Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes /issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.008
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.121
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.011
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.119
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.151
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.009
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2026.005
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.170
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.169
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.167
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.166
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.164
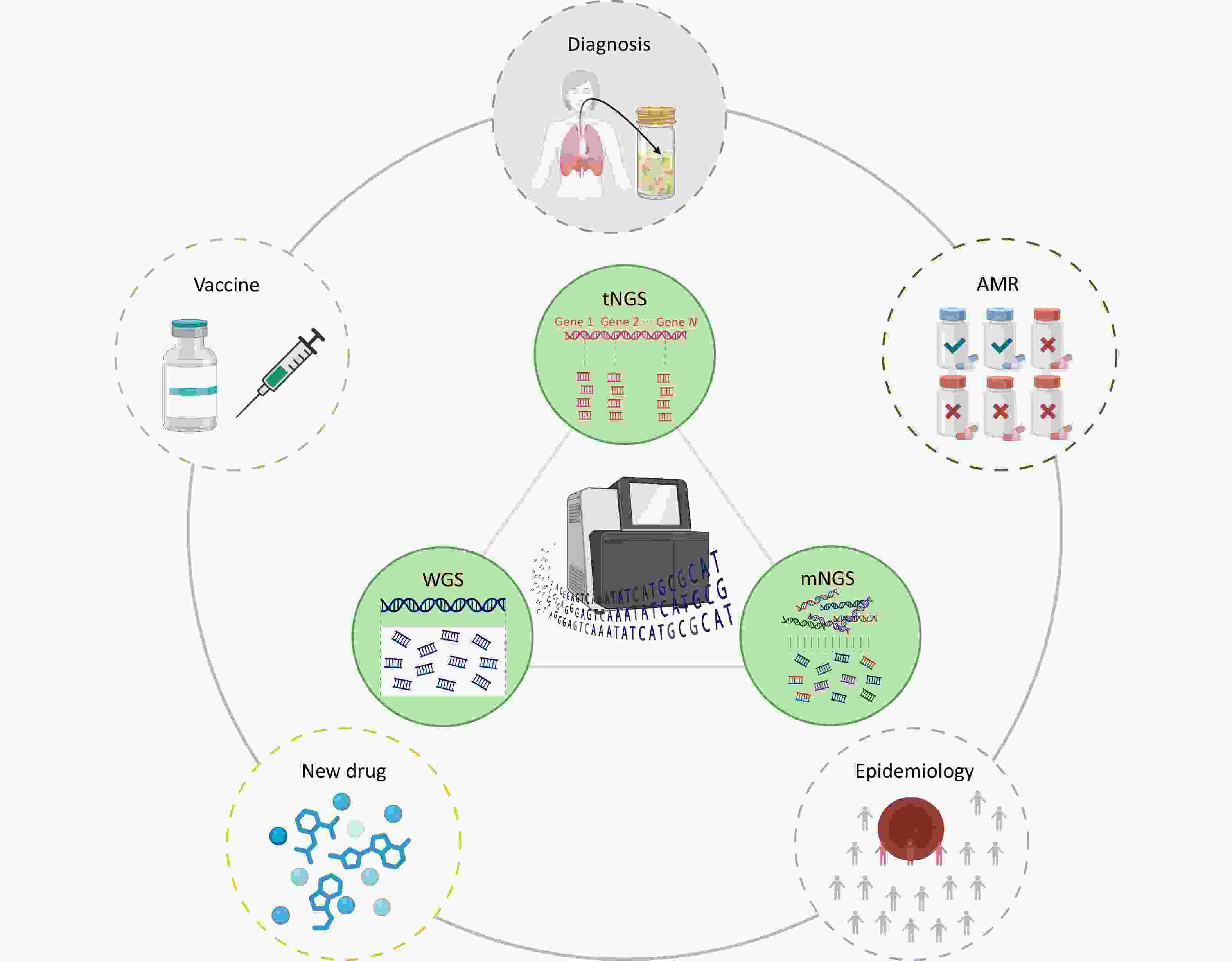
Tuberculosis (TB) continues to pose a significant threat to global public health, necessitating rapid and precise diagnostic methods and comprehensive detection of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to facilitate timely clinical management. Traditional diagnostic techniques suffer from extended turnaround times and limited ability to comprehensively profile AMR, often resulting in delayed therapeutic interventions. High-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies have revolutionized pathogen research by significantly improving diagnostic speed and accuracy. In the context of TB, diverse sequencing strategies and platforms are being employed to fulfill specific research goals, ranging from elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying AMR to characterizing the genomic diversity among clinical isolates. This review systematically examines current progress in the application of HTS for rapid pathogen identification, comprehensive AMR profiling, epidemiological studies, advances in novel drugs, and vaccine development. Furthermore, we address existing technological limitations and bioinformatics challenges and explore the future directions necessary for effectively integrating HTS-based methodologies into global TB control efforts.
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.163
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.162
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.161
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.160
In press
, Available online ,
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.159
Column
2026, 39(1): 3-14.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.113
Objective This study aims to investigate the joint associations of sarcopenia and social isolation with mortality risk. Methods Using data from the Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey (CLHLS) and the UK Biobank, sarcopenia was diagnosed according to European and Asian Working Groups for Sarcopenia criteria. Social isolation was assessed using standardized questionnaires, including questions on solitude, frequency of social activities, contact with others, and marital status (for the CLHLS only). Results During the follow-up period, 8,249 deaths occurred in the CLHLS and 26,670 deaths in the UK Biobank groups. While no significant interaction was observed between sarcopenia and social isolation in predicting all-cause mortality in the CLHLS cohort, the association between social isolation and mortality was stronger among individuals with sarcopenia in the UK Biobank (P-interaction = 0.03, relative risk due to interaction: 0.23, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.06–0.41). Further joint analyses showed that participants with sarcopenia and high levels of social isolation had the highest mortality risk (hazard ration [HR]: 1.99; 95% CI: [1.74–2.28] in the CLHLS and 1.69 [1.55–1.85] in the UK Biobank) compared to those without either condition. Conclusion The combination of social isolation and sarcopenia synergistically increases the risk of mortality in middle-aged and older adults across diverse populations.
