-
COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing worldwide, which is a serious public health event of current concern[1-4]. Although studies have shown favorable prognosis for most COVID-19 patients, treatment outcomes for patients with comorbidities are unfavorable compared to patients without comorbidities[5-7], which has been reported by previous studies reported the treatment outcomes of COVID-19 with hypertension, diabetes, tuberculosis, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases[8-11].
Brucellosis is one of the seven neglected endemic zoonoses, remaining to be the commonest among them, endemic in more than 170 countries and areas, with about 500,000 new cases reported each year, and is still a worldwide issue[12-15]. Despite brucellosis had high cure rate, whereas, relapses, chronicity, potential mortality and sequels, are reasons for considering brucellosis to be a serious threat[16-19]. Currently, limited studies demonstrated the epidemic of COVID-19 combined with brucellosis[20-22]. However, no study on follow-up after discharge have been conducted, which is very important for policy-makers. Our study presented the clinical characteristics, treatment outcome, and follow up after discharge of four COVID-19 patients with brucellosis in Heilongjiang Infectious Disease Hospital from January 15, 2020 to April 29, 2022. Moreover, we also systematically demonstrated the similar cases reported in the literature, two COVID-19 patients and brucellosis coinfection from two case reports had favorable outcome[20-21], we assume that the four COVID-19 cases with brucellosis had good treatment outcome before and after recovery, the results provide reference for clinicians to diagnose and treat patients co-infected with novel coronavirus and brucellosis.
-
All patients were admitted from January 15, 2020 to April 29, 2022 in Infectious Disease Hospital of Heilongjiang Province in China. All COVID-19 patients with brucellosis were laboratory confirmed. The inclusion criteria for COVID-19 patients with brucellosis wereenrolled: (1) confirmed COVID-19 cases with laboratory confirmed; (2) history of brucellosis or diagnosed brucellosis after COVID-19. Patients were excluded if they met any of the following: (1) subjects who refused to participate, (2) lost to follow-up and unable to be contacted.
-
COVID-19 The severity of COVID-19 in our study followed China’s Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for COVID-19 was referred to the Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for COVID-19 of China. (1) Mild cases: the clinical symptoms were mild, and no sign of pneumonia was observed on CT image; (2) moderate cases: only having fever and respiratory symptoms with radiological findings of pneumonia on CT image; (3) severe cases were defined as having any of the following: ① respiratory distress and need invasive ventilation, ② pulse oxygen saturation ≤ 93%, or ③ arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2)/oxygen concentration ≤ 300 mmHg.
Brucellosis Brucellosis was diagnosed according to the Diagnosis of Brucellosis of China[23]: The confirmed patients were diagnosed if they had any of the following: (1) epidemiological contact history: close contact with domestic animals, wild animals (including ornamental animals), livestock products, brucellosis cultures, etc., or residents living in the epidemic area; (2) clinical symptoms and signs should exclude other suspected diseases; (3) laboratory examination: pathogen isolation, test-tube agglutination test, complement binding test and anti-human globulin test were positive.
-
The study was performed following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA)[24]. A systematic review has been conducted with regard to clinical characteristics, treatment outcome, and follow-up after discharge for COVID-19 patients with brucellosis.
A comprehensive literature search was conducted in both English database including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Chinese database CNKI, CSTJ, CBM, Wanfang Data for clinical studies, following search terms: (“COVID-19” OR “2019-nCoV” OR “SARS-CoV-2” OR “the Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia” OR “NPC”) AND (“Brucellosis”) from the inception date to December 31, 2022. References of important articles were searched manually for possible relevant studies. The inclusion criteria are as follows: (1) unlimited language; (2) clinical research (3) COVID-19 patients with brucellosis; (4) with sufficient patients’ information, including demographic, clinical, laboratory and radiological findings, treatment and outcome. Exclusion criteria are as follows: (1) abstracts from conference proceedings; (2) review articles.
-
Categorical variables were expressed as frequency and percentages (%), and continuous variables were presented as median (IQR) or as mean and standard deviation (SD) based on compliance with normal distribution. All data analyses were performed with SAS version 9.1 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). The detailed course after discharge were drawn using the Python Matplotlib package (version 3.2.1).
-
Case A Case A is a 54-year-old man with active brucellosis and was screened positive with COVID-19 nucleic acid screening with no other symptoms on January 15, 2020. He had a 36-year history of smoking and a 35-year history of drinking, was admission to the hospital on the same day. He had hyperbilirubinemia according to blood routine examination. Chest CT presented calcification in the upper lobe of the right lung and bulla in the upper lobe of the left lung. The patient was treated with antiviral therapies including abidor and interferon, additionally, he has been treated with doxycycline and rifampin for brucellosis. He had dry throat three days after admission (January 18), and was advised to be treated Lianhua Qingwen granule after inviting doctors of TCM to participate in the consultation. Five days after admission (January 20), antiviral therapies were suspended due to the clinical symptoms improved. On January 24, qualitative serological tests were resulted positive for both IgG and IgM firstly. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was negative on January 27 and 28, respectively. He was cured and discharged from the hospital on January 29, 2021. As of December 31, 2022, the patient was still receiving treatment for the active brucellosis, but had no re-positive or other discomfort symptoms through 23-months’ follow-up after discharge.
