000 U/mL, North China pharmaceutical Group Corporation, China) at 37 ℃ in a BSL-2 laboratory several days until the color changes, and then MIC (minimal inhibitory concentrations) testing and whole-genome sequencing was performed.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was carried out using a broth microdilution method based on the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI document M43A) completely. Erythromycin (14-membered ring macrolide antibiotic), azithromycin (15-membered ring macrolide antibiotic) and medemycin (16-membered ring macrolide antibiotic) were used in this analysis, and they were all provided by the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing, China. M. pneumoniae reference strain FH (ATCC 15531) and M129 (ATCC 29342) were used as antibiotic-susceptible control strains. All tests were performed in triplicate. They were performed with the use of 96 well cell culture plates (Greiner Bio-One, Germany). Serial dilutions of antibiotics were made with final concentration of 512 μg/mL to 0.000125 μg/mL; M. pneumoniae suspensions were prepared in PPLO broth containing 105 CFU/mL.
-
Clinical strains and reference strains M129 and FH were harvested for DNA preparation by centrifugation (11, 200 g at 4 ℃, 30 min) of 100 mL of same-batch subculture suspension. The same batch of culture (after cultured 6 days) was used for genomic extractions to avoid nucleotide differences among subcultures. Genomic DNA was extracted using the QIAamp Mini DNA kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions, and the optical density was determined with rule out protein (OD260 range: 107-154 ng/μL), and DNA was sonicated using a Diagenode Bioruptor (Diagenode SA, Liège, Bele MAUVE). Illumina Hiseq2000 sequencing platform was used in this study. For the 10 newly assembled genome sequences, SOAPsnp was used to score single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from aligned reads[15]. The short reads were first aligned onto the M129 reference genome using the SOAP2 program[16]. To obtain reliable alignment hits, a maximum of two mismatches was allowed between the read and the reference sequence. For paired-end data, mapping locations for each read were restricted to sites within 500 bp of the mapping location of the partner sequence. For the other data, strain-specific SNPs were manually reviewed by taking into account whether SNPs were detected by MAUVE[17].
-
Coding genes and pseudo genes were predicted throughout the genome sequences using Glimmer and were annotated by comparison with the NCBI database. The genome sequence was annotated by Rapid Annotation using Subsystem Technology (RAST). The annotation results were verified using Artemis. In addition, the coding sequences were searched against the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Database (ARDB) to obtain resistance information (http://ardb.cbcb.umd.edu)[18]. Comparisons between antibiotic resistant genes were performed for the pre-existing genome sequences in the NCBI database (reference strains M129 and FH, they were international standard sensitive strains) and the 10 genome sequences derived from this study.
To verify the accuracy of whole-genome sequencing, some target DNA fragments were amplified by our standard PCR[19-20], and then sequenced using an ABI-3730 genetic analyser (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), including: 23S rRNA, 16S rRNA, P1 and P30, Mpn1 and Mpn13-16.
-
The efflux pump inhibitors reserpine (RSP) and carbonyl cyanide mchlorophenyl-hydrazone (CCCP) were from Sigma-Aldrich Shanghai Trading Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China. Preliminary experiments were performed to ensure that the concentrations of the efflux pump inhibitors used in this study were at least four-fold below their lethal dose. RSP and CCCP were tested in the broth microdilution assay against all strains[21]. Each strain in this study was exposed to macrolide antibiotics in the presence of efflux pump inhibitors RSP (20 μg/mL) and CCCP (7.5 μg/mL) alone or in combination. Tests were performed in 96-well plates at 37 ℃ for 7 days.
Ethical Approval
Clinical Isolates of M. pneumoniae and Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Determination
Genomic DNA Preparation, Library Construction, and DNA Sequencing
Comparative Genome Analysis
MIC Determination of Antibiotics in the Presence of Efflux Pump Inhibitors
-
The 10 clinical M. pneumoniae isolates analysed in this study all showed resistance to macrolide antibiotics based on the CLSI criteria (MIC > 1 μg/mL), and all harboured A2063G mutations in the domain V of the 23S rRNA gene (correspond to A2058G in E. coli numbering). M. pneumoniae reference strain FH was susceptible to all antibiotics tested (MIC < 1 μg/mL) (Table 1).