2026, 39(1): 15-25.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.165
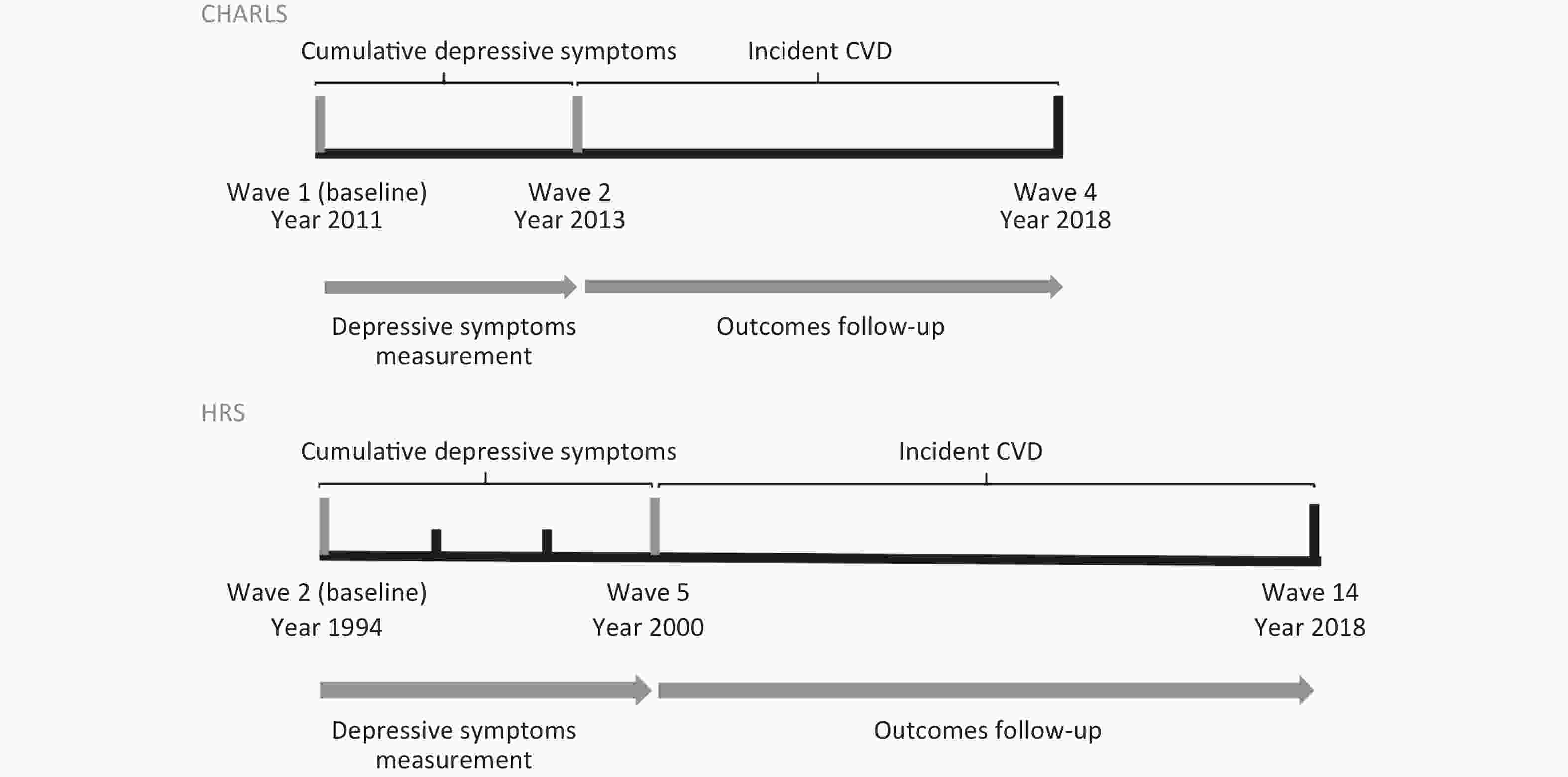
Objective Elevated depressive symptoms are well-documented among geriatric adults with cardiovascular disease (CVD); however, few studies have accounted for long-term cumulative depressive symptom exposure. This study determined the relationship between cumulative depressive symptoms and CVD. Methods Individual participant data were obtained from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) and Health and Retirement Study (HRS). Eligible participants had access to assessment information on depressive symptoms and had no history of CVD at baseline. Long-term cumulative depressive symptoms were estimated by calculating the area under the curve based on the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale. Results Herein, 8,861 participants from CHARLS (mean age: 58.58 years; male: 48.6%) and 7,284 from HRS (60.94 years; 35.0%) were enrolled. The median follow-up period was 5 years for the CHARLS and 10 years for the HRS. Compared with the first quartile of cumulative depressive symptoms, the HRs (95% CI) in the fourth quartile were 1.73 (1.48, 2.02) for predicting CVD (P < 0.001), 1.83 (1.52, 2.19) for heart disease (P < 0.001), 1.53 (95% CI: 1.17, 1.99) for stroke (P = 0.002) in CHARLS. For HRS, the HRs (95% CI) were 1.41 (95% CI: 1.27, 1.57; P < 0.001), 1.42 (95% CI: 1.26, 1.59; P < 0.001), and 1.30 (95% CI: 1.06, 1.58; P = 0.010) respectively. Strong dose-response relationships were observed, with similar results for the two cohorts. Conclusion Long-term cumulative depressive symptoms were significantly associated with incident CVD in middle-aged and older adults, providing insights into controlling long-term depressive symptoms to improve this cohort’s health.