Case B Case B is a 35-year-old man with 2 years of non-active brucellosis and a 13-year history of smoking conducted COVID-19 nucleic acid screening and was detected RT-PCR positive with no other apparent symptoms. He was admitted to the hospital on January 16, 2021. Chest CT presented that no lesions in both lungs. He was diagnosed with sinus bradycardia, hyperuricemia, urine occult blood, and was treated with abidor and interferon, Lianhua Qingwen granule, bacillus licheniformis capsule. Antiviral therapy was discontinued three days after admission (January 19), and Lianhua Qingwen granule was replaced with Yiqi Jiedu decoctioneight days after admission (January 24). During the period of hospitalization, the patient’s condition was stable without aggravation. The patient was discharged on February 4, 2021 in good clinical condition after two subsequent negative nasopharyngeal swabs. As of December 31, 2022, the patient had anxiety and fatigue, but no recurrence of COVID-19 or brucellosis thourgh 22-months’ follow-up after discharge.
Case C Case C is a 57-year-old man with one year of brucellosis and intermittent headaches for 4 days, he was detected SARS-CoV-2-positive with a nasopharyngeal swab, and was admitted to hospital on January 16, 2021. Chest CT presented texture enhanced, bronchi tree-like changes, and surrounding light flake shadow in both lungs. He was diagnosed as moderate COVID-19, and was treated with antiviral therapies including abidor and interferon, Lianhua Qingwen Granules. He developed fever until 38.6 °C 11 days after admission (January 26, 2021). His temperature returned to normal the next day after taking antipyretic medicine. He started complaining about cough and phlegm 15 days after admission (January 30, 2021). After group consultations with doctors practicing Chinese and Western medicine, he was treated with Yiqi Jiedu decoction, meanwhile all other medications were stopped. In the following days, and clinical symptoms relieved gradually. The patient was discharged in good clinical condition with two subsequent negative nasopharyngeal swabs on February 6, 2021. As of December 31, 2022, the patient had no discomfort, also no recurrence of COVID-19 or brucellosis through 22-months’ follow-up after discharge. Additionally, we compared chest CT images before and after recovery (Figure 1).
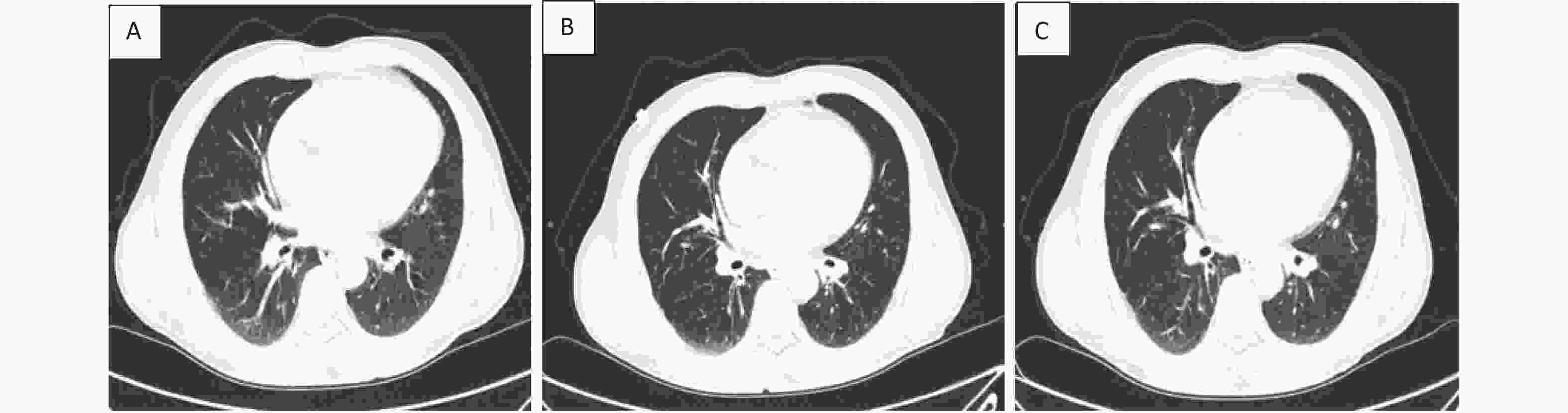
Figure 1. Chest CT images of a 57-year-old COVID-19 patient with brucellosis before and after recovery. Case C: (A): On admission, the bronchus of both lungs showed dendritic changes, with surrounding light patchy shadows and blurred margins, suggesting pulmonary bronchitis. (B): before recovery: lung lesions absorbed and reduced compared to that measured at admission. (C): follow up of one week after recovery: there was no deterioration of lung lesions and little change compared with that measured before recovery.
Case D Case D is a 72-year-old man with four years of brucellosis, with fever of 38.0 °C and no other apparent symptoms on April 20, 2022. He was detected SARS-CoV-2 positive with a nasopharyngeal swab on April 20, 2022. When COVID-19 nucleic acid screening, and was admitted to hospital on the same day, he was treated only with Yinlian Qingwen detoxification oral liquid. During the hospitalization, the patient’s condition was stable without aggravation. The patient was discharged in good clinical condition after two subsequent negative nasopharyngeal swabs on April 29, 2021. As of December 31, 2022, the patient had no discomfort, also no recurrence of COVID-19 or brucellosis through 22-months’ follow-up after discharge.
The detailed information of the four cases is shown in Figure 2, Tables 1–2.