Strain No. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (μg/mL) Erythromycin Azithromycin Medemycin ERY2 alone +RSP3 +CCCP4 +RSP +CCCP5 AZM6alone +RSP +CCCP +RSP +CCCP MED7 alone +RSP +CCCP +RSP +CCCP FH (ATCC15531) < 1 / / / < 1 / / / < 1 / / / 1CIP10349 64 64 32 8 32 32 4 1 2 2 < 1 < 1 CIP10361 64 64 32 4 64 64 8 2 2 2 1 < 1 CIP12206 512 512 128 64 512 512 64 64 8 8 4 1 CIP12235 64 64 16 < 1 256 256 4 < 1 4 4 4 < 1 CIP12261 128 128 64 32 256 256 16 8 4 4 2 1 CIP12265 128 128 128 128 512 512 64 64 64 64 4 4 CIP12267 128 128 128 64 256 256 8 8 16 16 2 1 CIP12311 64 64 64 32 > 512 > 512 32 16 8 8 4 2 CIP12355 64 64 64 8 128 64 8 < 1 4 4 1 < 1 CIP12357 32 32 16 2 > 512 256 8 2 8 8 8 1 Note. 1CIP: Capital Institute of Pediatrics; 2ERY: Erythromycin tested alone; 3RSP: Reserpine and agent tested in combination with 20 μg/mL reserpine; 4CCCP: Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl-hydrazone and agent tested in combination with 7.5 μg/mL CCCP; 5(+RSP+CCCP): Agent tested in combination with 20 μg/mL reserpine and 7.5 μg/mL CCCP; 6AZM: Azithromycin tested alone; 7MED: medemycin tested alone. Table 1. Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations and the Effect of Efflux Pump Inhibitors on 10 Clinical Strains of M. pneumoniae Isolated in Beijing
-
The basic whole genome sequencing statistics are shown in Table 2. The mapped depth ranged between 70 × and 730 ×, and the percent of the reference genome covered was 99.97%-99.99%. Genome sequence analysis of the 10 clinical strains revealed that the draft genome sequences of eight clinical M. pneumoniae strains isolated in 2012 were similar in size (800, 977 to 807, 092 bp); however, the strains isolated in 2010 had smaller genomes (777, 576 bp for CIP10349 and 778, 884 bp for CIP10361). The minimal sequencing depth was 137 × among the 10 clinical isolates, and all isolates had a G + C content of 39%. The PCR results of some target DNA fragments showed that the levels of identity were 99.7%.
Strain Read Length (bp) Paired Read Number Raw Data (M) Mapping to Reference M129 2SNP Percent (%) Depth (X) 1CIP 12265 116 2994424 1, 011 99.98 730 336 CIP 12311 116 483739 112 99.97 70 335 CIP10349 110 722615 159 99.97 100 330 CIP10361 110 764851 168 99.98 100 350 CIP 12357 116 706950 164 99.99 190 346 CIP 12206 116 1285328 298 99.98 330 356 CIP 12235 116 1161819 270 99.99 310 350 CIP 12261 116 628844 146 99.99 170 351 CIP 12267 116 1124693 261 99.99 310 362 CIP 12355 116 633894 147 99.97 170 352 Note.1CIP: Capital Institute of Pediatrics; 2SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism. Table 2. Sequencing Statistics for the M. pneumoniae Isolates
Comparative genomic analyses were performed using the genome sequence of reference strains M129 and FH (International standard sensitive strains). The numbers of SNPs in each of the clinical isolates ranged between 330 and 362 when compared with reference strain M129. Gene function predictions based on M129 gene annotation showed that SNPs located within hypothetical proteins and intergenic regions were the most common variations. Other mutations included those located within genes encoding: type Ⅰ restriction enzyme EcoKI specificity protein, cytadherence protein, the membrane export protein family protein, ABC transporters, amino acid permease and cell division protein FtsH (Figure 1). Of the SNPs identified, 56 were shared by 10 clinical isolates but were absent from the M129 and FH reference strains. Of the 56 SNPs, 19 were synonymous mutations, 30 were non-synonymous mutations, and seven were located within non-coding sequences. Among 30 non-synonymous SNPs, there were 4 SNPs clustered in the gene encoding a macrolide-specific efflux pump protein of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family (Table S1, available in BES online, www.besjournal.com).