2026, 39(1): 26-35.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.089
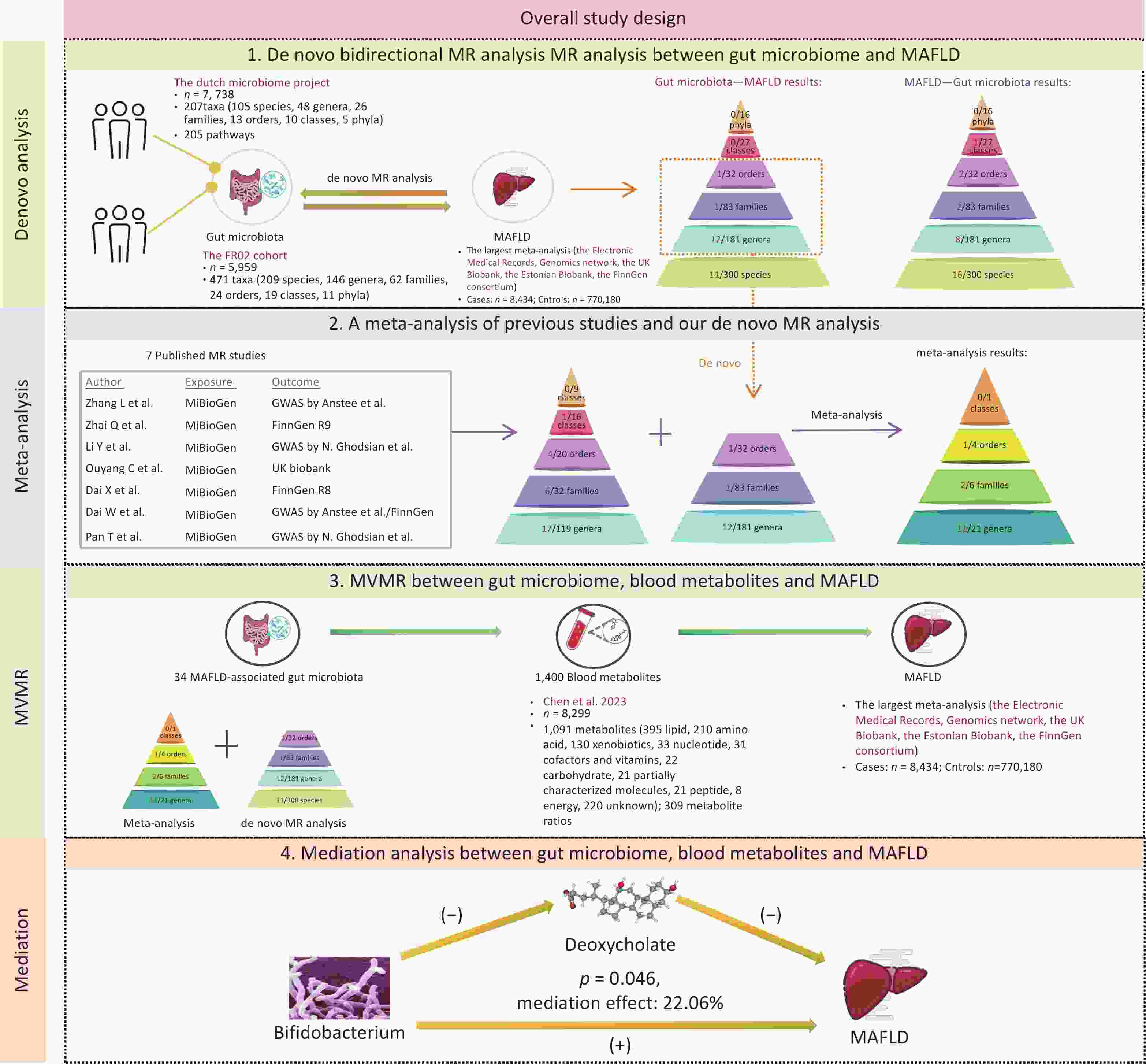
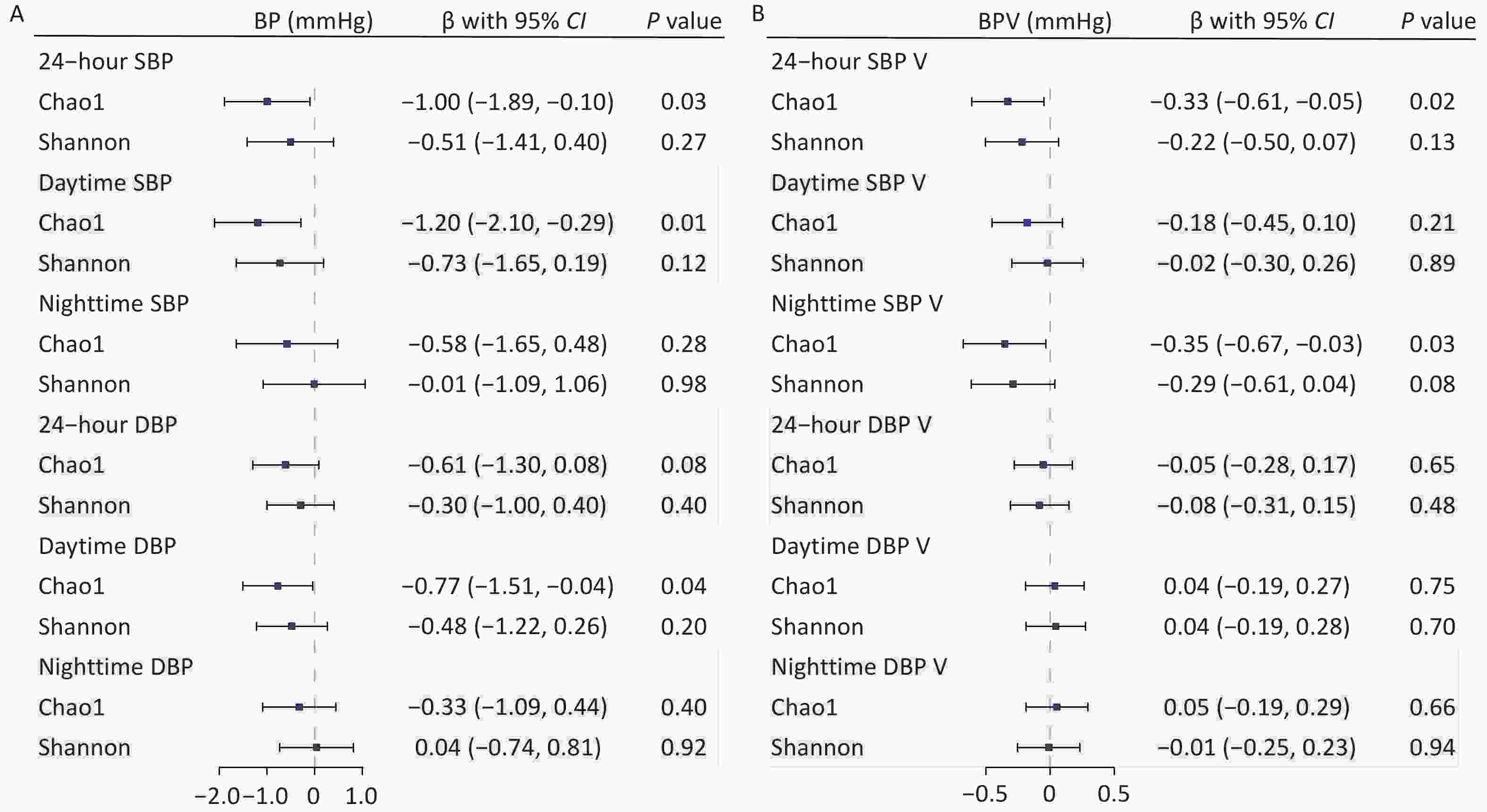
Objective Evidence suggests that depleted gut microbial α-diversity is associated with hypertension; however, whether metabolic markers affect this relationship remains unknown. We aimed to determine the potential metabolites mediating the associations of α-diversity with blood pressure (BP) and BP variability (BPV). Methods Metagenomics and plasma targeted metabolomics were conducted on 523 Chinese participants from the MetaSalt study. The 24-hour, daytime, and nighttime BP and BPV were calculated based on ambulatory BP measurements. Linear mixed models were used to characterize the relationships between α-diversity (Shannon and Chao1 index) and BP indices. Mediation analyses were performed to assess the contribution of metabolites to the observed associations. The influence of key metabolites on hypertension was further evaluated in a prospective cohort of 2,169 participants. Results Gut microbial richness (Chao1) was negatively associated with 24-hour systolic BP, daytime systolic BP, daytime diastolic BP, 24-hour systolic BPV, and nighttime systolic BPV (P < 0.05). Moreover, 26 metabolites were strongly associated with richness (Bonferroni P < 0.05). Among them, four key metabolites (imidazole propionate, 2-hydroxy-3-methylbutyric acid, homovanillic acid, and hydrocinnamic acid) mediated the associations between richness and BP indices (proportions of mediating effects: 14.1%–67.4%). These key metabolites were also associated with hypertension in the prospective cohort. For example, each 1-standard