Table 1. Demographics, clinical characteristics, treatment medicines and outcomes of the four COVID-19 patients with brucellosis
Variables Case A Case B Case C Case D Age (years) 54 35 57 72 Gender Male Male Male Male Occupation Farmer Farmer Farmer Farmer Smoking YES YES YES NO Drinking YES NO YES YES Classification of brucellosis Active Non-active Non-active Non-active History of brucellosis (years) 5 2 1 4 History of COVID-19 vaccination NO NO NO YES Comorbidities (except brucellosis) Hyperbilirubinemia Sinus bradycardia;
HyperuricemiaBronchitis NO Date of admission 2021.01.15 2021.01.16 2021.01.16 2022.04.20 Date of positive RT-PCR 2021.01.14 2021.01.16 2021.01.14 2022.04.20 Clinical classification of COVID-19 Mild Asymptomatic Moderate Moderate Symptoms on admission Body temperature, °C 36.7 36.2 36.7 37.9 Cough NO NO NO NO Sore throat NO NO NO NO Fatigue NO NO NO NO Headache NO NO YES NO Asthma NO NO NO NO Anorexia NO NO NO NO Diarrhea NO NO NO NO Nasal obstruction NO NO NO NO Rhinorrhea NO NO NO NO Treatment medicines COVID-19 Western medicines Antivirals Abidor, interferon Abidor, interferon Abidor, interferon NO Antibiotics NO NO NO NO Hormonal drugs and others NO NO NO NO Traditional Chinese medicine Yiqi detoxification soup, Lianhua Qingwen capsule Yiqi detoxification soup, Lianhua Qingwen capsule Yiqi detoxification soup, Lianhua Qingwen capsule Unionpay Qingwen detoxification oral liquid Brucellosis Doxycycline YES NO NO NO Rifampicin YES NO NO NO Others NO NO NO NO Date of the first negative RT-PCR 2021.01.27 2021.01.22 2021.02.04 2022.04.27 Date of discharge 2021.01.29 2021.02.04 2021.02.06 2022.04.29 Duration of viral shedding (days) 13 6 21 7 Duration of hospitalization (days) 14 19 21 9 Worsened NO NO NO NO Table 2. Laboratory and CT findings of four cases at admission and discharge
Variables Case A Case B Case C Case D Admission Discharge Admission Discharge Admission Discharge Admission Discharge Laboratory funding NEU, ×109/L (2−7) 6.34 6.73 2.97 3.22 2.52 3.44 3.71 1.66(↓) LY, ×109/L (0.8−4.5) 1.99 1.86 2.85 3.03 2.03 1.95 0.69(↓) 2.03 HGB, g/L (120−160) 165.00(↑) 161.00(↑) 158.00 162.00(↑) 155.00 154.00 150.00 165.00(↑) HCT, % (36−50) 48.90 48.10 47.20 49.20 47.10 46.20 44.50 49.20 MCH, pg (26.0−31.0) 32.10(↑) 31.70(↑) 32.80(↑) 32.30(↑) 31.60(↑) 31.50(↑) 33.70(↑) 33.80(↑) WBC, ×109/L (4−10) 8.84 9.26 6.56 6.86 4.98 6.22 4.83 4.17 CRP, mg/L (0−10) < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 TBIL, μmol/L (3−17) 64.00(↑) 14.30 6.20 11.10 8.40 5.90 9.50 10.70 DBIL, μmol/L (0−7) 6.70 2.80 1.80 2.50 1.60 1.80 2.2 2.20 IBIL, μmol/L (0−17) 57.26(↑) 11.46 4.44 8.64 6.80 4.11 7.28 8.53 PLT, ×109/L (100−300) 207.00 168.00 306.00(↑) 320.00(↑) 186.00 332.00(↑) 128.00 149.00 AST, U/L (2−40) 19.00 16.00 24.00 28.00 27.00 35.00 16.00 19.00 ALT, U/L (0−78) 29.00 27.00 27.00 31.00 23.00 35.00 30.00 32.00 ALP, U/L ( 50−135) 96.01 95.20 62.15 75.87 81.45 89.27 86.30 92.97 CK, U/L (46−171) 93.00 53.90 53.30 75.60 61.00 43.90(↓) 91.90 84.70 LDH, U/L (110−240) 180.00 144.00 133.00 110-240 146.00 154.00 151.00 140.00 D-Dimer, μg/mL (0−0.55) 0.13 0.07 0.04 NR 0.04 0.14 0.09 NR UREA, mmol/L (2.5−6.4) 7.80(↑) 5.12 6.21 6.35 4.12 4.82 2.99 4.17 PCT, % (0.108−0.272) 0.20 0.16 0.28(↑) 0.31(↑) 0.20 0.29(↑) 0.14 0.18 Creatinine, μmol/L (42−97) 59.40 63.30 70.70 71.00 68.20 83.10 75.90 75.70 CT findings No abnormal lesions No No Yes Yes No No No No Unilateral lung lesions No No No No No No No No Bilateral lung lesions Yes Yes No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Note. NEU, Neutrophil count; LY, lymphocyte count; HGB, hemoglobin; HCT, human chorionic thyrotropin; MCH, mean corpuscular hemoglobin; WBC, white blood cell count; CRP, C-reactive protein levels; TBIL, total bilirubin; DBIL, direct bilirubin; IBIL, Indirect bilirubin; PLT, platelet count; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; CK, creatine kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PCT , Procalcitonin; CT, computed tomography “↑”indicates higher than normal; “↓” lower than normal; Admission, admitted to hospital; Discharge, discharged from hospital. -
The demographic characteristics of participants are shown in the Table 1. All the four patients were enrolled, and the median age was 55.5 (39.75, 68.25) years. All cases were male (100.0%); among them, 2 patients (50.0%) were moderate, one was mild (25.0%) and one was asymptomatic (25.0%), respectively; three cases were smokers and drinkers (75.0%). Additionally, one case was diagnosed with dycardia, hyperuricemia and bronchitis. Additionally, all 4 patients were detected in COVID-19 nucleic acid screening. Case C and D had only headache and fever on admission, respectively. One patient had active brucellosis before covid and 3 patients had nonactive brucellosis before brucellosis.