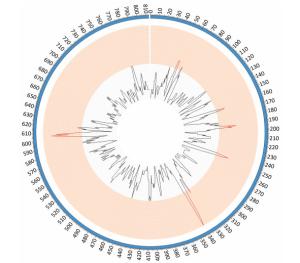
Figure 1. SNP density map constructed using circos. Red bars indicate the regions of high SNP density, these include the genes encoding: hypothetical proteins, intergenic regions, type Ⅰ restriction enzyme EcoKI specificity protein, cytadherence protein, the membrane export protein family protein, ABC transporter, amino acid permease and cell division protein FtsH.

Table Table S1. Fifty-six Mutations in All 10 Clinical Isolates which were Different from the M129 and FH Reference Strains
-
To identify new mutations associated with drug resistance, coding genes were identified in all isolates. BLAST searches against the ARDB showed that a total of seven different resistance profiles were found: polymyxin, bacitracin, trimethoprim, kasugamycin, macrolide, tetracycline, and thiostrepton. However, only macrolide antibiotics were investigated further as they are clinically relevant in treating M. pneumoniae pneumonia in children. BLAST analysis against the ARDB showed that SNPs associated with drug resistance were focused on the macb gene which belongs to resistance-nodulation-cell division transporter system and multidrug resistance efflux pump and macrolide-specific efflux system gene encoding a macrolide ABC transporter ATP-binding protein.
-
The MIC values for macrolides tested in the presence and absence of efflux pump inhibitors are presented in Table 1. The efflux pump inhibitor RSP produced little or no change in susceptibility. In only two of the 10 strains, the MIC value for AZM was decreased two-fold by RSP (CIP12355 from 128 to 64 μg/mL and CIP12357 from > 512 to 256 μg/mL). However, unlike RSP, CCCP produced a strong decrease in the macrolide MIC values, with the exception of strains CIP12265, CIP12267, CIP12311, and CIP12355 to erythromycin and strains CIP12235 and CIP12357 to midecamycin (Table 1). Surprisingly, on combining CCCP and RSP, the MIC values showed a greater decrease than for CCCP alone, with strains CIP10349, CIP10361, CIP12355, and CIP12235 even becoming susceptible ( < 1 μg/mL) to between one and three types of macrolides (Table 1).
Antimicrobial-susceptibility Testing of the M. pneumoniae Clinical Isolates
Genome Sequence Analysis of the 10 Clinical Isolates
Comparative Genome Analysis
Effect of Efflux Pump Inhibitors on Macrolide Susceptibility
-
M. pneumoniae is a common pathogen of the respiratory tract, especially in children. Antibiotics have been widely used to treat M. pneumoniae infections, likely contributing to the rapid increase in drug resistant pathogens, a growing health concern globally[3-6, 22-23]. Point mutations within the 23S rRNA gene of M. pneumoniae have been considered to be the major contributor to drug resistance in this organism[24]. Isolates harbouring these mutations are often highly resistant to 14-membered ring macrolides and moderately resistant to 15-and 16-membered ring macrolides in vitro. However, there have been no previous reports of mutations in other genes mediating antibiotic resistance. We therefore used the whole-genome sequencing approach and comparative genome analysis to investigate the possible involvement of other mechanisms in the resistance to macrolides in M. pneumoniae.
In this study, 10 clinical isolates of M. pneumoniae were found to be highly resistant to macrolide antibiotics in vitro, with MICs higher than those set by the CLSI in 2011. However, the MICs for the 16-membered ring macrolide medemycin were lower than for the 14-membered ring macrolide erythromycin and the 15-membered ring macrolide azithromycin. These findings may reflect the fact that medemycin was not commonly used to treat children in Beijing.