deviation unit increase in hydrocinnamic acid significantly reduced the risk of prevalent (OR [95% CI] = 0.90 [0.82, 0.99]; P = 0.03) and incident hypertension (HR [95% CI] = 0.83 [0.71, 0.96]; P = 0.01). Conclusion Our results suggest that gut microbial richness correlates with lower BP and BPV, and that certain metabolites mediate these associations. These findings provide novel insights into the pathogenesis and prevention of hypertension.
2026, 39(1): 36-45.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.069
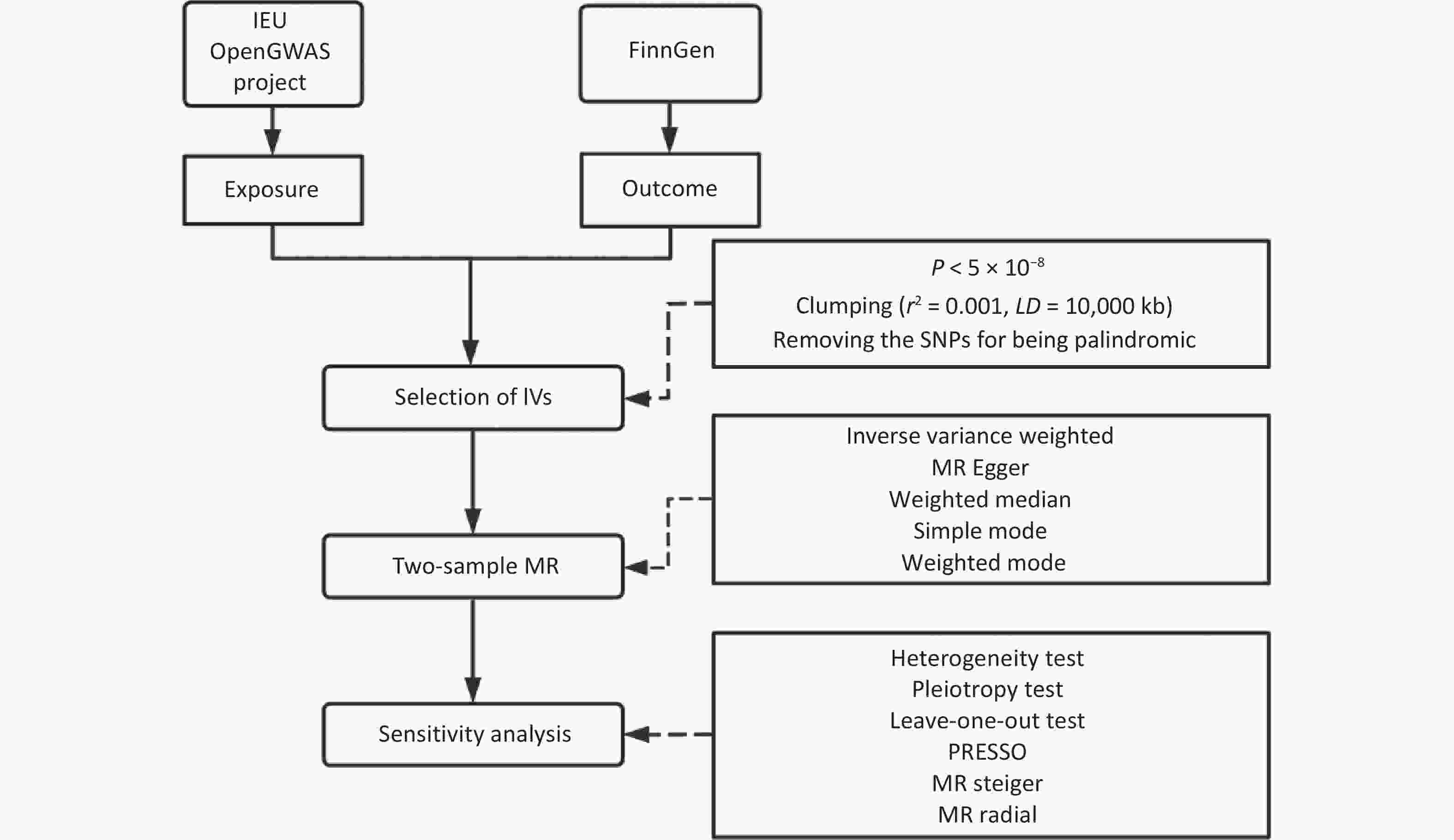
Objective Previous studies link lower body mass index (BMI) with increased obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) risk, yet other body mass indicators may be more etioloically relevant. We dissected the causal association between body fat mass (FM) and OCD. Methods Summary statistics from genome-wide association studies of European ancestry were utilized to conduct two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Heterogeneity, horizontal pleiotropy, and sensitivity analyses were performed to assess the robustness. Results The inverse variance weighting method demonstrated that a genetically predicted decrease in FM was causally associated with an increased OCD risk [odds ratio (OR) = 0.680, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.528–0.875, P = 0.003]. Similar estimates were obtained using the weighted median approach (OR = 0.633, 95% CI: 0.438–0.915, P = 0.015). Each standard deviation increases in genetically predicted body fat percentage corresponded to a reduced OCD risk (OR = 0.638, 95% CI: 0.455–0.896, P = 0.009). The sensitivity analysis confirmed the robustness of these findings with no outlier instrument variables identified. Conclusion The negative causal association between FM and the risk of OCD suggests that the prevention or treatment of mental disorders should include not only the control of BMI but also fat distribution and body composition.
2026, 39(1): 46-59.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.093
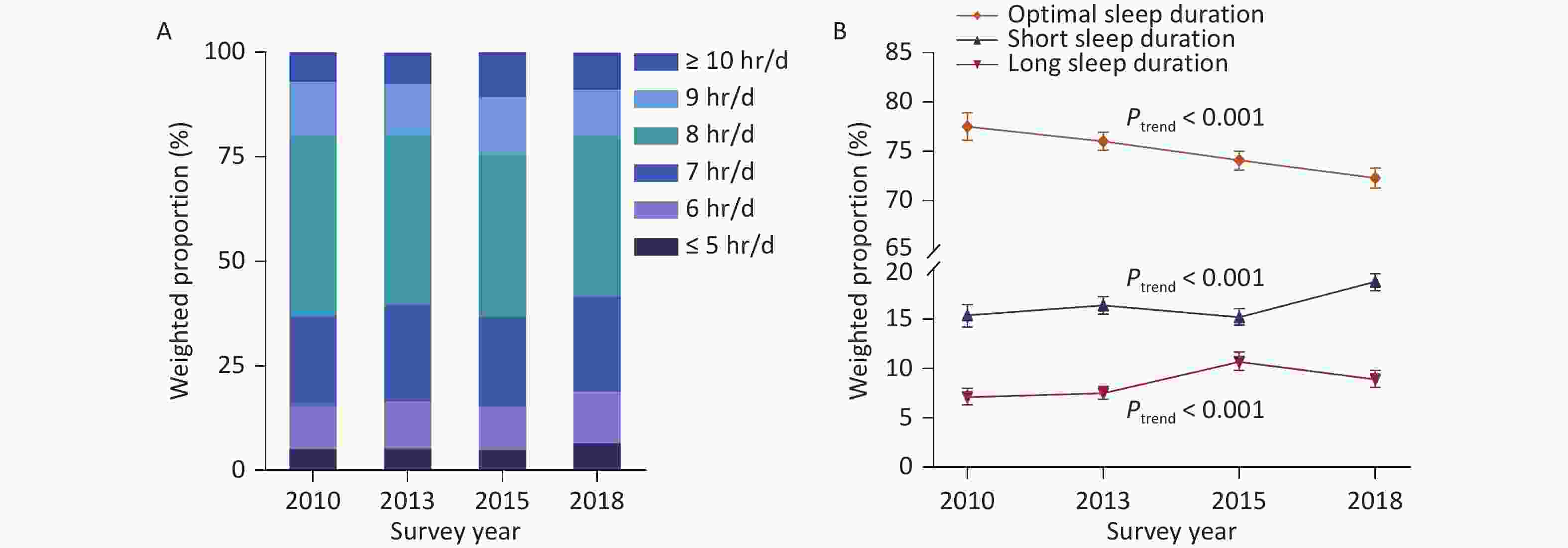
Objective This study aimed to determine the temporal trends in sleep duration among Chinese adults. Methods In this series of repeated nationally representative cross-sectional surveys (China Chronic Disease and Risk Factors Surveillance) conducted between 2010 and 2018, a total of 645,420 adult participants (97,741 in 2010; 175,749 in 2013; 187,777 in 2015; and 184,153 in 2018) were included in the trend analysis. Linear and logistic regression models were utilized to assess trends in sleep duration. Results In 2018, the estimated overall mean sleep duration among the Chinese adult population was 7.58 (SD, 1.45) hours per day, with no significant trend from 2010. A significant increase in short sleep duration (≤ 6 hours) was observed in the total population, from 15.3% (95% CI: 14.1%–16.5%) in 2010 to 18.5% (95% CI: 17.7%–19.3%) in 2018 (P < 0.001). Similarly, the trend in long sleep duration (> 9 hours) was also significant, increasing in weighted prevalence from 7.2% (95% CI: 6.3%–8.1%) in 2010 to 9.0% (95% CI: 8.2%–9.9%) in 2018 (P < 0.001). Conclusion The prevalence of both short and long sleep durations significantly increased among Chinese adults from 2010 to 2018, highlighting the urgency of health initiatives to promote optimal sleep duration in China.
2026, 39(1): 60-72.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.146
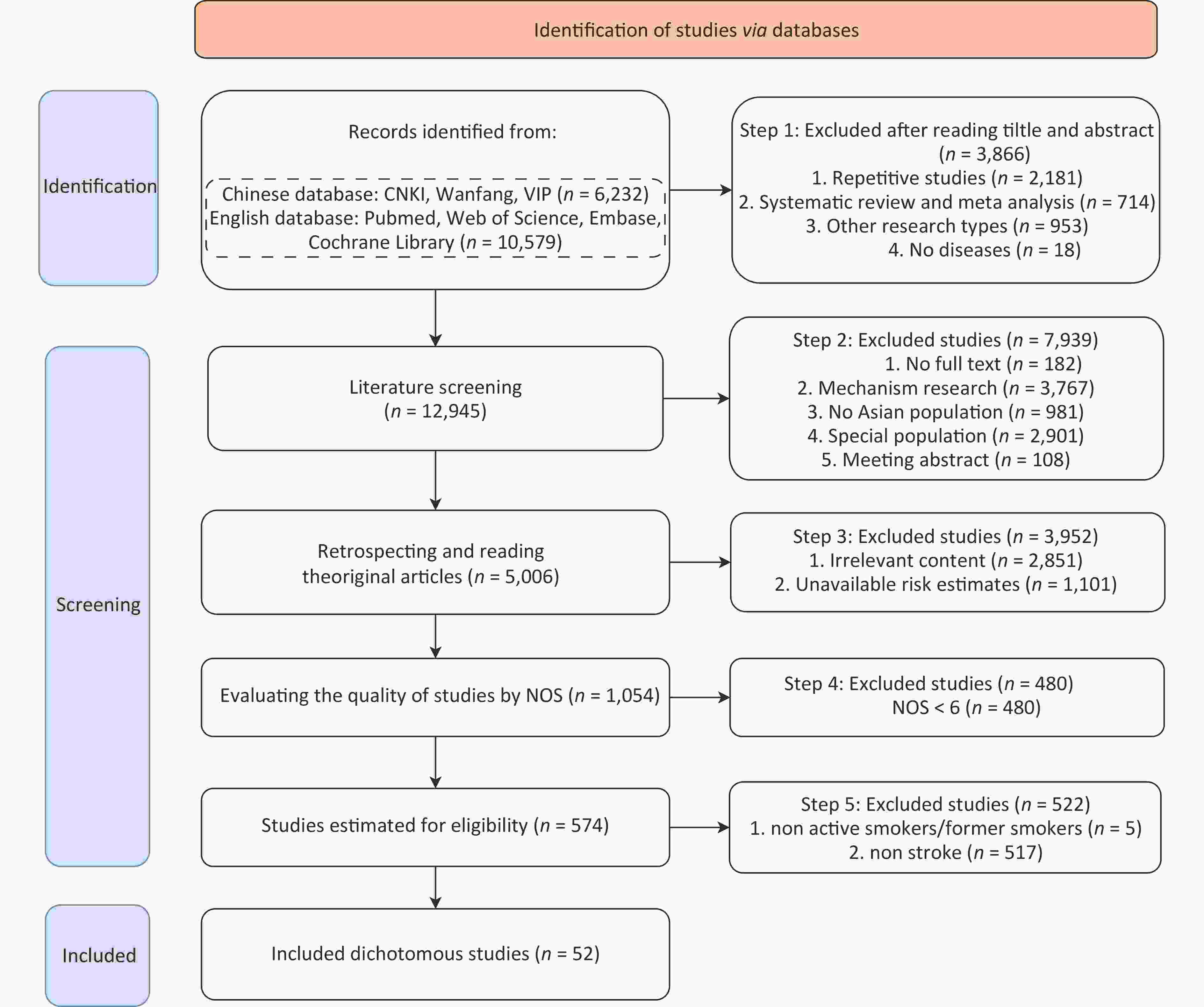
Objective Stroke is the third leading cause of death worldwide, with the highest incidence in Asia, particularly in China, where smoking remains a major risk factor. The smoking prevalence in China is similar to that in Asia. Whether the risk estimates for smoking-related stroke in China and all Asian countries are still unknown which is worth evaluating. Thus, this study aims to compare the Relative Risk (RR) of smoking-attributed stroke among the Chinese and Asian populations. Methods A literature search was conducted from the inception to September 10, 2022. Studies meeting the criteria were included. The articles were screened, and related information was extracted. Pooled RRs stratified by smoking status and sex were analyzed, including subgroup analyses for China, other Asian countries, and Asia overall. Finally, publication bias and sensitivity analyses were conducted. Results Thirty-seven articles on the Chinese population and 15 on other Asian populations were included, with a mean Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) score of 7.25. About ever smokers, there had no statistical difference existed in both sexes and females between China and other Asian countries, while the RR of males in other Asian countries [2.31 (1.38, 3.86)] was higher than that in China [1.21 (1.15, 1.26)]; further subgroup analysis indicated that other Asian countries had higher RR [3.76 (3.02, 4.67)] in the morbidity subgroup. The RRs of both sexes, males and females, between China and the whole of Asia were not statistically different. As for current and former smokers, no meaningful statistical difference was observed in the pooled RRs of both sexes, males and females, in China, other Asian countries, and all of Asia. Conclusion The RR of males ever smokers in China was smaller than that in other Asian countries due to the few articles of morbidity subgroup, but had no statistical difference with the whole of Asia; other groups of ever smokers, current smokers, and former smokers were not statistically significant with other Asian countries or the whole of Asia.
2026, 39(1): 73-81.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.086
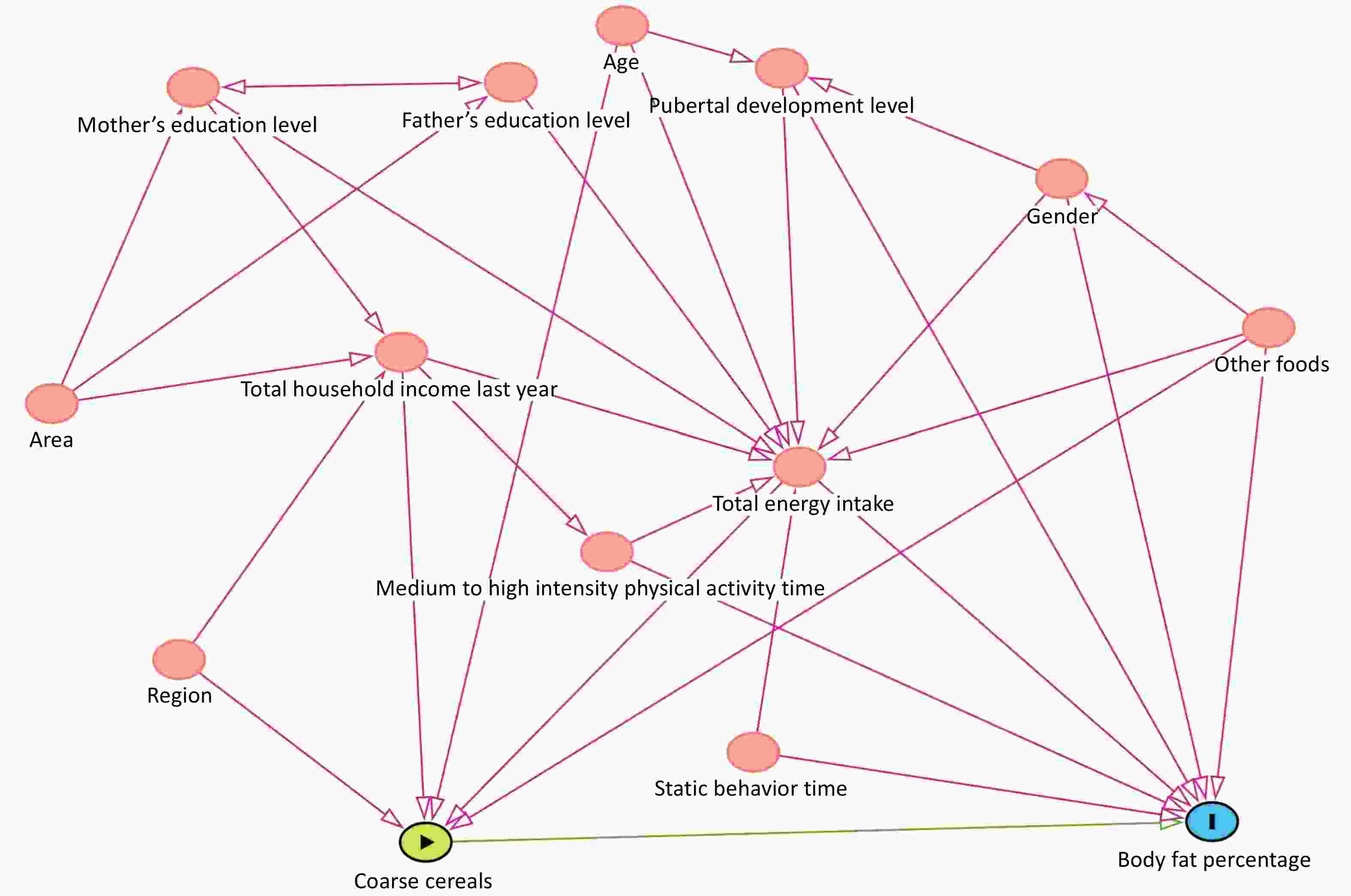
Objective The rising prevalence of childhood obesity is closely associated with suboptimal dietary patterns. To address this public health concern, we conducted a comprehensive study to examine the association between coarse cereals consumption and body fat percentage (BFP) in Chinese children and adolescents. Methods The study included 48,305 children aged 6–17 years from 28 districts/counties in 14 provinces across seven regions of China (24,152 girls and 24,153 boys). BFP was examined using bioelectrical impedance analysis in the early morning. Coarse cereals consumption was assessed using a Food Frequency Questionnaire and categorized into three groups: 0 g/1,000 kcal per day, 0–10 g/1,000 kcal per day, and > 10 g/1,000 kcal per day (daily consumption of coarse cereals × 1,000/total energy consumption). Quantile regression model was used to analyze the association between coarse cereals and BFP, adjusting for potential confounders such as age, pubertal development stage, urban/rural and regional factors, total daily dietary energy consumption, sedentary time, moderate-to-high physical activity, household income, parental education, and consumption of other foods. Results Boys aged 6–10, 11–14, and 15–17 years had median daily coarse cereals consumptions of 6.6 g, 7.1 g, and 5.7 g, with BFP of 19.6%, 19.5%, and 17.5% (all P < 0.05). Girls in the same age groups showed consumption of 7.1 g, 8.4 g, and 6.7 g, with BFP of 20.3%, 26.4%, and 31.0% (all P < 0.05). The quantile regression results for boys showed that daily consumption of coarse cereals was significantly correlated with their BFP in the 0.15, 0.25, and 0.50 quartiles, with regression coefficients of −0.257, −0.221, and −0.330, respectively, after adjusting for potential confounders (P < 0.05). For girls, there was a significant correlation with PBF at the 0.05, 0.15, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, and 0.85 quartiles, with regression coefficients of −0.258, −0.366, −0.372, −0.431, −0.472, and −0.503 (P < 0.05 for all). Conclusions Coarse cereals consumption among Chinese children and adolescents remains relatively low. Higher consumption was inversely associated with BFP in children aged 6–17 years. Future interventional studies should assess how increased coarse cereals consumption prevents childhood obesity.
2026, 39(1): 82-104.
doi: 10.3967/bes2025.104
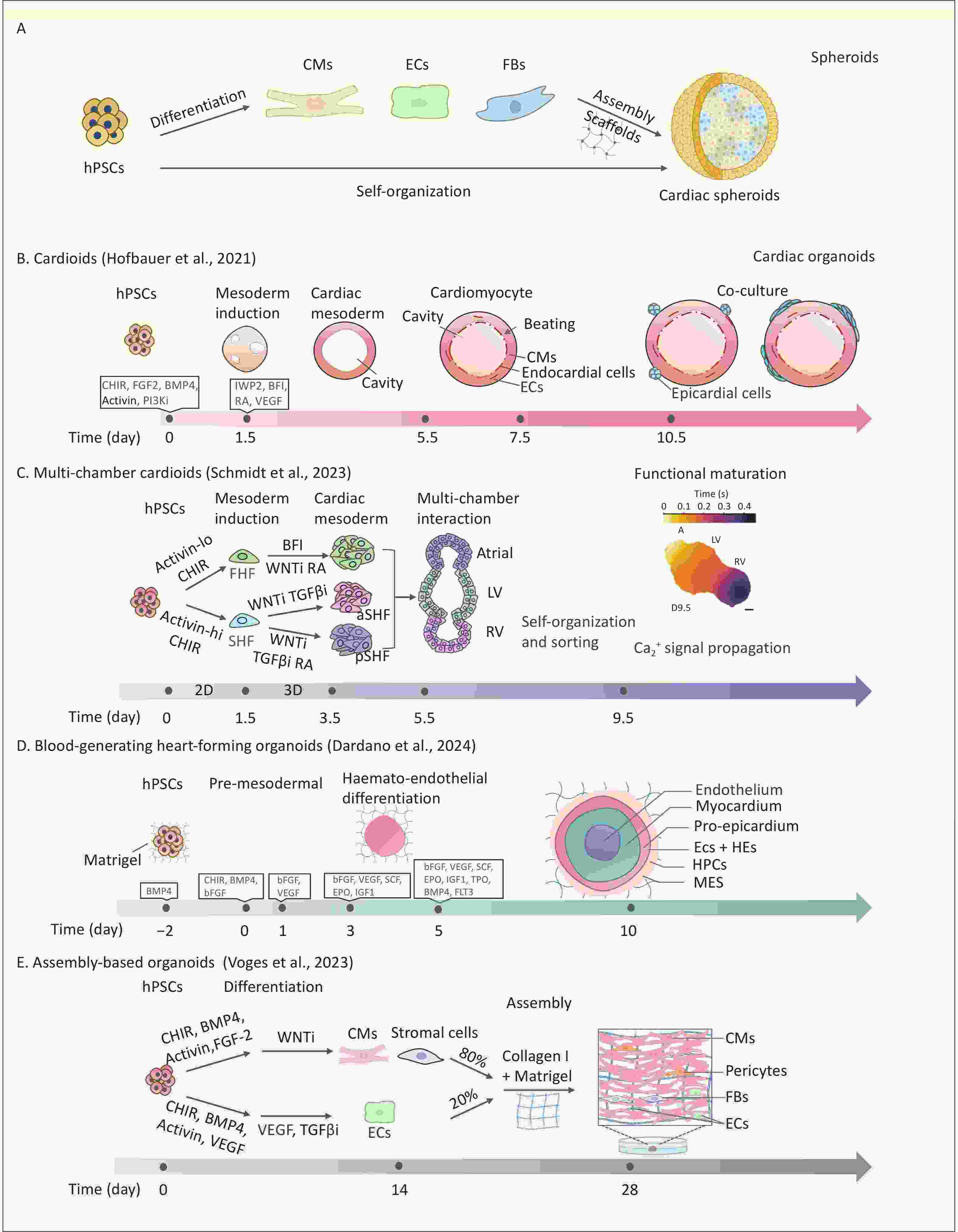
Human cardiac organoids have revolutionized the study of cardiac development, disease modeling, drug discovery, and regenerative therapies. This review systematically discusses strategies and progress in the construction of cardiac organoids, categorizing them into three main types: cardiac spheroids, self-organizing/assembloid organoids, and organoid-on-a-chip systems. This review uniquely integrates the advances in vascularization, organ-on-chip design, and environmental cardiotoxicity modeling within cardiac organoid platforms, offering a critical synthesis that is absent in the literature. In the context of escalating environmental threats to cardiovascular health, there is an urgent need for physiologically relevant models to accurately identify cardiac toxicants and elucidate their underlying mechanisms of action. This review highlights advances in cardiac organoid applications for disease modeling—including congenital heart defects and acquired cardiovascular diseases—drug development, toxicity screening, and the study of environmentally induced cardiovascular pathogenesis. In addition, it critically examines ongoing challenges and underscores opportunities brought by bioengineering approaches. Finally, we propose future directions for developing standardized cardiac organoid platforms with clinical predictability, aiming to expand the utility of this technology across broader research applications.
2015, 28(1): 57-71.
doi: 10.3967/bes2015.006
2022, 35(7): 573-603.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.079
2023, 36(8): 669-701.
doi: 10.3967/bes2023.106
2018, 31(2): 87-96.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.011
2012, 25(3): 317-324.
doi: 10.3967/0895-3988.2012.03.010
2019, 32(8): 559-570.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.074
2014, 27(8): 606-613.
doi: 10.3967/bes2014.093
2018, 31(3): 208-214.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.026
2003, 16(3): 246-255.
2019, 32(9): 659-672.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.085
2022, 35(5): 381-392.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.054
2022, 35(7): 648-651.
doi: 10.3967/bes2022.084
2024, 37(9): 949-992.
doi: 10.3967/bes2024.162
2016, 29(3): 212-218.
doi: 10.3967/bes2016.026
2018, 31(9): 637-644.
doi: 10.3967/bes2018.088
2019, 32(8): 578-591.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.076
2019, 32(10): 769-778.
doi: 10.3967/bes2019.096
Current Issue
-
2024 Impact Factor 4.1
-
2024 Journal Citation Reports





















 Quick Links
Quick Links