Among the laboratory indexes of the 4 patients, IBIL and UREA were increased in case A, PCT was increased in case B, and LY was decreased in case D, while the other indexes showed no obvious abnormal changes. After treatment, all patients showed different degrees of improvementThree patients (75.0%) showed abnormal bilateral lung lesions on admission, and one patient had abnormal unilateral lung lesions. After treatment, lung lesions presented different degrees of absorption (Table 2).
-
All patients (100%) were treated with Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), and 3 patients (75.0%) received TCM and western medicine (WM). The median durations of viral shedding and hospitalization were 10.0 (6.25, 19.00) and 16.5 (10.25, 20.50) days, respectively. Four patients were cured and discharged after treatment without adverse reaction during hospitalization (Table 1).
-
As of December 31, 2022, four patients completed 8- to 22-months’ follow up, one (25.0%) case had still active brucellosis and no re-positive COVID-19, and three cases (75.0%) have no symptoms of discomfort except one case with fatigue and anxious during the follow-up period.
-
Two papers were finally included according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria[18-19], and no observational clinical trials were found. Furthermore, there were 2 case reports including 2 COVID-19 with brucellosis[18-19], the two cases were presented a detailed course during hospitalization (Tables 3−4).
Table 3. Demographics, comorbidities, clinical presentation, and treatment medicines and outcome of two cases coinfected COVID-19 and brucellosis in systematic review
Variables Case 1[18] Case 2[19] Age (years) 89 20 Gender Male Male Occupation NR NR Country (region) Iran Turkey Clinical Classification of COVID-19 NR NR History of brucellosis (Years) 8 NR History of Vaccinations NR NR Comorbidities (Except Brucellosis) NR NR Symptoms on Admission Fever YES YES Fatigue YES YES Dyspnea YES NO Joint Pain NO YES Treatment medicines COVID-19 Antivirals NR Hydroxychloroquine Antibiotics NR NR Hormonal Drugs Prednisolone, Dexamethasone NR Others Respiratory Support Enoxaparin Brucellosis YES YES Doxycycline YES YES Rifampicin YES YES Others NR NR Date of the negative RT-PCR NR NR Worsened YES NO Table 4. Laboratory and CT findings of two cases coinfected COVID-19 and brucellosis in systematic review
Variables Case 1[18] Case 2[19] Admission Before recovery Admission Before recovery Laboratory findings WBC, ×109/L {Case 1 (4–10); Case 2 (3.59–9.64)} 12.6 13.18 12.5 NR RBC, ×109/L {Case 1 (4–6)} 4.75 5.37 NR NR NEU, ×109/L {Case 1(1.9–8.0); Case 2 (1.64–5.95)} NR 11.67 9.5 NR LY, ×109/L {Case 1 (0.9–5.2); Case 2 (1.12–3.33)} 2.2 0.78 2.8 NR HGB, g/dL {Case 1(12–17); Case 2 (13.2–17.2)} 13.8 NR 12.4 NR CRP, mg/dL {Case 1 (1–6) (0–0.5); Case 2 (0–0.5)} 1 NR 2.6 NR PLT, ×109/L {Case 1 (100-300); Case 2 (148–339)} 203 NR 163 NR AST, U/L {Case 1 (10–37); Case 2 (5–34)} 27 NR 22 NR ALT, U/L {Case 1(10–37); Case 2 (0–55)} 15 NR 40 NR ALP, U/L {Case 1 (70–330)} 164 NR NR NR LDH, IU/L {Case 1 (Adult < 480)} NR NR NR NR D-Dimer, ng/mL, {Case 1 (Negative < 2)} NR 100 NR NR UREA, mg/dL {Case 1 (17–45)} 55 50 NR NR Creatinine, (mg/dL){ Case 1 (0.6–1.3)} 1.3 1.2 NR NR ESR, (mm/h) {Case 2 (0–20)} NR NR 32 NR CT findings Bilateral lung lesions NR Bilateral lung lesions NR Note. WBC, white blood cell count; RBC, red blood cell; NEU, neutrophil count; LY, lymphocyte count; HGB, hemoglobin; CRP, C-reactive protein; PLT, platelet count; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CT, computed tomography. NR, indicates not record data. The first case report[18] was from Iran, a 89-year-old male with COVID-19 admitted to the hospital because of weakness, malaise, weight loss, and lethargy, cough and dyspnea. His chest CT scan presented nodular opacities, with a variable low P O2, elevated transaminases, and a high D- dimer concentration. The patient was admitted to the intensive care unit requiring endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation for refractory hypoxia on day 6.
He had brucellosis 8 years ago and brucella symptoms a few months ago. Then he was detected a positive brucella titer of 1:160 for wright, subsequently, he was diagnosed with active brucellosis, and he then was treated with doxycycline and rifampicin in addition to anti-COVID-19 treatment. The patient was discharged in good clinical condition respiratory symptoms improved after two subsequent RT-PCR-negative. However, the length of hospital stay and nucleic acid turn negative were not described in this paper, and patients were not followed up after discharge.
The second case report[19] was from Turkey, the case of a 20-year-old male with COVID-19 admitted to the hospital because of weakness, fatigue, fever, and joint pain. Chest CT presented that bilateral pulmonary infiltrate. He was treated with hydroxychloroquine and enoxaparin for 5 days and instructed to maintain isolation at home. However, he complained persistent fever and joint pain after four days, and he developed fever until 38 °C. PCR-test of a second oropharyngeal swab sample was negative for SARS-CoV-2. He was then diagnosed as brucellosis after positive serologic diagnosis of brucellosis and positive at a titer of 1/160 of brucella agglutination, was received doxycycline and rifampicin after diagnosis of brucellosis, and fever and joint pain improved after 10 days of antibiotic treatment. Whereas, the case report did not describe duration of nucleic acid turn negative, also without follow up of COVID-19 after discharge.
-
To our best knowledge, this is the first study to explore treatment outcome before and after recovery. Our study demonstrated that treatment outcome of four COVID-19 patients with brucellosis are favorable without recurrence of COVID-19. In literature, COVID-19 and brucellosis co-infection in two patients from two case reports are also recovered, nonetheless, which lacked of follow up results after discovery.
Studies have revealed that male brucellosis patients were more than female patients, and presented with obvious occupational characteristics[25]. In our study, 4 patients were all male, and without severe cases, which was consistent with previous studies[20-21]. Additionally, in our study, one patient had active brucellosis before COVID-19, notably, none of the other 3 patients with a history of brucellosis developed active brucellosis. Based on limited study about COVID-19 and brucellosis, it is still unclear whether brucellosis will lead to COVID-19 or whether COVID-19 will further activate brucellosis.
There were few studies on treatment of COVID-19 and brucellosis, two patients of COVID-19 and brucellosis in two case reports were received with western medicine, although two patients recovered from COVID-19, they were diagnosed with active brucellosis during hospitalization[20-21]. In our study, four patients were treated with TCM during hospitalization, notably, Among the four patients, one patient was treated with traditional Chinese medicine only. However, after 9 days of hospitalization, he recovered and was discharged from the hospital, and there was no recurrence or other sequelae during the follow-up, suggesting that traditional Chinese medicine treatment alone has a favorable outcome for COVID-19 complicated with brucellosis, which can provide reference for clinicians.
Sequelae are a global concern in COVID-19 patients after recovery, which includes fatigue, dyspnoea, arthromyalgia, depression, anxiety, memory loss, concentration difficulties, and insomnia, etc.[4,26-29] literature published observed that 49% and 19.8% of patients reported at least one symptom at a 12-month and 24-month follow-up, respectively[30-31]. Previous studies had reported that chronic musculoskeletal sequelae of brucellosis occurred in up to 50% of patients with chronic disease[32]. Our results found that only one case felt fatigue and anxious at 22-month follow up, the other three patients did not experience symptoms of discomfort during the 8–22-month follow-up period, and the incidence of sequelae was lower than other studies[30]. Relapse are also a major problems after recovery in COVID-19 and brucellosis, previous study reported 30%–40% of relapse rates in brucellosis[33], and a meta-analysis including 3,644 COVID-19 patients from 41 studies demonstrated 15% of relapse rate, and up to 37% of relapse in Korea[34]. Whereas, no study reported results of follow up after discharge in COVID-19 patients with brucellosis. In our study, no case reoccurred in COVID-19 and brucellosis (except Case A of brucellosis who has not recovered), the findings indicated that COVID-19 patients with brucellosis had favorable prognosis after recovery. The results may be related to the national policy in the context of COVID-19, and the early detection of patients through active testing. Moreover, four cases are non-severe, above reason may had favorable outcome.
-
There are several limitations in the present study. Firstly, this study was conducted in a single center. Secondly, the sample is small. Thirdly, also small sample of only two cases in some literature data is incompleteness, such as the detailed CT findings before recovery, clinical classification of COVID-19, date of recovery for COVID-19, and comorbidities (except brucellosis). Thus, the conclusions of small sample might have bias. Further studies with large-sample, multi-center clinical research need to be conducted to confirm our findings.
-
In summary, to our best knowledge, this study is the first study to describe treatment outcome of COVID-19 with brucellosis before and after recovery, including persistence of symptoms and recurrence of disease, our findings indicated that patients with COVID-19 and brucellosis were treated TCM with/without WM had favorable outcome before and after recovery.
-
This study has been registered in by the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2100042177) and was approved by the Institutional Review Bboard of the Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (No. P20009/PJ09).
doi: 10.3967/bes2023.035
Treatment Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients with Brucellosis: Case Series in Heilongjiang and Systematic Review of Literature
-
Abstract:
Objective Clinical characteristics and outcome in COVID-19 with brucellosis patients has not been well demonstrated, we tried to analyze clinical outcome in local and literature COVID-19 cases with brucellosis before and after recovery. Methods We retrospectively collected hospitalization data of comorbid patients and prospectively followed up after discharge in Heilongjiang Infectious Disease Hospital from January 15, 2020 to April 29, 2022. Demographics, epidemiological, clinical symptoms, radiological and laboratory data, treatment medicines and outcomes, and follow up were analyzed, and findings of a systematic review were demonstrated. Results A total of four COVID-19 with brucellosis patients were included. One patient had active brucellosis before covid and 3 patients had nonactive brucellosis before brucellosis. The median age was 54.5 years, and all were males (100.0%). Two cases (50.0%) were moderate, and one was mild and asymptomatic, respectively. Three cases (75.0%) had at least one comorbidity (brucellosis excluded). All 4 patients were found in COVID-19 nucleic acid screening. Case C and D had only headache and fever on admission, respectively. Four cases were treated with Traditional Chinese medicine, western medicines for three cases, no adverse reaction occurred during hospitalization. All patients were cured and discharged. Moreover, one case (25.0%) had still active brucellosis without re-positive COVID-19, and other three cases (75.0%) have no symptoms of discomfort except one case fell fatigue and anxious during the follow-up period after recovery. Conducting the literature review, two similar cases have been reported in two case reports, and were both recovered, whereas, no data of follow up after recovery. Conclusion These cases indicate that COVID-19 patients with brucellosis had favorable outcome before and after recovery. More clinical studies should be conducted to confirm our findings. -
Key words:
- COVID-19 /
- Brucellosis /
- Treatment outcomes /
- Sequelae /
- Relapse
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
&These authors contributed equally to this work.
注释:1) AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS: 2) CONFLICT OF INTEREST: -
Figure 1. Chest CT images of a 57-year-old COVID-19 patient with brucellosis before and after recovery. Case C: (A): On admission, the bronchus of both lungs showed dendritic changes, with surrounding light patchy shadows and blurred margins, suggesting pulmonary bronchitis. (B): before recovery: lung lesions absorbed and reduced compared to that measured at admission. (C): follow up of one week after recovery: there was no deterioration of lung lesions and little change compared with that measured before recovery.
Table 1. Demographics, clinical characteristics, treatment medicines and outcomes of the four COVID-19 patients with brucellosis
Variables Case A Case B Case C Case D Age (years) 54 35 57 72 Gender Male Male Male Male Occupation Farmer Farmer Farmer Farmer Smoking YES YES YES NO Drinking YES NO YES YES Classification of brucellosis Active Non-active Non-active Non-active History of brucellosis (years) 5 2 1 4 History of COVID-19 vaccination NO NO NO YES Comorbidities (except brucellosis) Hyperbilirubinemia Sinus bradycardia;
HyperuricemiaBronchitis NO Date of admission 2021.01.15 2021.01.16 2021.01.16 2022.04.20 Date of positive RT-PCR 2021.01.14 2021.01.16 2021.01.14 2022.04.20 Clinical classification of COVID-19 Mild Asymptomatic Moderate Moderate Symptoms on admission Body temperature, °C 36.7 36.2 36.7 37.9 Cough NO NO NO NO Sore throat NO NO NO NO Fatigue NO NO NO NO Headache NO NO YES NO Asthma NO NO NO NO Anorexia NO NO NO NO Diarrhea NO NO NO NO Nasal obstruction NO NO NO NO Rhinorrhea NO NO NO NO Treatment medicines COVID-19 Western medicines Antivirals Abidor, interferon Abidor, interferon Abidor, interferon NO Antibiotics NO NO NO NO Hormonal drugs and others NO NO NO NO Traditional Chinese medicine Yiqi detoxification soup, Lianhua Qingwen capsule Yiqi detoxification soup, Lianhua Qingwen capsule Yiqi detoxification soup, Lianhua Qingwen capsule Unionpay Qingwen detoxification oral liquid Brucellosis Doxycycline YES NO NO NO Rifampicin YES NO NO NO Others NO NO NO NO Date of the first negative RT-PCR 2021.01.27 2021.01.22 2021.02.04 2022.04.27 Date of discharge 2021.01.29 2021.02.04 2021.02.06 2022.04.29 Duration of viral shedding (days) 13 6 21 7 Duration of hospitalization (days) 14 19 21 9 Worsened NO NO NO NO Table 2. Laboratory and CT findings of four cases at admission and discharge
Variables Case A Case B Case C Case D Admission Discharge Admission Discharge Admission Discharge Admission Discharge Laboratory funding NEU, ×109/L (2−7) 6.34 6.73 2.97 3.22 2.52 3.44 3.71 1.66(↓) LY, ×109/L (0.8−4.5) 1.99 1.86 2.85 3.03 2.03 1.95 0.69(↓) 2.03 HGB, g/L (120−160) 165.00(↑) 161.00(↑) 158.00 162.00(↑) 155.00 154.00 150.00 165.00(↑) HCT, % (36−50) 48.90 48.10 47.20 49.20 47.10 46.20 44.50 49.20 MCH, pg (26.0−31.0) 32.10(↑) 31.70(↑) 32.80(↑) 32.30(↑) 31.60(↑) 31.50(↑) 33.70(↑) 33.80(↑) WBC, ×109/L (4−10) 8.84 9.26 6.56 6.86 4.98 6.22 4.83 4.17 CRP, mg/L (0−10) < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 < 10.00 TBIL, μmol/L (3−17) 64.00(↑) 14.30 6.20 11.10 8.40 5.90 9.50 10.70 DBIL, μmol/L (0−7) 6.70 2.80 1.80 2.50 1.60 1.80 2.2 2.20 IBIL, μmol/L (0−17) 57.26(↑) 11.46 4.44 8.64 6.80 4.11 7.28 8.53 PLT, ×109/L (100−300) 207.00 168.00 306.00(↑) 320.00(↑) 186.00 332.00(↑) 128.00 149.00 AST, U/L (2−40) 19.00 16.00 24.00 28.00 27.00 35.00 16.00 19.00 ALT, U/L (0−78) 29.00 27.00 27.00 31.00 23.00 35.00 30.00 32.00 ALP, U/L ( 50−135) 96.01 95.20 62.15 75.87 81.45 89.27 86.30 92.97 CK, U/L (46−171) 93.00 53.90 53.30 75.60 61.00 43.90(↓) 91.90 84.70 LDH, U/L (110−240) 180.00 144.00 133.00 110-240 146.00 154.00 151.00 140.00 D-Dimer, μg/mL (0−0.55) 0.13 0.07 0.04 NR 0.04 0.14 0.09 NR UREA, mmol/L (2.5−6.4) 7.80(↑) 5.12 6.21 6.35 4.12 4.82 2.99 4.17 PCT, % (0.108−0.272) 0.20 0.16 0.28(↑) 0.31(↑) 0.20 0.29(↑) 0.14 0.18 Creatinine, μmol/L (42−97) 59.40 63.30 70.70 71.00 68.20 83.10 75.90 75.70 CT findings No abnormal lesions No No Yes Yes No No No No Unilateral lung lesions No No No No No No No No Bilateral lung lesions Yes Yes No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Note. NEU, Neutrophil count; LY, lymphocyte count; HGB, hemoglobin; HCT, human chorionic thyrotropin; MCH, mean corpuscular hemoglobin; WBC, white blood cell count; CRP, C-reactive protein levels; TBIL, total bilirubin; DBIL, direct bilirubin; IBIL, Indirect bilirubin; PLT, platelet count; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; CK, creatine kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PCT , Procalcitonin; CT, computed tomography “↑”indicates higher than normal; “↓” lower than normal; Admission, admitted to hospital; Discharge, discharged from hospital. Table 3. Demographics, comorbidities, clinical presentation, and treatment medicines and outcome of two cases coinfected COVID-19 and brucellosis in systematic review
Variables Case 1[18] Case 2[19] Age (years) 89 20 Gender Male Male Occupation NR NR Country (region) Iran Turkey Clinical Classification of COVID-19 NR NR History of brucellosis (Years) 8 NR History of Vaccinations NR NR Comorbidities (Except Brucellosis) NR NR Symptoms on Admission Fever YES YES Fatigue YES YES Dyspnea YES NO Joint Pain NO YES Treatment medicines COVID-19 Antivirals NR Hydroxychloroquine Antibiotics NR NR Hormonal Drugs Prednisolone, Dexamethasone NR Others Respiratory Support Enoxaparin Brucellosis YES YES Doxycycline YES YES Rifampicin YES YES Others NR NR Date of the negative RT-PCR NR NR Worsened YES NO Table 4. Laboratory and CT findings of two cases coinfected COVID-19 and brucellosis in systematic review
Variables Case 1[18] Case 2[19] Admission Before recovery Admission Before recovery Laboratory findings WBC, ×109/L {Case 1 (4–10); Case 2 (3.59–9.64)} 12.6 13.18 12.5 NR RBC, ×109/L {Case 1 (4–6)} 4.75 5.37 NR NR NEU, ×109/L {Case 1(1.9–8.0); Case 2 (1.64–5.95)} NR 11.67 9.5 NR LY, ×109/L {Case 1 (0.9–5.2); Case 2 (1.12–3.33)} 2.2 0.78 2.8 NR HGB, g/dL {Case 1(12–17); Case 2 (13.2–17.2)} 13.8 NR 12.4 NR CRP, mg/dL {Case 1 (1–6) (0–0.5); Case 2 (0–0.5)} 1 NR 2.6 NR PLT, ×109/L {Case 1 (100-300); Case 2 (148–339)} 203 NR 163 NR AST, U/L {Case 1 (10–37); Case 2 (5–34)} 27 NR 22 NR ALT, U/L {Case 1(10–37); Case 2 (0–55)} 15 NR 40 NR ALP, U/L {Case 1 (70–330)} 164 NR NR NR LDH, IU/L {Case 1 (Adult < 480)} NR NR NR NR D-Dimer, ng/mL, {Case 1 (Negative < 2)} NR 100 NR NR UREA, mg/dL {Case 1 (17–45)} 55 50 NR NR Creatinine, (mg/dL){ Case 1 (0.6–1.3)} 1.3 1.2 NR NR ESR, (mm/h) {Case 2 (0–20)} NR NR 32 NR CT findings Bilateral lung lesions NR Bilateral lung lesions NR Note. WBC, white blood cell count; RBC, red blood cell; NEU, neutrophil count; LY, lymphocyte count; HGB, hemoglobin; CRP, C-reactive protein; PLT, platelet count; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CT, computed tomography. NR, indicates not record data. -
[1] Du Y, Zhang J, Wu LJ, et al. The epidemiology, diagnosis and prognosis of long-COVID. Biomed Environ Sci, 2022; 35, 1133−9. [2] Ma Y, Mishra SR, Han XK, et al. The relationship between time to a high COVID-19 response level and timing of peak daily incidence: an analysis of governments' Stringency Index from 148 countries. Infect Dis Poverty, 2021; 10, 96. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00880-x [3] Coccia M. Optimal levels of vaccination to reduce COVID-19 infected individuals and deaths: A global analysis. Environ Res, 2022; 204, 112314. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112314 [4] Wang JY, Zong XY, Wu GH, et al. 3- to 24-month follow-up on COVID-19 with pulmonary tuberculosis survivors after discharge: results from a prospective, multicenter study. Biomed Environ Sci, 2022; 35, 1091−9. [5] Ji YL, Wu Y, Qiu Z, et al. The pathogenesis and treatment of COVID-19: a system review. Biomed Environ Sci, 2021; 34, 50−60. [6] The Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team. The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) - China, 2020. China CDC Wkly, 2020; 2, 113−22. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2020.032 [7] Ma Y, Zhu DS, Chen RB, et al. Association of overlapped and un-overlapped comorbidities with COVID-19 severity and treatment outcomes: a retrospective cohort study from nine provinces in China. Biomed Environ Sci, 2020; 33, 893−905. [8] Pepera G, Tribali MS, Batalik L, et al. Epidemiology, risk factors and prognosis of cardiovascular disease in the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic era: a systematic review. Rev Cardiovasc Med, 2022; 23, 28. [9] Qian Z, Li ZH, Peng J, et al. Association between hypertension and prognosis of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Hypertens, 2022; 44, 451−8. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2022.2071914 [10] Wang JY, Zong XY, Wu GH, et al. 3- to 24-month follow-up on COVID-19 with pulmonary tuberculosis survivors after discharge: results from a prospective, multicenter study. Biomed Environ Sci, 2022; 35, 1091−9. [11] Chen Z, Peng YY, Wu XL, et al. Comorbidities and complications of COVID-19 associated with disease severity, progression, and mortality in China with centralized isolation and hospitalization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health, 2022; 10, 923485. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.923485 [12] Dash SK, Jena L, Panigrahy R, et al. Brucella melitensis lurking threat in eastern part of Odisha - a case report. J Pure Appl Microbiol, 2022; 16, 2949−53. doi: 10.22207/JPAM.16.4.12 [13] Pappas G, Papadimitriou P, Akritidis N, et al. The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis, 2006; 6, 91−9. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70382-6 [14] Godfroid J, Cloeckaert A, Liautard JP, et al. From the discovery of the Malta fever's agent to the discovery of a marine mammal reservoir, brucellosis has continuously been a re-emerging zoonosis. Vet Res, 2005; 36, 313−26. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2005003 [15] Madzingira O, Fasina OF, Kalinda C, et al. Seroprevalence of brucellosis among clinically suspected human cases presenting at health facilities in Namibia from 2012 to 2017. Biomed Environ Sci, 2021; 34, 232−5. [16] Bosilkovski M, Krteva L, Dimzova M, et al. Human brucellosis in Macedonia—10 years of clinical experience in endemic region. Croat Med J, 2010; 51, 327−36. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2010.51.327 [17] Pappas G. The peculiar ways of Brucella survival: looking through the keyhole. Virulence, 2010; 1, 473−4. doi: 10.4161/viru.1.6.13200 [18] Ariza J, Pigrau C, Cañas C, et al. Current understanding and management of chronic hepatosplenic suppurative brucellosis. Clin Infect Dis, 2001; 32, 1024−33. doi: 10.1086/319608 [19] Young EJ. An overview of human brucellosis. Clin Infect Dis, 1995; 21, 283−90. doi: 10.1093/clinids/21.2.283 [20] Shabani S, Ghadimi S. COVID-19 co-infection in a patient with brucellosis. Clin Case Rep, 2022; 10, e6367. [21] Güven M. Brucellosis in a patient diagnosed with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). J Infect Dev Ctries, 2021; 15, 1104−6. doi: 10.3855/jidc.13899 [22] Kucuk GO, Gorgun S. Brucellosis mimicking COVID-19: a point of view on differential diagnosis in patients with fever, dry cough, arthralgia, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cureus, 2021; 13, e15848. [23] National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Diagnosis of Brucellosis (WS 269-2019). http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/s9491/201905/b109b71e7a624256985b573944b5d292.shtml. [2023-01-10]. (In Chinese) [24] Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med, 2009; 6, e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097 [25] Yang Y, Duan BF, Dong GD, et al. Research progress on brucellosis in human and animals. China Anim Health Inspec, 2020; 37, 76−83. [26] Han Q, Zheng B, Daines L, et al. Long-term sequelae of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of one-year follow-up studies on post-COVID symptoms. Pathogens, 2022; 11, 269. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020269 [27] Wang N, Yang MB, Yang PY, et al. A case series of olfactory dysfunction in imported COVID-19 patients: a 12-month follow-up study. Biomed Environ Sci, 2022; 35, 402−11. [28] Proal AD, VanElzakker MB. Long COVID or post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC): an overview of biological factors that may contribute to persistent symptoms. Front Microbiol, 2021; 12, 698169. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.698169 [29] Adeloye D, Elneima O, Daines L, et al. The long-term sequelae of COVID-19: an international consensus on research priorities for patients with pre-existing and new-onset airways disease. Lancet Respir Med, 2021; 9, 1467−78. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00286-1 [30] Huang LX, Yao Q, Gu XY, et al. 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet, 2021; 398, 747−58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01755-4 [31] Yang XY, Hou C, Shen Y, et al. Two-year health outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 survivors in China. JAMA Netw Open, 2022; 5, e2231790. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.31790 [32] Barreto-Argilagos GA, De La Caridad Rodríguez-Torrens H. At least one zoonosis silently spreads during COVID-19: brucellosis. MEDICC Rev, 2021; 23, 8. [33] Franco MP, Mulder M, Smits HL. Persistence and relapse in brucellosis and need for improved treatment. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 2007; 101, 854−5. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2007.05.016 [34] Hoang T. Characteristics of COVID-19 recurrence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Glob Health, 2021; 87, 28. doi: 10.5334/aogh.3163 -




 下载:
下载:



 Quick Links
Quick Links