Three main mechanisms of antibiotic resistance have been reported to date: drug inactivation, active efflux and modification of target sites by methylation or mutation[25-26]. Active efflux system which takes part in the antibiotic resistance has been confirmed in M. hominis. S. Raherison et al. reported that the presence of an active efflux system, possibly an ABC-type efflux pump, implicated in the resistance to ciprofloxacin in the M. hominis[27]. S. Pereyre et al. also found that addition of an ABC transporter inhibitor could increase the level of erythromycin uptake more than two times; this also suggested the existence of an active efflux process in M. hominis[28]. Previous studies have shown that mutations in the 23S rRNA gene or the ribosomal proteins L4 and L22 of M. pneumoniae mediate macrolide resistance[29-30]. However, an active efflux mechanism in M. pneumoniae has remained speculation since there has been no definitive evidence to prove the existence of such a system involved in drug resistance in M. pneumoniae. In this study, all 10 clinical isolates of M. pneumoniae studied were found to harbour an A to G mutation located at nucleotide 122119 within the genome sequence (this locus corresponds to nucleotide 2, 063 within domain V of the 23S rRNA gene of M. pneumoniae, GenBank: X68422.1). However, no mutations were identified at nucleotides 2, 064 or 2, 617 of the 23S rRNA gene or within the genes encoding the ribosomal proteins L4 and L22. When all genome sequences of the 10 M. pneumoniae clinical isolates were compared against the ARDB to look for potential macrolide-resistant genes or mutations, seven types of antibiotic resistance genes were detected in the genome sequences. But only the macrolide-specific efflux pump gene was investigated further in this study as macrolides are the only clinically relevant antibiotics in paediatric patients. It was first identified as a macrolide antibiotic-specific transporter in E. coli, where it belongs to the family of ATP-binding cassette-type transporters that utilize ATP hydrolysis as a driving force[31-32]. This indicates the possibility that the macrolide-specific efflux system is one of the mechanisms responsible for macrolide resistance in M. pneumoniae, and it may be also an escape mechanism of M. pneumoniae to against antibiotics, like Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobaeter baumannii, Helicobacter pylori, and so on[33-36].
Two efflux pump inhibitors were employed in this study to address whether an efflux system is involved in macrolide resistance in this organism. RSP can inhibit members of the resistance nodulation-cell division efflux system and the major facilitator family of transporters, although the exact mechanism of this activity has not been clarified. Usually, it was used as an inhibitor of Multiple Drug Resistance (MDR) efflux pumps, including as an ATP-dependent efflux pump inhibitor[37-38]. CCCP, a proton shuttling carrier, can rapidly collapse proton-dependent electrochemical gradients across the cytoplasmic membranes of many bacteria[39]. In the presence of RSP or CCCP, the MIC values decreased to varying degrees. In particular CCCP alone resulted in decreased MIC values and CCCP in combination with RSP further reduced the MICs, in some cases with strains even becoming susceptible to antibiotics. Our data suggest that an active efflux system, possibly an ABC-type efflux pump, operates in M. pneumoniae playing a role in macrolide resistance.
As we have noted, our current work has some limitations. First and foremost, we used M129 and FH genome sequences as the sensitive control which published in NCBI, and we have not had clinical isolates without the 23S rRNA mutation as references, so no experiments were done within the presence of efflux pump mutations to show that they have an elevated MIC. Moreover, questions about how the efflux pump gene influences the macrolide-resistance in M. pneumoniae still exist. Therefore, further study is necesary to expound this efflux mechanism of resistance.
In summary, the genome sequences reported here have provided new insight into the molecular mechanisms of macrolide resistance in M. pneumoniae, and this is the first report of the macrolide special efflux resistance gene in clinical macrolide-resistant strains of M. pneumoniae isolated in Beijing, China. The efflux pump inhibitor CCCP effectively inhibited the efflux system of M. pneumoniae to macrolide antibiotics, and when combined with RSP led to even greater decreases in MIC values. These findings demonstrate that an active efflux mechanism may lead to drug resistance of M. pneumoniae to macrolide antibiotics. Further research is now required to fully elucidate this M. pneumoniae efflux mechanism.
the grants from National Nature Science Foundation of China 81672062
the Beijing Natural Science Foundation 7152025
the grants from National Nature Science Foundation of China 81601778
Beijing Talents Fund 2015000021469G192







 Quick Links
Quick Links
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: